Influenza A Nucleoprotein antibody | AA5H
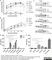

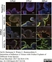


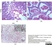
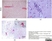





Mouse anti Influenza A Nucleoprotein
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- AA5H
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Specificity
- Influenza A Nucleoprotein
| Mouse anti Influenza A Nucleoprotein antibody, clone AA5H recognizes an epitope within Influenza virus A nucleoprotein. Mouse anti Influenza A Nucleoprotein antibody, clone AA5H can be used in influenza A IFA typing in conjunction with MCA401 (clone GA2B). |
- Target Species
- Viral
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A from tissue culture supernatant.
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Influenza A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 34 (H1N1) and A/Bangkok / 1 / 79 (H3N2) viruses.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from BALB/c mice were fused with cells of the P3 Ag8.653 mouse myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence | |||
| Immunohistology - Paraffin | |||
| Western Blotting |
References for Influenza A Nucleoprotein antibody
-
Herold, S. et al. (2006) Alveolar epithelial cells direct monocyte transepithelial migration upon influenza virus infection: impact of chemokines and adhesion molecules.
J Immunol. 177 (3): 1817-24. -
Thompson, C.I. et al. (2006) Infection of human airway epithelium by human and avian strains of influenza a virus.
J Virol. 80: 8060-8. -
Ehrhardt, C. et al. (2007) Influenza A virus NS1 protein activates the PI3K/Akt pathway to mediate antiapoptotic signaling responses.
J Virol. 81: 3058-67. -
Ehrhardt, C. et al. (2007) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling by the nonstructural NS1 protein is not conserved among type A and B influenza viruses.
J Virol. 81: 12097-100. -
Ehrhardt, C. et al. (2007) A polyphenol rich plant extract, CYSTUS052, exerts anti influenza virus activity in cell culture without toxic side effects or the tendency to induce viral resistance.
Antiviral Res. 76: 38-47. -
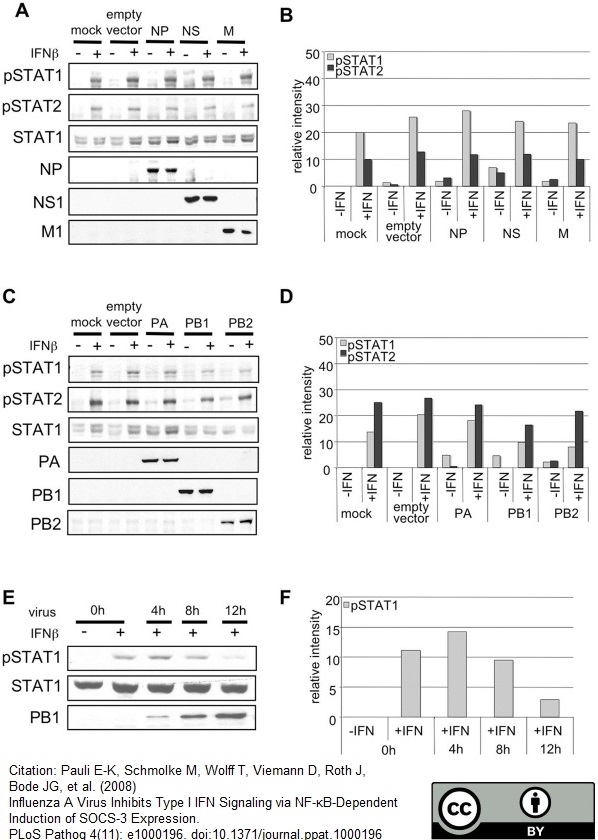
Pauli, E.K. et al. (2008) Influenza A virus inhibits type I IFN signaling via NF-kappaB-dependent induction of SOCS-3 expression.
PLoS Pathog. 4(11): e1000196. -
Nencioni, L. et al. (2009) Bcl-2 expression and p38MAPK activity in cells infected with influenza A virus: impact on virally induced apoptosis and viral replication.
J Biol Chem. 284: 16004-15. -
Jamali, A. et al. (2010) A DNA vaccine-encoded nucleoprotein of influenza virus fails to induce cellular immune responses in a diabetic mouse model.
Clin Vaccine Immunol. 17: 683-7.
View The Latest Product References
-
Seitz, C. et al. (2010) High yields of influenza A virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells are promoted by an insufficient interferon-induced antiviral state.
J Gen Virol. 91: 1754-63. -
Luig, C. et al. (2010) MAP kinase-activated protein kinases 2 and 3 are required for influenza A virus propagation and act via inhibition of PKR.
FASEB J. 24: 4068-77. -
Shu, Y. et al. (2010) Avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses can directly infect and replicate in human gut tissues.
J Infect Dis. 201: 1173-7. -
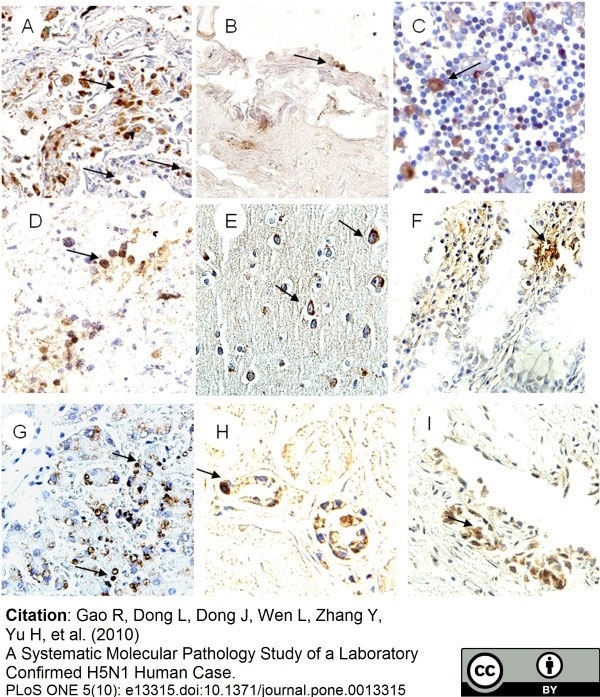
Gao, R. et al. (2010) A systematic molecular pathology study of a laboratory confirmed H5N1 human case.
PLoS One. 5: e13315. -
Matarrese, P. et al. (2011) Pepstatin A alters host cell autophagic machinery and leads to a decrease in influenza A virus production.
J Cell Physiol. 226 (12): 3368-77. -
Gabay, C. et al. (2011) Impact of synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on antibody responses to the AS03-adjuvanted pandemic influenza vaccine: a prospective, open-label, parallel-cohort, single-center study.
Arthritis Rheum. 63 (6): 1486-96. -
Hrincius, E.R. et al. (2011) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) is activated by influenza virus vRNA via the pathogen pattern receptor Rig-I to promote efficient type I interferon production.
Cell Microbiol. 13: 1907-19. -
Calmy, A. et al. (2012) Strong serological responses and HIV RNA increase following AS03-adjuvanted pandemic immunization in HIV-infected patients.
HIV Med. 13 (4): 207-18. -
Koerner, I. et al. (2012) Altered receptor specificity and fusion activity of the haemagglutinin contribute to high virulence of a mouse-adapted influenza A virus.
J Gen Virol. 93 (Pt 5): 970-9. -
Hassan, I.H. et al. (2012) Influenza A viral replication is blocked by inhibition of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) stress pathway.
J Biol Chem. 287 (7): 4679-89. -
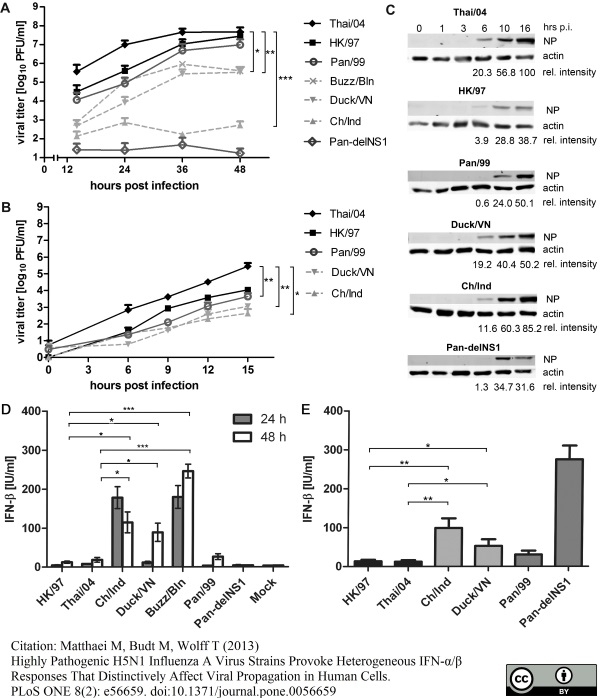
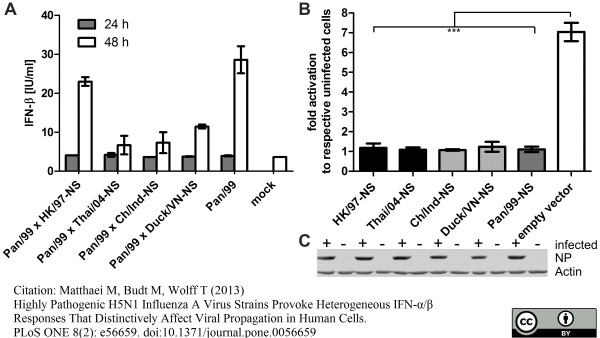
Matthaei M et al. (2013) Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus strains provoke heterogeneous IFN-α/β responses that distinctively affect viral propagation in human cells.
PLoS One. 8 (2): e56659. -
Dick, A. et al. (2015) Role of nucleotide binding and GTPase domain dimerization in dynamin-like myxovirus resistance protein A for GTPase activation and antiviral activity.
J Biol Chem. 290 (20): 12779-92. -
Shoji, M. et al. (2015) Bakuchiol Is a Phenolic Isoprenoid with Novel Enantiomer-selective Anti-influenza A Virus Activity Involving Nrf2 Activation.
J Biol Chem. 290 (46): 28001-17. -
Wörmann, X. et al. (2016) Genetic characterization of an adapted pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza virus that reveals improved replication rates in human lung epithelial cells.
Virology. 492: 118-29. -
Kim HR et al. (2016) Ostrich ( Struthio camelus ) Infected with H5N8 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus in South Korea in 2014.
Avian Dis. 60 (2): 535-9. -
Thulasi Raman, S.N. et al. (2016) DDX3 Interacts with Influenza A Virus NS1 and NP Proteins and Exerts Antiviral Function through Regulation of Stress Granule Formation.
J Virol. 90 (7): 3661-75. -
Sadewasser, A. et al. (2017) Quantitative Proteomic Approach Identifies Vpr Binding Protein as Novel Host Factor Supporting Influenza A Virus Infections in Human Cells.
Mol Cell Proteomics. 16 (5): 728-42. -
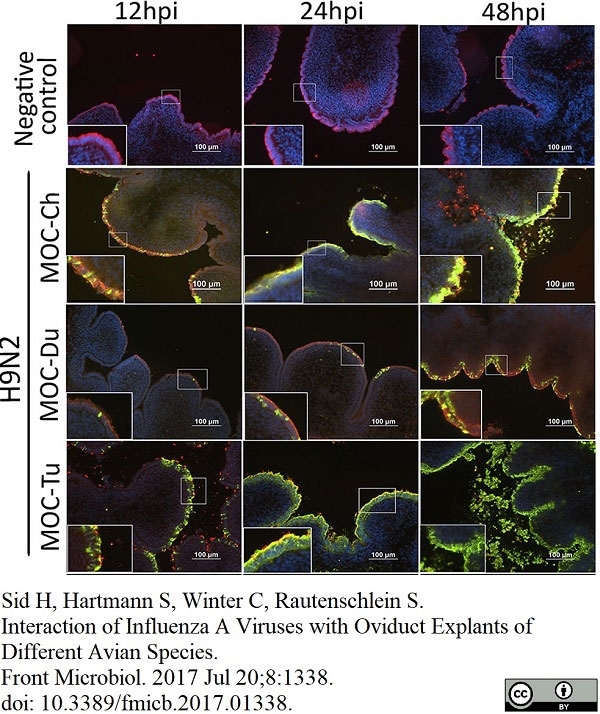
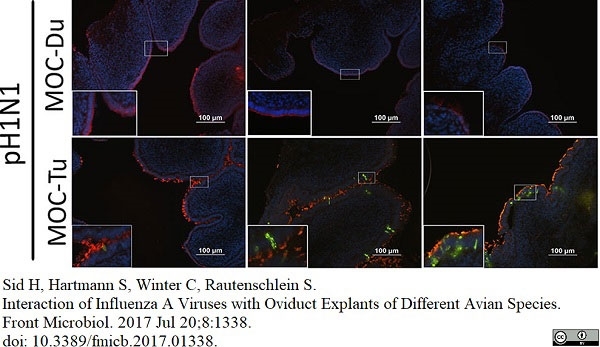
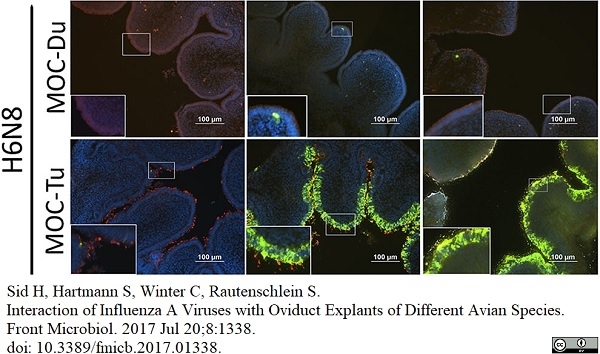
Sid, H. et al. (2017) Interaction of Influenza A Viruses with Oviduct Explants of Different Avian Species.
Front Microbiol. 8: 1338. -
Youchan, B. et al. (2018) Pathological lesions and antigen localization in chicken, ducks and Japanese quail naturally infected by novel highly pathogenic avian influenza (H5N6), Korea, 2016
J Prev Vet Med. 42 (3): 91-8. -
Mayr, J. et al. (2018) Unravelling the Role of O-glycans in Influenza A Virus Infection.
Sci Rep. 8 (1): 16382. -
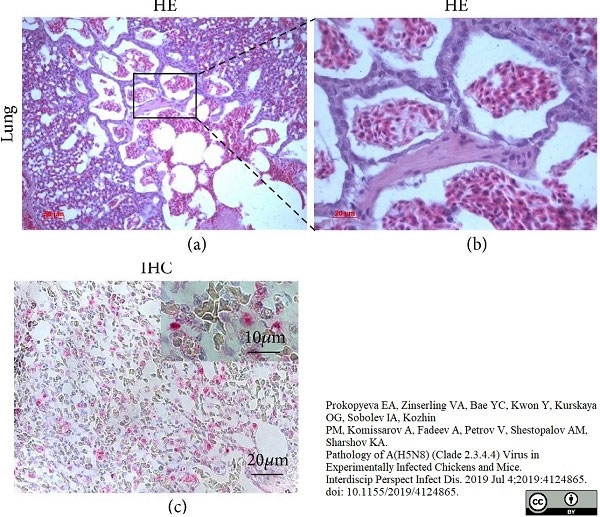
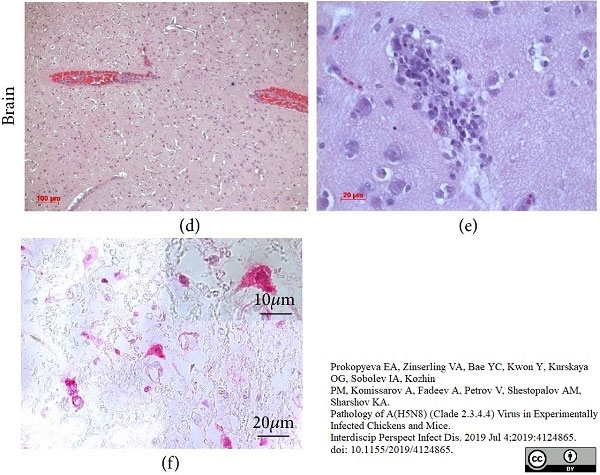
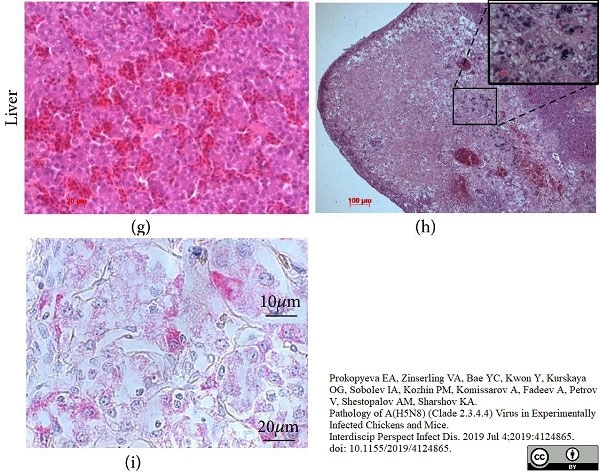
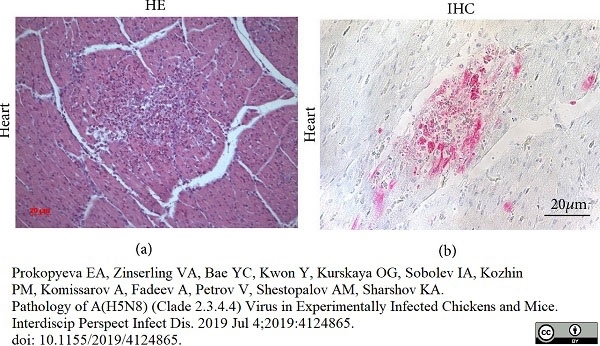
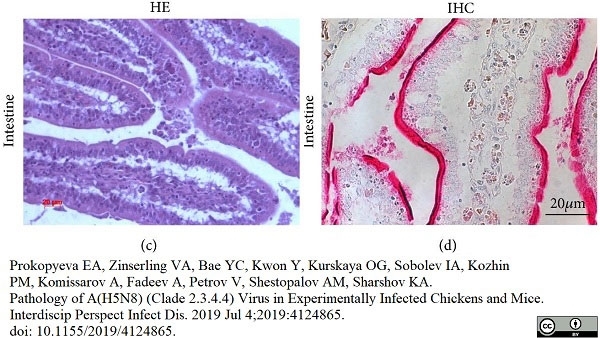
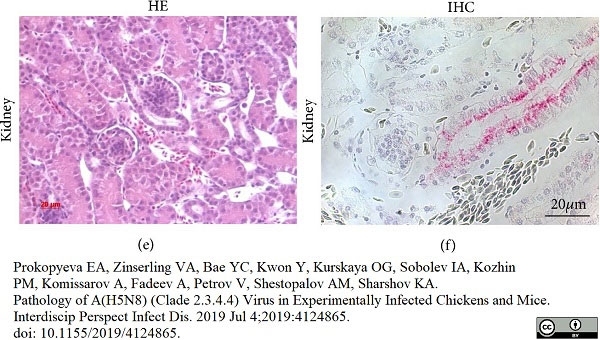
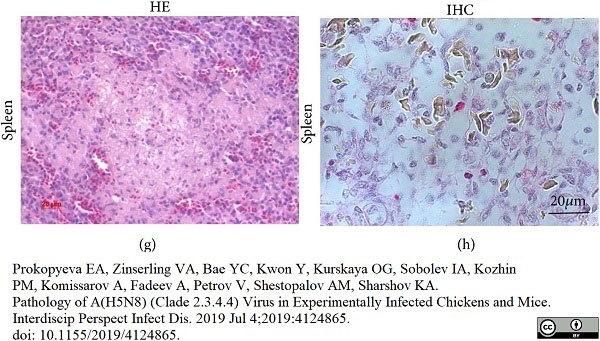
Prokopyeva, E.A. et al. (2019) Pathology of A(H5N8) (Clade 2.3.4.4) Virus in Experimentally Infected Chickens and Mice.
Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2019: 4124865. -
MacKerracher, A. et al. (2022) PLGA particle vaccination elicits resident memory CD8 T cells protecting from tumors and infection.
Eur J Pharm Sci. : 106209. -
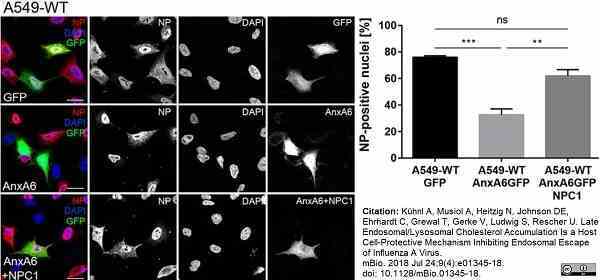
Kühnl, A. et al. (2018) Late Endosomal/Lysosomal Cholesterol Accumulation Is a Host Cell-Protective Mechanism Inhibiting Endosomal Escape of Influenza A Virus.
mBio. 9 (4): e01345-18. -
Forbester, J.L. et al. (2020) IRF5 Promotes Influenza Virus-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Myeloid Cells and Murine Models.
J Virol. 94 (9): e00121-20.
- RRID
- AB_2151884
MCA400
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Viral ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up