Complement Component C4d and Biomarkers of Transplantation Rejection
Overview
The complement system, a component of the innate immune system, consists of three pathways that participate in the recognition and clearance of pathogens. More recently, it has also been demonstrated to modulate adaptive immunity and bridge innate and adaptive immune responses. Dysregulation of this complex enzymatic system may cause inflammation as observed in autoimmune disease. Accurately assessing the activity of the complement system is an important diagnostic indicator of overall health.
In the classical and lectin pathways of complement activation, the C1r/C1s complex or MBL associated serine proteases cleave complement 4 (C4) to form C4a and C4b. As a result of C4 cleavage, an internal thiolester of C4b is exposed. This internal motif is highly reactive and will form a covalent bond with nearby protein or carbohydrate. This most often results in binding of C4b to an antibody or the surface of a cell such as vascular endothelial cells. Further cleavage of the C4b alpha chain by Factor I forms C4d and C4c, where C4d remains bound close to the site of C4b binding. The longer half-life of covalently bound C4d versus C4b makes it a perfect marker of complement activation long after weakly bound antibodies have been cleared by the blood stream (Sacks and Chowdhury 2002). For more information on all three complement pathways, read the complement system mini-review.
As a marker of complement activation, C4d has been used as an indicator in the evaluation of cellular and antibody mediated rejection in a variety of tissues such as kidney, heart, and pancreas. (Colvin and Smith 2005). Figure 1 shows C4d staining of human kidney in a patient with Lupus. The presence of C4d in renal peritubular capillaries has been found to be a key indicator for acute antibody mediated rejection (AMR) (Collins et al. 1999), shown in Figure 2 below, using the C4d polyclonal antibody. The C4d Rabbit Anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody (0300-0230) and Mouse Anti-Human C4d Antibody (2222-8004), clone 10-11, are ideal markers used in the detection of acute AMR for kidney, heart, pancreas, and lung allografts.
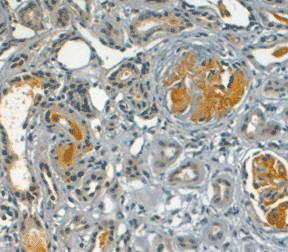
Fig. 1. Formalin fixed paraffin embedded human kidney for a patient with Lupus erythematosus stained with Rabbit Anti-Human C4d Antibody (0300-0230) following sodium citrate (pH 6.0) mediated antigen retrieval.
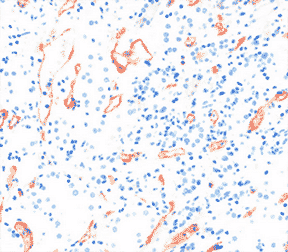
Fig. 2. Immunohistochemical staining of human kidney with Rabbit Anti-Human C4d Antibody (0300-0230) showing localization to the peritubular capillaries.
C4d Antibodies
| Description | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse Anti-Human C4d (Neoantigen) | 057-51.5.1.6 | IHC-F, E | (1) | MCA2649 |
| Mouse Anti-Human C4d | 10-11 | IHC-F, E, IF, IHC-P*, WB | (9) | 2222-8004 |
| Mouse Anti-Human C4d | TDM16 | E, IHC- P* | (0) | MCA5766GA |
| Rabbit Anti-Human C4d | IHC-F, IF, IHC-P* | (6) | 0300-0230 |
Abbreviations: E, ELISA; IF, immunofluorescence; IHC-F, immunohistology - frozen sections; IHC-P, immunohistology - paraffin sections; WB, western blotting.
Biomarkers of Transplantation Rejection
In addition to C4d, there are many other markers that can be used to monitor immunosuppression and ultimately act as an indicator of graft rejection. The table below lists a number of these markers for both acute and chronic allograft rejection in humans (Carpio et al. 2014 and Roedder et al. 2011), alongside cell type and organ expression. Many of these markers can be used on blood or urine thus avoiding the need for more invasive tissue sampling, using various techniques such as flow cytometry for example.
Allograft Rejection Markers.
| Marker | Cell Expression | Organ | Measurement as an Indication of Rejection | Anti-Human Antibody |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Rejection | ||||
| C4d | Endothelial cells | Kidney | 2222-8004 / 0300-0230 / MCA5766GA | |
| CD138 | B cells | Kidney | Antibody mediated | MCA2459 |
| FasLigand / CD178 | T cells, NK cells | Kidney | Cytotoxic proteins | MCA2409 / MCA2408GA |
| Granzyme B | Cytolytic lymphocytes | Kidney | Cytotoxic proteins | MCA2118 / MCA2119 / MCA2120 |
| CXCL10 (IP-10) | Neutrophils, epithelial cells, monocytes | Kidney /lung / liver / heart | Cytokine expression | MCA5985GA / MCA1693 |
| CXCL9 | Dendritic cells, Microglia | Cytokine expression | MCA6252 | |
| CD38 | Monocytes, T cells, plasma cells | Kidney | Antibody mediated | MCA1019 |
| CD20 | B cells | Kidney | T cell mediated | MCA1710/ VPA00099 |
| MICA | T cells, NK cells | Kidney | Antibodies against non-HLA antigens | MCA2403 |
| PECAM-1 (CD31) | Endothelial cells, platelets, granulocytes | Kidney | Proteogenomic | MCA1738 |
| Chronic Rejection | ||||
| CCL2 (MCP-1) | Monocytes, macrophages, Dendritic cells, Endothelial cells | Kidney | Antibody mediated | MCA5981 |
| CTGF | Endothelial cells | Kidney/ Heart | Anti-fibrotic target | AHP1278 |
| TGF-beta | Macrophages | Growth factor | MCA797 / AHP1734 |
Table adapted from Roedder et al. 2011.
References
-
Carpio VN et al. (2104). Expression patterns of B cells in acute kidney transplant rejection.
Exp Clin Transplant 12(5), 405-14. - Collins AB et al. (1999). Complement activation in acute humoral renal allograft rejection: diagnostic significance of C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephorl. 10, 2208-2214.
- Colvin RB and Smith RN (2005). Antibody-mediated organ-allograph rejection. Nat Rev Immunol 5, 807-817.
- Roedder S et al (2011). Biomarkers in solid organ transplantation: establishing personalized transplantation medicine. Genome Medicine 3, 37.
- Sacks SH and Chowdhury P (2002). Footprints of humoral rejection. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11(6), 627-8.







