Cell Proliferation and Viability Detection Reagents
What is Cell Proliferation and How to Analyze it?
Cell proliferation is the rapid expansion of a cell population due to cell growth and division. This cellular process has to be carefully regulated as the smallest alterations can result in an uncontrolled increase of cell numbers, and eventually cancer. To sustain homeostasis and ultimately prevent carcinogenesis, uncontrolled cell proliferation is often counteracted by an increase in apoptosis.
In eukaryotes the cell cycle can be grouped into three major stages:
- Interphase (a growth period, comprising of G1, S and G2 phase, in which the cell duplicates its DNA)
- Mitotic phase (the chromosomes get separated into two sets in preparation for division; M phase consists of 4 stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase)
- Cytokinesis (division to form two daughter cells)
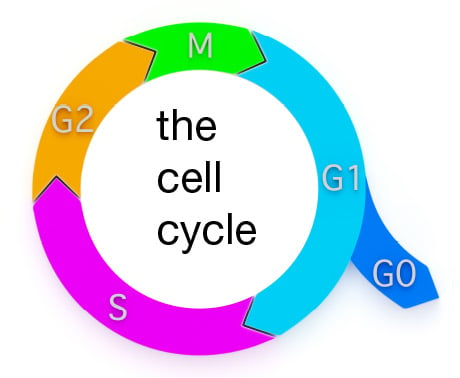
Schematic representation of the cell cycle. Ki-67 is expressed during G1, S, G2 and M phases. PCNA is present from G1 through to G2. MCM 2 is critical for replication in G1 while the BrdU method recognizes replicating cells during S phase.
Cell cycle deregulation and impaired cell cycle checkpoints are two of the most common causes of aberrant cell proliferation. Cell proliferation can be measured by quantifying protein levels of key proliferation markers such as Ki-67, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and minichromosome maintenance 2 (MCM2), and also by measuring incorporation of Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU).
BrdU is a thymidine analog, which is incorporated into the newly synthesized DNA of proliferating cells instead of thymidine when added to cell culture media. The incorporated BrdU can be detected and measured with the help of BrdU specific antibodies.
Learn more about cell proliferation assessments and the key cell proliferation biomarkers Ki-67, MCM2 and PCNA in our mini-review:
Top Cell Proliferation Products:
alamarBlue Reagent provides a rapid and sensitive way to measure cell proliferation. Just add and measure.
alamarBlue Reagent (BUF012A, BUF012B)
alamarBlue Assays are a convenient and quick way to measure cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in human and animal cell lines, bacteria and fungi. Key advantages over traditional MTT and XTT assays include:
- Increased sensitivity - as few as 50 cells can be detected
- Excellent stability - allowing for continuous reading over several days in culture
- Safety - nontoxic to cells, users, and the environment
Access the alamarBlue Reagent page for FAQs, online calculators, example calculations, references, protocols or download the alamarBlue brochure.
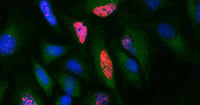
Immunostaining of BrdU labeled HeLa cells with Mouse Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a (MCA2483, red). Cytoplasm was stained with Rabbit Anti-GAPDH Antibody (AHP1628, green). PureBlu DAPI (1351303, blue) was used as a nuclear counterstain.
Mouse Monoclonal Anti-BrdU Antibody (MCA2483)
Mouse Anti-BrdU Antibody, clone Bu20a is one of the most commonly used anti-BrdU antibodies. The product is supported by comprehensive protocols for use in flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry, and 10 publications.
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence
Citations: >15
Find out more about BrdU
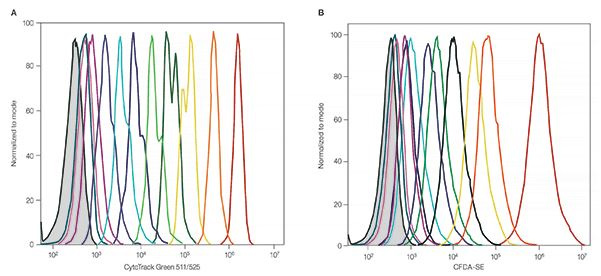
Excellent resolution of ten cell generations using CytoTrack Green 511/525 (A) compared to CFDA-SE (B).
Proliferation Dyes
CytoTrack Dyes allow you to measure cell proliferation in live cells. As the labeled cells divide, the concentration of the dye is halved and the proliferation can be measured based upon the varying levels of fluorescence in subsequent generations.
These dyes are available in a range of excitation and emission spectra for convenient incorporation into multicolor flow cytometry panels