CD68 Antibody
Overview
CD68 is a 110-kDa glycoprotein, being classified as a member of the scavenger receptor family, whose typical functions include clearance of cellular debris, promotion of phagocytosis, and the mediation, recruitment and activation of macrophages. CD68 is also a member of the lysosome associated membrane protein (LAMP) family, where CD68 predominantly localizes to lysosomes and endosomes with a smaller fraction circulating to the cell surface.
CD68 is highly expressed by monocytes and tissue macrophages, including Kupffer cells, microglia, histiocytes and osteoclasts, and to a lesser extent on dendritic cells and peripheral blood granulocytes. However CD68 expression is not unique to myeloid cells, it can also be found on hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells, and on carcinomas and melanomas especially in tumor stroma cells such as fibroblasts and endothelial cells. CD68 should perhaps be regarded as a phagocytic marker and used alongside other markers to define a cell type.
A flow cytometry protocol is available that provides detailed procedures for the treatment and staining of this intracellular marker.
CD68 antibodies at a glance
Most popular CD68 antibody options at a glance, click here to view all CD68 antibodies.
| Target | Clone | Application | Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Y1/81A | Flow cytometry | RPE |
| Human | KP1 | Flow cytometry | FITC |
| Human | 514H12 | IHC | Supernatant |
| Human | Ki-M7 | Flow cytometry | FITC |
| Mouse | FA-11 | Flow cytometry | Alexa Fluor dyes |
| Rat | ED1 | IHC | Biotin |
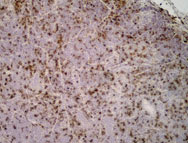
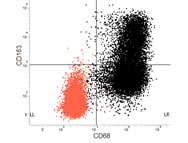
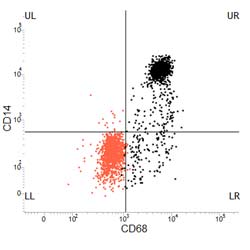
Explore CD68 antibody images by application
Other related macrophage markers by species reactivity
In addition to CD68, Bio-Rad also offers a wide range of other macrophage markers such as:
Anti-Rat Antibodies
References
Anti-rat CD68
-
Bao F et al. (2004). Early anti-inflammatory treatment reduces lipid peroxidation and protein nitration after spinal cord injury in rats.
J. Neuro-chem. 88:1335-1344. -
Zilka N et al. (2009). Human misfolded truncated tau protein promotes activation of microglia and leukocyte infiltration in the transgenic rat model of tauopathy.
J. Neuroimmunol. 209: 16-25. -
Machelska H et al. (2013). Selectins and integrins but not platelet–endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 regulate opioid inhibition of inflammatory pain.
British Journal of Pharmacology 142:772-780.
Anti-human CD68
-
Holness CL and Simmons DL. (1993). Molecular cloning of CD68, human macrophage marker related to lysosomal glycoproteins.
Blood. 1993 Mar 15;81(6):1607-13. -
Da Costa CE et al. (2005). Presence of osteoclast-like multinucleated giant cells in the bone and nonostoticlesions of Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
J. Exp Med. 201: 687-93. -
Muthana M et al. (2011). Use of macrophages to target therapeutic adenovirus to human prostate tumors.
Cancer Res. Jan 13. [Epub ahead of print]
Anti-mouse CD68
-
Smith M and Koch G. (1987). Differential expression of murine macrophage surface glycoprotein antigens in intracellular membranes.
J. Cell Sci. 87:113-9. -
Holness CL et al. (1993). Macrosialin, a mouse macrophage-restricted glycoprotein, is a member of the lamp/lgp family.
J.Biol Chem. 268(13):9661-6. -
Da Silva RP and Gordon S. (1999). Phagocytosis stimulates alternative glycosylation of macrosialin (mouse CD68), a macrophage-specific endosomal protein.
Biochem. J. 338: 687-694.
View all anti-CD68 references.