Huntingtin antibody | HDB4E10



Mouse anti Huntingtin
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- HDB4E10
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- Huntingtin
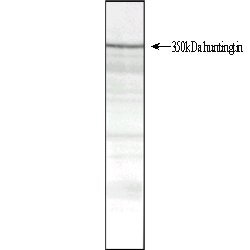
| Mouse anti Huntingtin antibody, clone HDB4E10 reacts with an epitope corresponding to the HDB region (amino acids 1844 - 2131) of the huntingtin protein. Mouse anti Huntingtin antibody, clone HDB4E10 detects a ~350 kDa band on western blots but also detects smaller degradation products of huntingtin. The combined use of Mouse anti Huntingtin antibody, clones HDB4E10 (MCA2050) and HDC8A4 (MCA2051) demonstrate that huntingtin is enriched in neuronal cells in the brain (Jones 1999). |
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Mouse Human Rabbit - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% sodium azide (NaN3)
- Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 1844 - 2131 of huntingtin.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunohistology - Frozen 1 | |||
| Immunoprecipitation | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1 Increased cytoplasmic staining, relative to nuclear, has been reported using formaldehyde as a fixative compared with acetone/methanol, see Wilkinson et al.
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Brain
References for Huntingtin antibody
-
Wilkinson, F. L. et al. (1999) Localization of rabbit huntingtin using a new panel of monoclonal antibodies.
Molecular Brain Research. 69: 10-20. -
Jones, A.L. (1999) The localization and interactions of huntingtin.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 354 (1386): 1021-7. -
Tao, T. & Tartakoff, A.M. (2001) Nuclear relocation of normal huntingtin.
Traffic. 2 (6): 385-94. -
Shirasaki, D.I. et al. (2012) Network organization of the huntingtin proteomic interactome in mammalian brain.
Neuron. 75 (1): 41-57. -
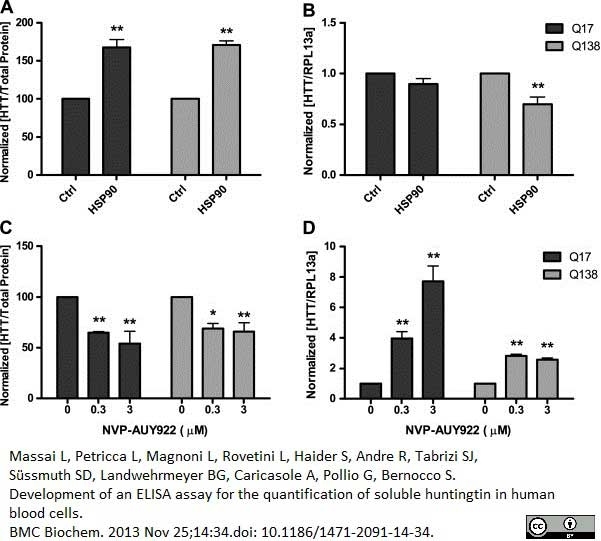
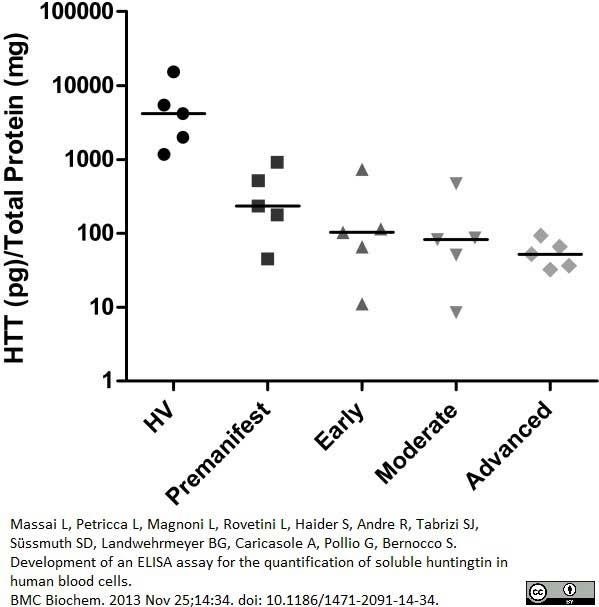
Massai, L. et al. (2013) Development of an ELISA assay for the quantification of soluble huntingtin in human blood cells.
BMC Biochem. 14: 34. -
Yao Y et al. (2015) A striatal-enriched intronic GPCR modulates huntingtin levels and toxicity.
Elife. 4: 4. -
Ni, C.L. et al. (2016) Polyglutamine Tract Expansion Increases S-Nitrosylation of Huntingtin and Ataxin-1.
PLoS One. 11 (9): e0163359.
- RRID
- AB_322302
- UniProt
- P42858
- Entrez Gene
- HTT
- GO Terms
- GO:0000132 establishment of mitotic spindle orientation
- GO:0002039 p53 binding
- GO:0005829 cytosol
- GO:0005783 endoplasmic reticulum
- GO:0005624 membrane fraction
- GO:0005634 nucleus
- GO:0005770 late endosome
- GO:0005776 autophagic vacuole
- GO:0005794 Golgi apparatus
- View More GO Terms
- GO:0006890 retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to ER
- GO:0007030 Golgi organization
- GO:0030424 axon
- GO:0030425 dendrite
- GO:0030659 cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
- GO:0034452 dynactin binding
- GO:0043234 protein complex
- GO:0045505 dynein intermediate chain binding
- GO:0047496 vesicle transport along microtubule
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
Always be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up