IgG antibody | MK 1 A6

Mouse anti Human IgG (Fc) CH2 Domain
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- MK 1 A6
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- IgG
- Region
- (Fc) (CH2 DOMAIN)
| Mouse anti Human IgG (Fc) CH2 domain, clone MK 1 A6 recognizes human IgG Fc (all subclasses). CH2 and hinge regions have an important role in effector functions of IgG. The epitope detected by clone MK 1 A6 lies within the CH2 domain as determined by haemagglutination and western blotting using IgG heavy chain and myelomas with defined domain deletions. |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Rhesus Monkey - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
0.09% Sodium Azide - Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Human IgG Polyclonal.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from BALB/c mouse were fused with cells from the mouse NS1 myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 1/1,000 | 1/10,000 | |
| Immunohistology - Frozen 1 | |||
| Immunohistology - Paraffin | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1The epitope recognised by this antibody is reported to be sensitive to formaldehyde fixation and tissue processing. Bio-Rad recommends the use of acetone fixation for frozen sections.
References for IgG antibody
-
Lund, J. et al. (1996) Multiple interactions of IgG with its core oligosaccharide can modulate recognition by complement and human Fc gamma receptor I and influence the synthesis of its oligosaccharide chains.
J Immunol. 157 (11): 4963-9. -
Rasti, N. et al. (2006) Nonimmune immunoglobulin binding and multiple adhesion characterize Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes of placental origin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103: 13795-800. -
Wozniak-Knopp, G. et al. (2010) Introducing antigen-binding sites in structural loops of immunoglobulin constant domains: Fc fragments with engineered HER2/neu-binding sites and antibody properties.
Protein Eng Des Sel. 23: 289-97. -
Raghuraman, S. et al. (2012) Spontaneous clearance of chronic hepatitis C virus infection is associated with appearance of neutralizing antibodies and reversal of T-cell exhaustion.
J Infect Dis. 205: 763-71. -
Hasenhindl, C. et al. (2013) Stability assessment on a library scale: a rapid method for the evaluation of the commutability and insertion of residues in C-terminal loops of the CH3 domains of IgG1-Fc.
Protein Eng Des Sel. 26 (10): 675-82. -
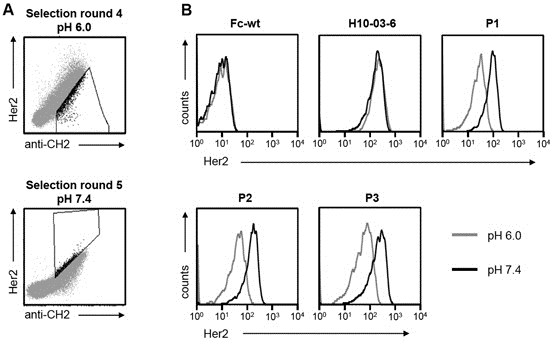
Traxlmayr, M.W. et al. (2014) Construction of pH-sensitive Her2-binding IgG1-Fc by directed evolution.
Biotechnol J. 9: 1013-22.
- RRID
- AB_321910
- UniProt
- P01857
- P01859
- P01861
- P01834
- P01860
- P0CG04
- Entrez Gene
- IGKC
- IGHG1
- IGHG2
- IGHG3
- IGHG4
- IGLV2-14
- GO Terms
- GO:0005515 protein binding
- GO:0003823 antigen binding
- GO:0005576 extracellular region
- GO:0006958 complement activation, classical pathway
- GO:0045087 innate immune response
- GO:0005624 membrane fraction
- GO:0006955 immune response
MCA647G
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up