The Lab Rat Model
Overview
Rats have been used as a model for humans for over 150 years. Rats were the original animal model with the use of mice becoming more prevalent due to the development of transgenic mice models.
Rats are however consistently more representative of humans compared to mice:
- Being metabolically similar - better for pharmacokinetics studies
- Having superior cognitive skills to mice – better for neurological disorders and behavioural studies
- Being physically more similar – therefore better suited to toxicology, cardiovascular and immunology studies
And simply due to their larger size, rats are easier to handle and are better suited to transplantation research and repeat bleeds.
Now that the rat genome has been mapped and knock in and knock out transgenic rat strains are available the rat model may become used more widely.
Rat Facts
Below are a few interesting facts about lab rats:
- Most laboratory rat strains are derived from the albino Wistar rat
- The Sprague Dawley rat is used extensively in medical research in part because of its calmness and ease of handling, with a life span of 2-3 years
- Rowett nudes are hairless rats that have no thymus
- Zucker rats are used as a model for obesity and hypertension
- The rat genome is 2.75 million base pairs long
- Rats have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes, the same as humans
- A 454 g rat has between 23 and 32 ml of blood
- Rat heart rate is 330-480 beats per minute
- Rat respiratory rate is 85 breaths per minute
- The body temperature of a rat is 35.9-37.5ºC
- Rats do not have gallbladders or tonsils
- Rats cannot vomit
Immune Cell Frequencies
When designing your experiment it is important to consider the target cell frequency. The numbers of cells that need to be stained to collect a statistically relevant number of positive or negative cells need to be understood. This way you can avoid having to repeat the experiment simply due to the lack of statistical significance. Table 1 shows the relative frequency of cells in commonly used rat tissues. Go to our dedicated cell frequencies page for more detailed information.
Table 1. Rat immune cell frequencies.
| Spleen | Thymus | Peripheral Blood | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cell Type |
Percent |
Cell Type |
Percent |
Cell Type |
Percent |
|
T cells |
31.5-33.5 |
CD4+ |
5.7-9.4 |
T cells |
51.5-66.5 |
|
CD4+ |
21.5-26.5 |
CD8+ |
2.3-6.9 |
CD4+ |
32-40 |
|
CD8+ |
14-18 |
CD4+/8+ |
83-87.6 |
CD8+ |
18-26 |
|
B cells |
31.5-33.5 |
CD4-/8- |
1.4-2.2 |
B cells |
22.7-40.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
Monocytes |
1-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
Neutrophils |
14-20 |
|
|
|
|
|
Eosinophils |
1-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Basophils |
Rare |
|
|
|
|
|
γδ T cells |
1-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
NK cells |
6-10 |
Lineage Specific Rat Markers
Table 2 lists markers that can be used to determine different immune cell lineages.
Table 2. Rat lineage markers and antibodies.
Cell |
Marker |
Antibodies (catalog #) |
|---|---|---|
|
Pan specific T cell |
CD3 |
|
|
Helper T cell |
CD4 |
|
|
Cytotoxic T cell |
CD8 alpha, CD8 beta |
|
|
Thymocytes |
CD90 |
|
|
Granulocytes |
Pan specific |
|
|
Macrophages |
CD11b, CD68, CD163, CD169 |
|
|
Dendritic cells |
CD80, CD86 |
|
|
Endothelial cells |
CD31, RECA-1 |
Key Rat Markers
As rats can be used in many research areas, there are a large number of commonly used markers. Table 3 lists key markers to identify various cell types.
Table 3. Key rat markers to target cell or research area along with available antibodies.
Key Marker |
Research Area / Target |
Antibodies (catalog #) |
|---|---|---|
|
CD3 |
T cells |
|
|
CD4 |
T cells and monocytes |
|
|
CD8 alpha |
T cells, NK cells and monocytes |
|
|
CD11b |
Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, granulocytes |
|
|
CD25 |
T cells and dendritic cells |
|
|
CD31 |
PECAM-1 expressed on endothelial cells, platelets and leucocytes |
|
|
CD43 |
Leucocytes except B cells |
|
|
CD45 |
Leucocytes |
|
|
CD45RA |
B cells |
|
|
CD68 |
Macrophages |
|
|
CD71 |
Proliferating cells of hematopoietic lineages |
|
|
CD86 (B7-2) |
Antigen presenting cells especially dendritic cells, macrophages and B cells |
|
|
CD90 |
Thymocytes, neuronal cells, stem cells and peripheral T cells |
|
|
CD161 |
NK cells and T cell subpopulations |
|
|
MHC Class I |
All nucleated cells |
|
|
MHC Class II |
B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages and certain epithelial cells |
|
|
IFN Gamma |
Cytokine |
|
|
TNF Alpha |
Cytokine |
|
|
GSK3 Beta (pSer9) |
Cell signaling |
|
|
P38 MAPK (pThr180/pTyr182) |
Cell signaling |
|
|
NMDAR Receptors |
Neuroscience |
Featured Key Markers CD44 and CD4
Mouse Anti-Rat CD44 Antibody, clone OX-50 recognizes the rat CD44 cell surface antigen, also known as Extracellular Matrix Receptor III. CD44 is a 482 amino acid ~85 kDa single pass type I transmembrane glycoprotein, expressed by T cells, B cells, macrophages and thymocytes. Mouse Anti-Rat CD4 (Domain 2) Antibody, clone OX-35 recognizes the rat CD4 cell surface antigen, a ~55kDa glycoprotein expressed by helper T cells and weakly by monocytes. Rat markers CD44 and CD4 have been used in flow cytometry (Figure 1), showing T cell, B cell and macrophage populations. Following this, CD4 has been used in immunohistochemistry showing T cells.
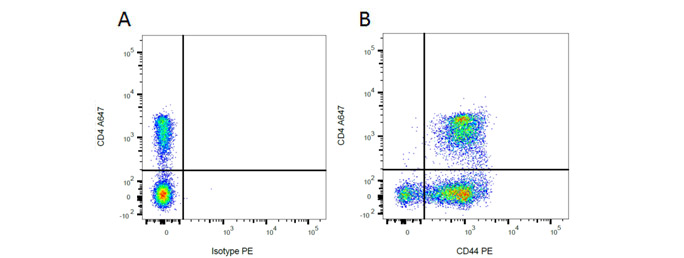
Fig. 1. Flow cytometry analysis of rat makers CD44 and CD4. A, A647 conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD4 (MCA153A647) and RPE conjugated Mouse IgG2a Isotype Control (MCA1210PE). B, A647 conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD4 (MCA153A647) and RPE conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD44 (MCA643PE). All experiments performed on red cell lysed rat blood gated on mononuclear cells.
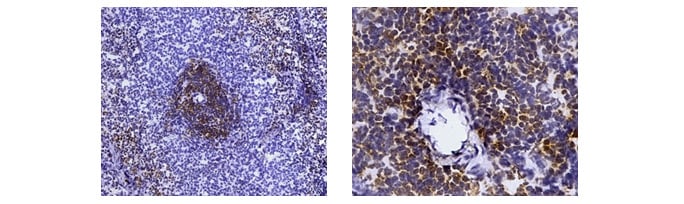
Fig. 2. Immunohistochemistry analysis of rat marker CD4. CD4+ T cells clustering around central arteriole in the white pulp of rat spleen (cryosection) stained with MCA153.
Anti-Rat Antibodies and Related Products
Bio-Rad has an extensive range of rat monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies guaranteed for use in applications such as flow cytometry, western blotting, immunoprecipitation, IHC and, ELISA. These antibodies are available in various formats, however if you can’t find the format you need, you can also choose from a range of easy-to-use conjugation kits.
These anti-rat antibodies are targeted against markers for study in various research areas specifically immunology, pathology, toxicology, neurology and transplantation.
The following types of antibody are available:
ED Clone Antibodies
Bio-Rad has one the most comprehensive range of ED clone anti-rat antibodies primarily for the study of macrophage subtypes but also other related molecules.
Table 4. ED clone anti-rat antibodies, marker and cell type.
Clone |
Target |
Marker |
Antibody (catalog #) |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ED1 |
Macrophages |
CD68 |
FC, IF/ICC, IHC-F, IHC-P, IP, WB |
|
|
ED2 |
Macrophages |
CD163 |
FC, IF/ICC, IHC-F, IHC-P, IP, WB |
|
|
ED3 |
Macrophages |
CD169 |
FC, IF/ICC, IHC-F, IP |
|
|
ED7 |
Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, granulocytes |
CD11b |
FC, FN, IHC-F |
|
|
ED8 |
Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, granulocytes |
CD11b |
FC, IHC-F |
|
|
ED9 |
Myeloid cells, neurons |
CD172a (SIRP) |
FC, IHC-F, IP, WB |
Abbreviations: E, ELISA; FC, flow cytometry; IF/ICC, immunofluorescence/immunocytochemistry; IHC-F, immunohistochemistry-frozen; IHC-P, immunohistochemistry-paraffin; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, western blotting.
Find out more about ED clone antibodies
Featured ED Clone Antibody CD11b
Mouse Anti-Rat CD11b Antibody, clone ED8 recognizes a membrane antigen on rat macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells and granulocytes. It also recognizes small ramified microglia in the central nervous system. Mouse Anti-Rat CD106 Antibody, clone MR106 specifically recognizes rat CD106, otherwise known as VCAM-1 (vascular adhesion molecule 1), an 110kDa inducible type I transmembrane glycoprotein. It is predominantly expressed on vascular endothelium, and also on bone marrow stromal cells, follicular dendritic cells and some macrophages. Rat markers CD11b and CD106 have been used in flow cytometry (Figure 3), showing myeloid cell populations. In Figure 4 immunofluorescence staining of CD11b alongside CD4 in rat spleen shows macrophages and T cells.
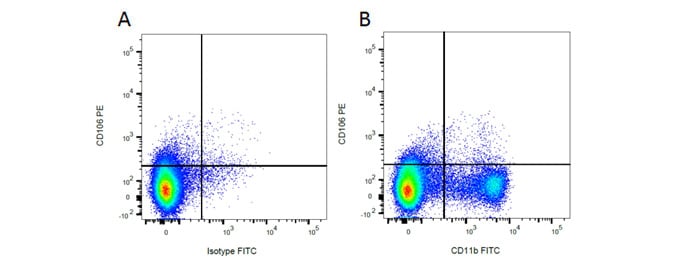
Fig. 3. Flow cytometry analysis of rat makers CD11b and CD106. A, PE conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD106 (MCA4633PE) and FITC conjugated Mouse IgG2a Isotype Control (MCA1210F). B, PE conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD106 (MCA4633PE) and FITC conjugated Mouse Anti-Rat CD11b (MCA619F). All experiments performed on red cell lysed rat bone marrow gated on mononuclear cells.
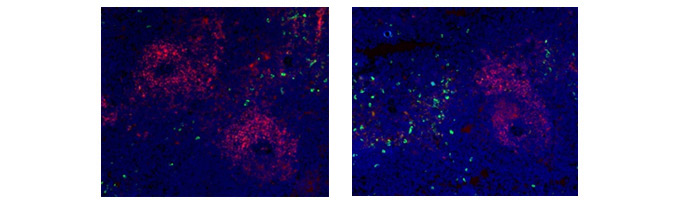
Fig. 4. Immunofluorescence analysis of rat marker CD11b and CD4. CD4+ T cells (red) stained with MCA153 and CD11b positive macrophages (green) stained with MCA619 in rat spleen (cryosection).
Antibodies for Rat in Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry, a method to measure and characterize cells, can be used in standard procedures such as cell counting, cell sorting, biomarker detection and protein engineering. Bio-Rad offers many anti-rat antibodies that are guaranteed for use in flow cytometry and come conjugated to a variety of different fluorescent dyes, in addition to pre-prepared 2, 3 and 4 color cocktails. Bio-Rad also provides all the reagents required in a flow assay, such as viability dyes, FC block and flow cytometry kits and a large range of mouse isotype controls.
Finally you have access to a wealth of educational resources to support your flow assay including guides, posters, webinars and practical help and advice.
Rat Flow Cytometry Panels
Table 5 shows example panels with common surface and intracellular markers for rat peripheral blood and secondary lymphoid tissue to identify different cell populations.
Table 5. Rat flow cytometry panels.
Marker |
Antibody (catalog #) |
Formats |
|---|---|---|
|
General panel; T cell, B cell, NK cell and myeloid |
|
|
|
CD3 |
A647 |
|
|
CD45RA |
PE-A647 |
|
|
CD11b |
A488 |
|
|
CD161 |
PE |
|
|
T cell panel |
|
|
|
CD3 |
FITC |
|
|
CD4 |
PE-A750 |
|
|
CD8a |
A647 |
|
|
CD45RA |
PE |
|
|
B cell panel |
|
|
|
CD45RA |
PE-A647 |
|
|
RT1B |
PE |
|
|
IgM |
FITC |
|
|
CD3 |
A647 |
|
|
Myeloid |
|
|
|
CD43 |
FITC |
|
|
CD11b |
Pacific Blue |
|
|
RT-1B |
A647 |
|
|
CD86 |
PE |
|
|
Macrophages in tissues |
|
|
|
CD68 |
A488 |
|
|
CD11b |
Pacific Blue |
|
|
CD163 |
A647 |
|
|
CD45 |
PE-A750 |
Note: Rat T cell panels must contain CD3 as monocytes are positive for CD4.






