BrdU Products and Resources for Flow Cytometry

- On This Page
- Products
- Protocol
- Resource
Incorporation of BrdU is a well-established technique to determine cell proliferation rates. We offer a range of anti-BrdU antibodies to meet your needs, along with protocols and information to optimize your results.
Products
BrdU Antibodies
Anti-BrdU antibodies recognize BrdU that has been incorporated into DNA, instead of thymidine, during the S-phase of a cell cycle. To support your proliferation studies, Bio-Rad has expanded its range of highly validated PrecisionAb Anti-BrdU Antibodies.
These antibodies are tested in multiple applications and for cross-reactivity with thymidine and other thymidine analogs. Detailed protocols for various immunodetection applications provide guidance to optimize their use. Check out the wide range of PrecisionAb Anti-BrdU Antibodies below (and the appropriate application use) and find the right one for your experimental needs.
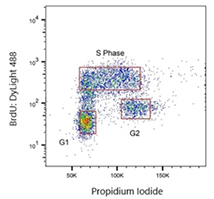
Fig. 1. Jurkat cells were treated with 100 μM BrdU and stained with Rat anti-BrdU Antibody clone RF04-2 (MCA6143). As a secondary antibody, Rabbit F(ab')2 anti-Rat IgG: DyLight488 conjugated Antibody (STAR16D488GA) was used at a 1/400 dilution. ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide was used to stain total DNA.
PrecisionAb Rat Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF04-2
The Rat anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF04-2 (MCA6143) has been tested in immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. The antibody cross-reacts with CIdU, EdU, and IdU in flow cytometry.
We provide a detailed protocol including BrdU labeling and DNA denaturation step. This denaturation step allows anti-BrdU antibodies to access the incorporated BrdU in the single-stranded DNA. The isotype of the antibody is IgG2b.
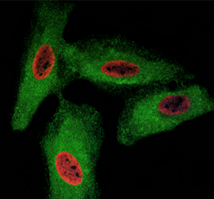
Fig. 2. HeLa cells were treated with BrdU and stained with Rat anti-BrdU Antibody clone RF06 (MCA6144). Goat anti-Rat IgG (H/L):TRITC Conjugated Antibody (red) (305003) was used as a secondary antibody. PureBlu DAPI (1351303) was used as nuclear counterstain. Co-staining with Rabbit anti-GADPH, with Sheep anti-Rabbit IgG:DyLight488 Conjugated Antibody (green) as the secondary detection antibody, was also performed to visualize the cytoplasm and confirm specificity of BrdU staining to the nucleus.
PrecisionAb Rat Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF06
The Rat anti-BrdU Antibody, clone RF06 (MCA6144) has been tested in immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry. Immunocytochemical BrdU labeling is a quick and highly reproducible method, widely used to study the cytokinetics of normal and neoplastic cells.
An easy-to-follow, step-by-step protocol outlining how to perform immunofluorescent BrdU staining is available. The isotype of the antibody is IgG2a.
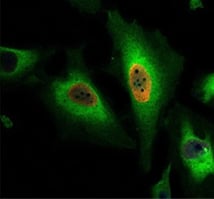
Fig. 3. HeLa cells were treated with 100 μM BrdU and stained with Human anti-BrdU Antibody (HCA320) at a 1/500 dilution. Sheep anti-Rabbit: DyLight549 Conjugated Antibody at a 1/500 dilution was used as a secondary antibody. PureBlu DAPI (1351303) was used as nuclear counterstain.
PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kg
The Human anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kg (HCA320) is a recombinant, chimeric human/rabbit IgG antibody selected from the HuCAL® phage display library. In this antibody, the VH-CH1 regions and light chains are human while the Fc region is derived from rabbit IgG.
The antibody has been tested in immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. It cross-reacts with CIdU in flow cytometry. Therefore, CIdU can be used in the studies instead of BrdU. A detailed protocol for using this clone AbD33758kg is available on the BrdU staining protocols webpage.
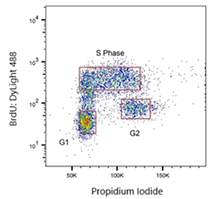
Fig. 4. Jurkat cells were treated with 100 μM BrdU. Cells were stained with Human anti-BrdU Antibody (HCA321) at a 1/2,000 dilution for 1 hr at RT. As a secondary antibody, Sheep anti-Rabbit:DyLight488 Conjugated Antibody was used at a 1/200 dilution. ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide was used to stain total DNA.
PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kg
The Human anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kg (HCA321) is a recombinant, chimeric human/rabbit IgG antibody selected from the HuCAL phage display library. In this antibody, the VH-CH1 regions and light chains are human, while the Fc region is derived from rabbit IgG.
The antibody has been tested in immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. It cross-reacts with CIdU in flow cytometry. Therefore, CIdU can be used in the studies instead of BrdU. A detailed protocol for using clone AbD33761kg in flow cytometry is available on the BrdU staining protocols webpage.
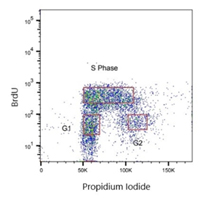
Fig. 5. Jurkat cells were treated with 100 μM BrdU. Cells were stained with Human anti-BrdU Antibody (HCA322) at a 1/2,000 dilution for 1 hr at RT. ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide was used to stain total DNA.
PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kg
The Human anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33758kg (HCA322) is a recombinant, chimeric human/rat IgG2a antibody selected from the HuCAL phage display library. In this antibody, the VH and VL regions are human while the CH1-CH3 and C-lambda regions are derived from rat IgG2a.
It is recommended to use in immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. In flow, it cross-reacts with CIdU and IdU. Therefore, CIdU and IdU can be used in the studies instead of BrdU. A detailed protocol for using clone AbD33758kg in flow cytometry can be found on the BrdU staining protocols webpage.
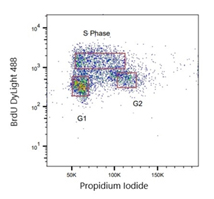
Fig. 6. Jurkat cells were treated with 100 μM BrdU. Cells were stained with Human anti-BrdU Antibody (HCA323) at a 1/2,000 dilution for 1 hr at RT. Sheep anti-Rat: DyLight488 Conjugated Antibody (STAR16D488GA) was used as a secondary antibody at a 1/200 dilution. Propidium Iodide was used to stain total DNA.
PrecisionAb Human Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kg
The Human anti-BrdU Antibody, clone AbD33761kg (HCA323) is a recombinant, chimeric human/rat IgG2a antibody selected from the HuCAL phage display library. In this antibody, the VH and VL regions are human, while the CH1-CH3 and C-lambda regions are derived from rat IgG2a.
The antibody is recommended for use in immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. In flow cytometry, it cross-reacts with CIdU. Therefore, CIdU can be used in the studies instead of BrdU. A detailed protocol for using clone AbD33761kg is available on the BrdU staining protocols webpage.
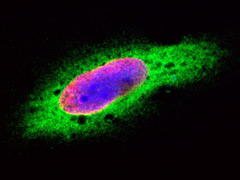
Fig. 7. HeLa cells were treated with BrdU for 3 hours and stained with Mouse anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a (MCA2483, red). Cytoplasm was stained with Rabbit anti-GAPDH antibody (AHP1628, green). PureBlu DAPI (1351303) was used as nuclear counterstain (blue).
Mouse Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a
The Mouse anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a, (MCA2483) has been tested in flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry. This antibody has been referenced in 14 publications.
It is available in three different sizes (0.2 mg, 0.1 mg, and 20 µg) and conjugated to FITC (MCA2483FA). In addition to flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry, the Bu20a clone is recommended for immunohistochemistry.
Rabbit Anti-BrdU Antibody
The Rabbit anti-BrdU Antibody (AHP2405) has been tested in flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry and we provide detailed protocols for using the antibody in these applications. In addition to these two applications, the antibody is also supported by immunohistochemistry data.
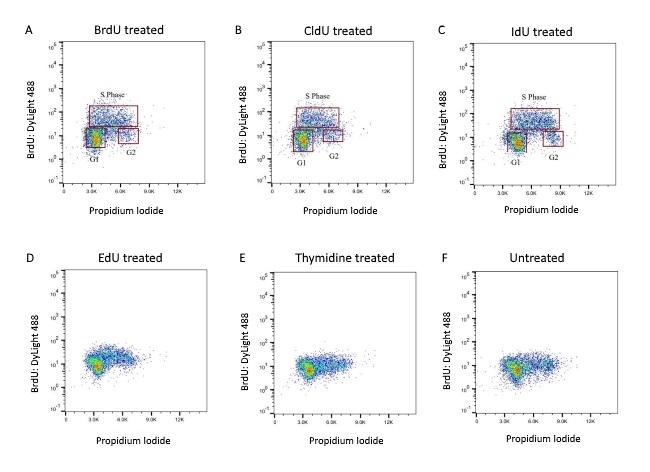
Fig. 8. BrdU-labeled human lymphoma cells were stained with Rabbit anti-BrdU Antibody (AHP2405) at a 1/50 dilution (A) and a 1/100 dilution (B). Sheep anti-Rabbit IgG DyLight Conjugated Secondary Antibody was used as the secondary detection reagent at a 1/50 dilution. ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide (1351101) was used to stain total DNA.
BrdU Antibodies
Bio-Rad's range of BrdU antibodies comes in a number of formats and can be used for applications including flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry.
Please use the filters to sort the attributes in the table below in order to find the antibody that fits your exact requirements. If you need any further assistance please do not hesitate to contact us.
Our BrdU Antibody Range
| Description | Target | Format | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|
Protocols
BrdU Staining of Cells for Cell Cycle Analysis
BrdU is an analog of thymidine readily incorporated into DNA during DNA synthesis. It provides an accurate method of monitoring proliferation and apoptosis. The Mouse anti-BrdU antibody, clone Bu20a, is suitable for flow cytometry. The following methods were used and provide a useful guide for using anti-BrdU antibodies.
Reagents
- 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
- 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5
- 2 M HCl containing 0.5% Triton X-100
- PBS
- PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin (PBS/BSA)
- Propidium iodide
Methods
- Add BrdU to the cell suspension in culture medium to a final concentration of 10 μM and incubate for at least 30 min at 37°C in a CO2 incubator.
- Wash cells twice with PBS/BSA, at 500 x g for 10 min at RT, decant supernatant.
- Resuspend in 2-5 ml cold (4oC) 70% ethanol. Add dropwise to cell pellet while vortexing. Fix for at least 30 min on ice.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in 2 ml of 2 M HCl containing 0.5% Triton X-100. Incubate for 30 min at RT (preferably on a rocking platform).
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant. Resuspend in 3 ml of 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5 for 2 min at RT.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend in RT PBS/BSA + 0.05% Tween 20. Adjust cell concentration to 1 × 107 cells/ml.
- Aliquot 100 μl of the cell suspension into required number of FACS tubes.
- Incubate with antibody at the recommended vendor dilution overnight at 4oC avoiding direct light.
- Resuspend in 2 ml of RT PBS/BSA. Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min at RT.
- If a secondary antibody is required, then decant the supernatant, add 100 μl of PBS/BSA and incubate with the secondary antibody at the vendor recommended dilution for at least 30 min at 4oC.
- Wash with 2 ml of PBS/BSA, centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min.
- Re-suspend cells in 1 ml of PBS. Add propidium iodide e.g. 1-2 drops of ReadiDrop™ Propidium Iodide (1351101).
- Analyze by flow cytometry. The propidium iodide should be read on the appropriate channel in the linear scale. Doublets should be gated out using the Area vs Height or Width depending on your instrument.
Notes
The acid treatment to unwind the DNA may affect surface immunophenotyping. Staining of cells with BrdU using DNAse I may be applicable if this is required.
Appropriate controls should be carried out for flow cytometry, consider including the following:
- A known positive sample
- Isotype controls (to determine if the staining is specific)
- Unstained cells (should always be included to monitor autofluorescence)
For all multicolor flow cytometry experiments include compensation controls and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls, which assist with identifying gating boundaries.
BrdU Staining of Cells with anti-BrdU Antibody (clone Bu20a)
For use with flow cytometry tested Mouse anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a (MCA2483).
This method provides a general procedure for use with the majority of Bio-Rad reagents. In some cases specific recommendations are provided on product datasheets, and these methods should always be used in conjunction with product and batch specific information provided with each vial. Note that a certain level of technical skill and immunological knowledge is required for the successful design and implementation of these techniques — these are guidelines only and may need to be adjusted for particular applications.
Reagents
- 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
- 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5
- 2 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) containing 0.5% Triton X-100
- DNA stains/cell viability dyes, such as propidium iodide
- Mouse Anti-BrdU Antibody (clone Bu20a, MCA2483)
- PBS
- PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin (PBS/BSA)
Methods
- Label cells with BrdU. Add BrdU to the cell suspension in culture medium to a final concentration of 10 µM and incubate for 30 min in a CO2 incubator at 37°C.
- Wash cells 2 times (2x) with PBS/BSA, centrifuge cells at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend in a minimum volume of PBS.
- Add cells slowly into 5 ml 70% ethanol chilled to -20°C, mix continuously by vortexing.
- Incubate on ice for 30 min.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, and decant supernatant.
- Add 2 ml of 2 M HCl containing 0.5% Triton X-100, and incubate the cells for 30 min at room temperature (RT) on a rocking platform set to 15 rpm. Denaturation of the DNA by HCl is critical for successful BrdU staining. Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend in 1 ml of 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend the cells in PBS/BSA plus 0.05 % Tween 20 to a concentration of 1 x 107 cells/ml.
- Aliquot 100 µl of the cell suspension into the required number of FACS tubes.
- Incubate cells with Mouse anti-BrdU Antibody (clone Bu20a) at the recommended dilution for 1 hr at RT. Alternatively, incubation can be performed overnight at 4°C.
-
To wash, add 2 ml of PBS/BSA, and centrifuge the cells at 500 x g for 5 min.
(Optional) When using an unconjugated Bu20a antibody format perform incubation with a secondary antibody. For this purpose decant the supernatant and perform secondary antibody incubation for 45 min at RT (refer to the respective datasheet about the recommended dilution). Wash cells by repeating step 10.
- Decant the supernatant and add 0.5 ml of sheath fluid.
- For total DNA staining, add DNA stains such as, ReadiDrop™ Propidium Iodide (1351101), ReadiDrop 7-AAD (1351102), or PureBlu™ Hoechst 33342 (1351304), to each tube.
- Analyze cells by flow cytometry following the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA stain should be read on the appropriate channel set to the height and linear scale and not log scale.
Notes
The acid treatment to unwind the DNA may affect surface immunophenotyping. Staining of cells with BrdU using DNAse I may be applicable if this is required.
Appropriate controls should be carried out for flow cytometry, consider including the following:
- A known positive sample
- Isotype controls (to determine if the staining is specific)
- Unstained cells (should always be included to monitor autofluorescence)
For all multicolor flow cytometry experiments include compensation controls and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls, which assist with identifying gating boundaries.
BrdU Staining of Cells with Rabbit anti-BrdU Antibody
For use with flow cytometry tested Rabbit anti-BrdU Antibody (AHP2405).
This method provides a general procedure for use with the majority of Bio-Rad reagents. In some cases specific recommendations are provided on product datasheets, and these methods should always be used in conjunction with product and batch specific information provided with each vial. Note that a certain level of technical skill and immunological knowledge is required for the successful design and implementation of these techniques — these are guidelines only and may need to be adjusted for particular applications.
Reagents
- 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
- 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5
- 2 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) containing 0.5% Triton X-100
- DNA stains/cell viability dyes, such as propidium iodide
- Rabbit Anti-BrdU Antibody (AHP2405)
- PBS
- PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin (PBS/BSA)
Methods
- Label cells with BrdU. Add BrdU to the cell suspension in culture medium to a final concentration of 10 µM and incubate for 30 min in a CO2 incubator at 37°C.
- Wash cells 2 times (2x) with PBS/BSA, centrifuge cells at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend in a minimum volume of PBS.
- Add cells slowly into 5 ml 70% ethanol chilled to -20°C, mix continuously by vortexing.
- Incubate on ice for 30 min.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, and decant supernatant.
- Add 2 ml of 2 M HCl containing 0.5% Triton X-100, and incubate the cells for 30 min at room temperature (RT) on a rocking platform set to 15 rpm. Denaturation of the DNA by HCl is critical for successful BrdU staining. Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend in 1 ml of 0.1 M Na2B4O7, pH 8.5.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min, decant supernatant, and resuspend the cells in PBS/BSA plus 0.05 % Tween 20 to a concentration of 1 x 107 cells/ml.
- Aliquot 100 µl of the cell suspension into the required number of FACS tubes.
- Incubate cells with Rabbit anti-BrdU Antibody at the recommended dilution for 1 hr at RT. Alternatively, incubation can be performed overnight at 4°C.
- To wash, add 2 ml of PBS/BSA, and centrifuge the cells at 500 x g for 5 min.
- Perform incubation with a secondary antibody. For this purpose decant the supernatant and perform secondary antibody incubation for 45 min at RT (refer to the respective datasheet about the recommended dilution). Wash cells by repeating step 10.
- Decant the supernatant and add 0.5 ml of sheath fluid.
- For total DNA staining, add DNA stains such as, ReadiDrop™ Propidium Iodide (1351101),ReadiDrop 7-AAD (1351102), or PureBlu™ Hoechst 33342 (1351304), to each tube.
- Analyze cells by flow cytometry following the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA stain should be read on the appropriate channel set to the height and linear scale and not log scale.
Notes
The acid treatment to unwind the DNA may affect surface immunophenotyping. Staining of cells with BrdU using DNAse I may be applicable if this is required.
Appropriate controls should be carried out for flow cytometry, consider including the following:
- A known positive sample
- Isotype controls (to determine if the staining is specific)
- Unstained cells (should always be included to monitor autofluorescence)
For all multicolor flow cytometry experiments include compensation controls and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls, which assist with identifying gating boundaries.
BrdU Staining of Cells with anti-BrdU Antibody (clone RF04-2, clone AbD33758kg, clone AbD33761kd, AbD33761kg, and AbD33758kd)
For use with flow cytometry tested Anti-BrdU antibody clone RF04-2 (MCA6143), clone AbD33758kg (HCA320), clone AbD33761kd (HCA323), AbD33761kg (HCA321), and AbD33758kd (HCA322).
This method provides a general procedure for use with the majority of Bio-Rad reagents. In some cases specific recommendations are provided on product datasheets, and these methods should always be used in conjunction with product and batch specific information provided with each vial. Note that a certain level of technical skill and immunological knowledge is required for the successful design and implementation of these techniques — these are guidelines only and may need to be adjusted for particular applications.
Reagents
- Anti-BrdU Antibody
- 100 mM BrdU stock solution
- FACS buffer
- 2M HCl
- Leucoperm Reagent (BUF09B)
- ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide (1351101)
- Secondary Antibody
Methods
- Seed Jurkat cells at a density of 2 x 106 cells/well in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS into a 6-well plate.
- Add BrdU stock solution to each well of the 6-well plate so that you have a final concentration of 100 µM BrdU (for instance for 3 ml of media, add 3 µl of the 100 mM stock solution of BrdU). Incubate for 1 hr at 37°C.
- Collect the treated cells in a 15 ml falcon tube. Wash cells twice with 15 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1300 rpm for 5 min at room temperature (RT) between each wash, and decanting the supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in 100 μl Leucoperm Reagent A (BUF09B). Incubate for 15 min at RT.
- Wash cells twice with 15 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1700 rpm for 5 min at RT between each wash and decant the supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in 100 μl Leucoperm Reagent B (BUF09B). Incubate for 5 min at RT.
- Wash cells twice with 1 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1700 rpm for 5 min at RT between each wash and decant the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in 0.5 ml of 2 M HCl. Incubate for 30 min at RT (preferably on a rocking platform).
- Wash cells twice with 1 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1700 rpm for 5 min at RT between each wash and decant the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in FACS buffer to a final density of 5 × 106 cells/ml.
-
Add 100 μl of cell suspension to a 5 ml FACS tube. Centrifuge the cells, discard the supernatant, and add the anti-BrdU antibody of choice at the required dilution. Incubate for
1 hr at RT or 4oC overnight, avoiding direct light. - Wash cells with 1 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1500 rpm for 5 min at RT between each wash and decant the supernatant.
- Incubate with a secondary antibody for 30 min at RT, avoiding direct light.
- Wash cells twice with 1 ml FACS buffer, centrifuging the cells at 1500 rpm for 5 min at RT between each wash and decant the supernatant.
- Prepare FACS buffer with ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide (1351101) by adding 1 drop of ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide per 500 μl of FACS buffer.
- Add 200 μl of FACS buffer with ReadiDrop Propidium Iodide to the cells. Analyze by flow cytometry.
Notes
Appropriate controls should be carried out for flow cytometry, consider including the following:
- A known positive sample
- Isotype controls (to determine if the staining is specific)
- Unstained cells (should always be included to monitor autofluorescence)
For all multicolor flow cytometry experiments, include compensation controls and fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls, which assist with identifying gating boundaries.
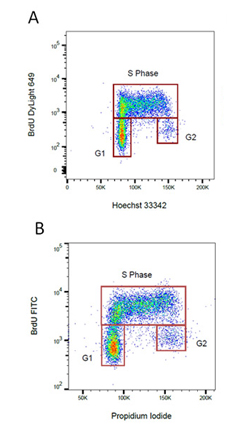
Fig. 9. BrdU staining for proliferation. Proliferating cells were stained for incorporated BrdU against total DNA content using A. Hoechst or B. Propidium Iodide. BrdU was detected by labeling a mouse primary anti-BrdU antibody (MCA2483) with the appropriate secondary antibody attached to a fluorophore.
Resource
Proliferation and Cell Cycle
Cell proliferation can be measured by flow cytometry using several methods. Whilst simple differences in the forward and side scatter will indicate if there are some changes in the cell cycle more accurate methods are available. One method is to stain with an antibody against a proliferation marker such as Ki67, MCM2, or PCNA. Alternatively, you can incubate your cells with BrdU, which incorporates into DNA during S-phase of the cell cycle. Incorporated BrdU can be detected using fluorescently labeled anti-BrdU antibodies. When combined with a DNA stain such as PI or DAPI, the relative proportion of cells in S-phase can be determined.
In addition to using antibodies, cytoplasmic dyes, such as CFDA-SE, can be used to measure proliferation. Cells are incubated with the protein binding dyes and as the labeled cells divide, the concentration of the dye is halved and the proliferation measured based upon the reduced levels of fluorescence in subsequent generations. The advantage of these dyes is that they are non-toxic and available in a wide variety of colors, so can be combined with immunophenotyping and do not require the sample to be fixed.
Cell Cycle Determination
The proportion of cells within each stage of the cell cycle can be determined using DNA binding dyes such as PI, 7-AAD, Hoechst 33342, and DAPI that bind in a stoichiometric manner. This way cells in G2, which have twice as much DNA as cells in G1, will fluoresce twice as bright. To ensure good staining the cells should be fixed in cold 70% ethanol. However this can interfere with other staining protocols, see our protocols section for advice on the different methods. Cell cycle analysis is usually measured on a linear scale unlike most flow cytometry which uses a logarithmic scale as the differences in fluorescence are usually smaller. It is important to gate out any doublets from the data and the data can be improved by using a low flow rate on the cytometer. Many flow cytometry software programs now offer algorithms to accurately estimate the cell cycle phases.








