When staining cytokines, a protein transport inhibitor should be added prior to fixation and permeabilization. We have provided some tips and tricks and useful products to help you get the best results when staining cytokines.
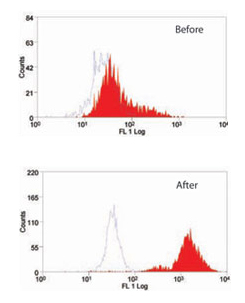
Fig.1. The effect of Leucoperm on (MCA519G) which recognizes MOMA-2, an intracellular antigen in mouse macrophages and monocytes.
Products
Leucoperm
Leucoperm™ makes intracellular antigen analysis using flow cytometry easy. The kit comes with a ‘Reagent A’ that fixes cells in suspension, and a ‘Reagent B’ that subsequently permeabilizes them.
- Results within the hour
- Negligible background staining
- Optimal staining patterns
- Excellent scatter characteristics
With Leucoperm, antibodies can access intracellular structures leaving the morphological scatter characteristics of the cells intact. Leucoperm is superb for detecting many intracellular antigens including:
- Cytokines e.g. IL-2 and IFN
- TdT, MPO, and CD3 involved in leukemia and lymphoma
- Platelets: P-selectin, CD63, and thrombospondin
- Nuclear Ki-67 and PCNA expression in proliferating cells
The Ideal Fixation and Permeabilization Kits
The specific formulation of Leucoperm reduces background staining and allows the simultaneous addition of permeabilization medium and fluorochrome-labeled antibodies.
Most commercially available monoclonal antibody conjugates can be used with Leucoperm reagents.
Erythrolyse Red Blood Cell Lysing Buffer
Bio-Rad Erythrolyse is designed for use in whole blood immunofluorescent staining procedures and is suitable for use with human, rat and mouse blood.
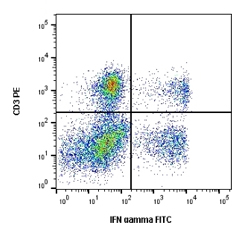
Fig.2. Cells stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 5 hours in the presence of brefeldin A (BUF075) were stained with RPE conjugated mouse anti human CD3 (MCA2184PE) and FITC conjugated mouse anti human IFN-gamma.
Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A Solution (1000x) is commonly used to enhance intracellular cytokine staining by inhibiting protein transport.
This solution causes many of the cytokines to accumulate in the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum.
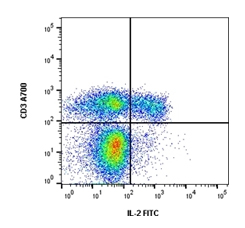
Fig.3. Cells stimulated with Cell Stimulation Reagent containing Brefeldin A (BUF077A) for 5 hours were stained with Alexa Fluor 700 conjugated Mouse anti Human CD3 (MCA463A700) and FITC conjugated Mouse anti Human IL-2 (MCA1553F).
Cell Stimulation Reagent (with Brefeldin A)
Cell Stimulation Reagent (with Brefledin A) 500x is a mixture of PMA (phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate), ionomycin and the protein transport inhibitor Brefeldin A. PMA and ionomycin activate cells and increase cytokine production.
Brefeldin A allows for these cytokines to accumulate in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus allowing for their detection by intracellular fluorescent staining.
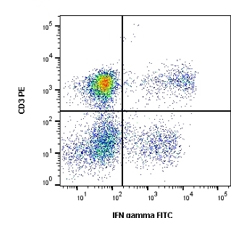
Fig.4. Cells stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 5 hours in the presence of monensin solution (BUF074) were stained with RPE conjugated mouse anti human CD3 (MCA2184PE) and FITC conjugated mouse anti human IFN-gamma.
Monensin Solution
Monensin Solution (1000x) is commonly used to enhance intracellular cytokine staining by inhibiting protein transport. This solution causes many of the cytokines to accumulate in the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum.
Protocol
Direct Immunofluorescence Staining of Intracellular Cytokines in Blood
For the staining of intracellular antigens in whole blood using directly conjugated antibodies.
This is a rapid and simple approach to the analysis of intracellular cytokines in whole blood. It permits the analysis of small samples and avoids generating artefacts due to the separation of peripheral blood cells by density gradient centrifugation. All blood samples must be collected into heparin anticoagulant. EDTA interferes with the cell stimulation process and therefore must be avoided.
The detection of intracellular antigens requires a cell permeabilization step prior to staining. The method described below has been found to provide excellent results in our hands; however other permeabilization techniques have been published and may also be successfully used in this application.
This method provides a general procedure for use with the majority of Bio-Rad reagents. In some cases specific recommendations are provided on product datasheets, and these methods should always be used in conjunction with the product and batch specific information provided with each vial. A certain level of technical skill and immunological knowledge is required for the successful design and implementation of these techniques; these are guidelines only and may need to be adjusted for particular applications.
Note: Resting cells often require stimulation in vitro prior to the detection of intracellular cytokines.
Reagents
- Leucoperm Accessory Reagent (Product code BUF09). Includes Reagent A (cell fixation agent) and Reagent B (cell permeabilization agent).
- Phosphate buffered saline (Product code BUF036A) containing 1% bovine serum albumin (PBS/BSA)
- Erythrolyse red blood cell lysing buffer (BUF04).
- Cell culture medium
- Monensin
- Ionomycin
- PMA
- Optional: 0.5% (w/v) paraformaldehyde in PBS (Note: dissolve on heated stirrer and cool before use)
Method
- Aliquot 500 μl of blood into as many tubes as required, including 2 extra control tubes, then add 500 μl of cell culture medium (without any additives) to each sample.
- To one tube (the resting population), add monensin to a final concentration of 3 μM.
-
To another tube (activated cells), add PMA to a final concentration of 10 ng/ml, ionomycin
(2 μM) and monensin (3 μM). - To the rest of the tubes (experimental samples) add monensin (3 μM) and treat as required by the experiment.
- Incubate for 2-4 hours at 37oC in a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- If required, perform staining of cell surface antigens using appropriate directly conjugated monoclonal antibodies at 4oC, avoiding direct light.
- Wash cells once with PBS/BSA and discard supernatant.
-
Add 100 μl of Leucoperm Reagent A (cell fixation agent) and incubate for 10 min at
2-8oC. - Add 2 ml cold (4oC) PBS/BSA and centrifuge for 5 min at 300-400 g at room temperature.
- Remove supernatant and add 100 μl Leucoperm Reagent B (cell permeabilization agent) per 1 x 106 cells. Add the directly conjugated antibody at the vendor-recommended dilution and incubate for at least 30 min at 4oC, avoiding direct light.
- Add 2 ml freshly prepared erythrolyse red blood cell lysing buffer to the blood suspension and mix well.
- Incubate for 10 min at room temperature.
- Centrifuge at 300-400 g for 5 min and discard the supernatant.
- Wash once in PBS/BSA, and then re-suspend in 200 μl PBS for immediate analysis or with 200 μl of 0.5% formaldehyde in PBS if required.
- Acquire data by flow cytometry. Analyze fixed cells within 24 hours.

Tips and Tricks for Intracellular Flow Cytometry
Resources
Intracellular Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry protocols and staining procedures vary depending on whether the antigen to be detected is located on the cell surface or intracellular. Detection of cell surface proteins, such as CD markers, is relatively straightforward, and apart from blocking of Fc receptors the protocol requires no extra steps. However, when staining intracellular proteins such as cytokines or transcription factors, both fixation and permeabilization steps are required prior to antibody staining.

Updated Flow Cytometry Basics Guide
Practical advice to get you started in flow cytometry.
Introduction to Flow Cytometry Basics
This flow cytometry guide aims to give you a basic overview of all the important aspects of flow cytometry.
With chapters on instrumentation, useful reagents, controls, experimental set up, and much more, this guide enables best practice to be followed and gives practical advice on building multicolor panels with example protocols.
This guide is invaluable to beginners wanting to start flow cytometry and is a handy tool for teaching others about this powerful application.
To further assist learning we have recently added a flow cytometry glossary of terms to this guide.






