Phosphorylated Protein Detection FAQs
s
Western Blot University
s
What are R-loops?
s
Cancer Pathway Posters
Compiling key proteins involved in key signaling pathways: cGAS-STING, EGF R, mTOR, NF-kB, and PI3/AKT pathways.
s
Recent Blog
During the “Western Blotting Tips for Phosphorylated Protein Detection” Coffee Chat and “Illuminating the Pathway to Confident Western Blot Detection of Phosphorylated Proteins” webinar, researchers asked questions to Bio-Rad’s application scientists about the detection of phosphorylation events by western blotting.
To help you overcome this challenging technique, we have combined our answers for the most frequently asked questions.
- Is it better to store lysates at -80oC or at -20oC to prevent degradation when looking at phosphorylated proteins?
- Should I prepare my samples with phosphatase inhibitors?
- Which blocking agent should I use?
- What percentage of BSA would you use for your blocking buffer?
- Which controls should I use?
- Do you have any suggestions on how to concentrate the protein amount or suggestions to enhance detection?
- With regards to using Stain-Free technology to get a total protein image, is it advisable to use the Stain-Free blot over the Stain-Free gel?
- Between alkaline phosphatase or lambda phosphatase, which would you use to perform phosphatase treatment?
- I’ve managed to acquire an antibody against my phosphorylated protein of interest, but it has the same host species as my samples. Is there a way I can use this antibody without detecting the endogenous IgG in my sample?
- Can I use stripping buffer to detect two different phosphorylated proteins with the same molecular weight?
Is it better to store lysates at -80oC or at -20oC to prevent degradation when looking at phosphorylated proteins?
Store your lysates at -80oC to prevent any degradation of phosphorylated proteins by phosphatases present in the lysate.
Should I prepare my samples with phosphatase inhibitors?
Use phosphatase and protease inhibitors and keep your samples on ice to inhibit protein degradation and conserve posttranslational modifications during sample preparation.
Which blocking agent should I use?
Start with bovine serum albumin (BSA) in tris-buffered saline (TBS). It is usually best to avoid using milk because some protein components may interfere with recognition of phosphorylated proteins. If using BSA, make sure it is thoroughly dissolved because any solid BSA will cause speckles on your blot.
What percentage of BSA would you use for your blocking buffer?
A good starting point can be 5% BSA with 0.1% Tween 20 in TBS but this may need to be optimized for your protein of interest.
Which controls should I use?
Consider the following controls:
- Positive and negative controls: confirm antibody specificity by including samples stimulated to induce phosphorylation at your site of interest and by performing phosphatase treatment. You can also include a negative control such as cells treated with a specific kinase inhibitor
- Total protein controls: present data for each phospho-specific antibody alongside data from an antibody recognizing the total protein. This will provide you with absolute confidence in the specificity of your phospho-specific antibody and determine if expression of the target protein is up- or downregulated (Figure 1)
-
Loading controls: popular loading controls include housekeeping proteins, such as beta-actin or beta-tubulin. As an alternative, you can also use dyes like Ponceau S or Bio-Rad’s Stain-Free imaging technology
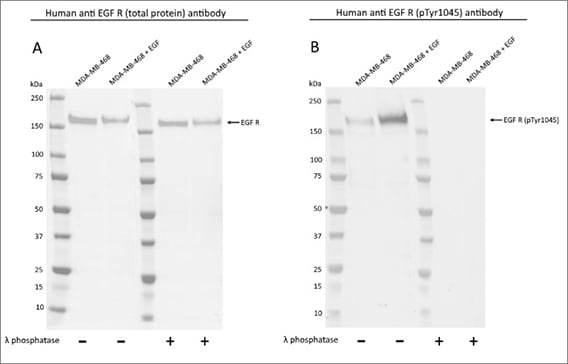
Fig. 1. Western blot detection of total and phospho EGF R. MDA-MB-468 untreated and EGF treated whole cell lysates were probed with A, Human Anti-EGF R Antibody (VMA00474) or B, Human Anti-EGF R (pTyr1045) Antibody (VMA00515) followed by detection with HRP conjugated Human Anti-Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase (HCA275P).
Do you have any suggestions on how to concentrate the protein amount or suggestions to enhance detection?
Try preparing your lysates in as little lysis buffer as possible. You could also immunoprecipitate your protein of interest before loading it onto your gel.
As far as enhancing detection, one good option is to use a sensitive chemiluminescent substrate such as Clarity Max ECL WB Substrate or fluorescent detection.
With regards to using Stain-Free technology to get a total protein image, is it advisable to use the Stain-Free blot over the Stain-Free gel?
It is better practice to use the Stain-Free blot image for total protein normalization, since variability in transferring your proteins to the membrane could result in differences between samples not captured by the Stain-Free gel image. To reduce the background in these images, use low-fluorescent PVDF membrane.
Visit bio-rad-antibodies.com/phospho-PrecisionAb. Contact your local sales representative, or our technical support team, for more information.
Between alkaline phosphatase or lambda phosphatase, which would you use to perform phosphatase treatment?
The phosphatase you use depends on the type of phosphorylation event you are interested in. Both lambda protein phosphatase and calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase have an activity towards phospho-tyrosine residues. In addition, lambda protein phosphatase also has an activity towards serine and threonine phospho residues.
I’ve managed to acquire an antibody against my phosphorylated protein of interest, but it has the same host species as my samples. Is there a way I can use this antibody without detecting the endogenous IgG in my sample?
Use a conformation specific secondary reagent, like Bio-Rad’s TidyBlot Reagent, which only detects the native conformation of an antibody (i.e. your primary antibody) and not the denatured endogenous IgG in your samples. This means that the heavy and light chains from the antibodies in your sample will not be detected. The only band that should appear on your blot is from your antibody detecting the phosphorylated target.
Can I use stripping buffer to detect two different phosphorylated proteins with the same molecular weight?
We recommend performing a multiplex fluorescent western blotting experiment rather than stripping and reprobing blots. This is because the signal from the first phospho-specific antibody might not be completely removed during the stripping process. You can learn more about Bio-Rad’s fluorescent western blotting workflow here.