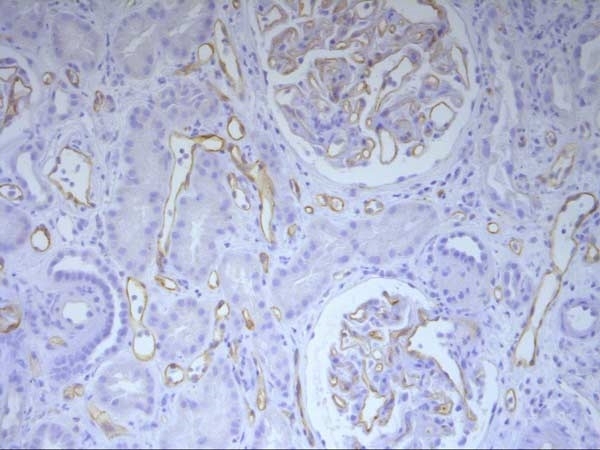
C4d antibody | 10-11
Mouse anti Human C4d
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- 10-11
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- C4d
| Mouse anti Human C4d antibody, clone 10-11 recognizes the secreted protein complement component 4d (C4d). The presence of C4d in renal peritubular capillaries is a key indicator for acute antibody-mediated rejection [AMR] (Collins et al. 1999.). C4d was accepted in 2003 into the Banff classification for identification of acute AMR (Racusen et al. 2003). Mouse anti Human C4d antibody, clone 10-11 is specific for C4d, a marker that can be used in the detection of acute AMR for kidney, heart, pancreas and lung allografts. C4d is regarded as a key marker of antibody-mediated cell injury and humoral rejection (Sacks and Chowdhury 2002). Complement 1 complex cleaves complement 4 (C4) to form C4b and C4a. C4b levels are strictly regulated. Single site cleavage of the C4b’s alpha chain by Factor I forms iC4b and blocks C3 convertase, inhibiting opsonization and activation of the classical pathway. This requires C4 binding protein or CR1 as a cofactor. iC4b is further degraded into C4d and C4c. C4b’s short half life means that C4d is present in serum at high enough concentrations to make it a useful marker for classical complement activation (Collins et al. 1999). Mouse anti Human C4d antibody, clone 10-11 is used to detect the biomarker C4d which has been described as a “footprint” of antibody mediated tissue rejection (Sacks and Chowdhury 2002). The internal thioester of C4b becomes exposed during cleavage to C4d and forms a covalent bond with the cell surface. The longer half-life of covalently bound C4d makes it a footprint of complement activation long after weakly bound antibodies have been cleared by the blood stream (Sacks and Chowdhury 2002). C4 has also been linked to susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (Yang et al. 2004) and rheumatoid arthritis (Makinde et al. 1989). |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Mouse Dog Bovine Cat Rabbit Rat Guinea Pig Sheep - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by Fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) from ascites
- Buffer Solution
- Borate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Native, from human plasma
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 1/5000 | 1/20000 | |
| Immunofluorescence | 1/250 | 1/600 | |
| Immunohistology - Frozen | 1/100 | 1/750 | |
| Immunohistology - Paraffin 1 | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1It has been reported that this antibody works very well on acetone-fixed, frozen renal biopsies. Strong staining is observed in the glomeruli and in some cases the peritubular capillaries.
Clone 10-11 has given variable results on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections. It has been observed that pre-treatment with 88% formic acid for 20 minutes at room temperature is beneficial (6).
References for C4d antibody
-
Collins, A.B. et al. (1999) Complement activation in acute humoral renal allograft rejection: diagnostic significance of C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 10 (10): 2208-14. -
Mauiyyedi, S. et al. (2001) Chronic humoral rejection: identification of antibody-mediated chronic renal allograft rejection by C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 12 (3): 574-82. -
Mauiyyedi, S. et al. (2002) Acute humoral rejection in kidney transplantation: II. Morphology, immunopathology, and pathologic classification.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 13 (3): 779-87. -
Knechtle, S.J. et al. (2003) Campath-1H induction plus rapamycin monotherapy for renal transplantation: results of a pilot study.
Am J Transplant. 3 (6): 722-30. -
Troxell, M.L. et al. (2010) Pancreas allograft rejection: analysis of concurrent renal allograft biopsies and posttherapy follow-up biopsies.
Transplantation. 90: 75-84. -
Rowe, P. et al. (2013) Increased complement activation in human type 1 diabetes pancreata.
Diabetes Care. 36 (11): 3815-7. -
Johnson, R.K. et al. (2013) Acute tubular injury is an important component in type I acute antibody-mediated rejection.
Transplant Proc. 45: 3262-8. -
Lattenist, L. et al. (2013) Renal and urinary levels of endothelial protein C receptor correlate with acute renal allograft rejection.
PLoS One. 8 (5): e64994.
View The Latest Product References
-
Verghese, P. et al. (2013) The impact of C4d and microvascular inflammation before we knew them.
Clin Transplant. 27 (3): 388-96. -
Dugum, M. et al. (2014) Re-examination of sinusoidal deposition of complement 4d in liver allografts: experience from a single institution.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7 (2): 784-91. -
Roden, A.C. et al. (2016) Transbronchial Cryobiopsies in the Evaluation of Lung Allografts: Do the Benefits Outweigh the Risks?
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 140 (4): 303-11. -
Sánchez-escuredo, A. et al. (2016) Borderline rejection in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation.
Clin Transplant. 30 (8): 872-9. -
Jain, D. et al. (2017) Detection of T and B cells specific complement-fixing alloantibodies using flow cytometry: A diagnostic approach for a resource limited laboratory.
Asian J Transfus Sci. 11 (2): 171-9. -
Verghese, P.S. et al. (2018) The clinical implications of the unique glomerular complement deposition pattern in transplant glomerulopathy.
J Nephrol. 31 (1): 157-64.
Further Reading
-
Makinde, V.A. et al. (1989) Reflection of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis by indices of activation of the classical complement pathway.
Ann Rheum Dis. 48 (4): 302-6. -
Stoltzner, S.E. et al. (2000) Temporal accrual of complement proteins in amyloid plaques in Down's syndrome with Alzheimer's disease.
Am J Pathol. 156 (2): 489-99. -
Sacks, S.H. & Chowdhury, P. (2002) Footprints of humoral rejection.
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 11 (6): 627-8. -
Racusen, L.C. et al. (2003) Antibody-mediated rejection criteria - an addition to the Banff 97 classification of renal allograft rejection.
Am J Transplant. 3 (6): 708-14. -
Yang, Y. et al. (2004) The intricate role of complement component C4 in human systemic lupus erythematosus.
Curr Dir Autoimmun. 7: 98-132. -
Troxell, M.L. & Lanciault, C. (2016) Practical Applications in Immunohistochemistry: Evaluation of Rejection and Infection in Organ Transplantation.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 140 (9): 910-25.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up