Eosinophil Major Basic Protein antibody | BMK-13
Mouse anti Human Eosinophil Major Basic Protein
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- BMK-13
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- Eosinophil Major Basic Protein
| Mouse anti Human Eosinophil Major Basic Protein antibody, clone BMK-13 recongises the Eosinophil Major Basic Protein (EMBP), a 117 amino acid protein, corresponding to residues 106-222 of Bone marrow proteoglycan (precursor). Mouse anti Human Eosinophil Major Basic Protein antibody, clone BMK-13 stains both resting and activated eosinophils of bronchial and skin sections of allergic and normal sites and may be considered a Pan eosinophil marker. Mouse anti Human Eosinophil Major Basic Protein antibody, clone BMK-13 cross reacts weakly with basophils which also contain low levels of EMBP. No cross reactivity with other human cells or proteins has been noted. |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Rat Guinea Pig Weak - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Antibody purified from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.02% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
0.1% Bovine Serum Albumin - Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 0.1mg/ml
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- Guaranteed until date of expiry. Please see product label.
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunohistology - Frozen 1 | 1/20 | 1/50 | |
| Immunohistology - Paraffin 2 | 1/20 | 1/50 |
- 1 It is recommended that sections are fixed in a 1:1 mixture of acetone and methanol and air-dried for 1 hour. Good results may be achieved via staining with the APAAP method.
- 2 This product requires enzymatic pre-treatment of paraffin sections prior to staining. Pepsin is recommended for this purpose. NB. Heat-mediated antigen retrieval methods should not be used.
References for Eosinophil Major Basic Protein antibody
-
Moqbel, R. et al. (1992) Application of monoclonal antibodies against major basic protein (BMK-13) and eosinophil cationic protein (EG1 and EG2) for quantifying eosinophils in bronchial biopsies from atopic asthma.
Clin Exp Allergy. 22 (2): 265-73. -
Hashimoto, Y. et al. (1993) Purification of the antibacterial fragments of guinea-pig major basic protein.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1203 (2): 236-42. -
Haczku, A. et al. (1995) T-cells subsets and activation in bronchial mucosa of sensitized Brown-Norway rats after single allergen exposure.
Immunology. 85 (4): 591-7. -
Underwood, S. et al. (1995) Time-course of antigen-induced airway inflammation in the guinea-pig and its relationship to airway hyperresponsiveness.
Eur Respir J. 8 (12): 2104-13. -
Mishima, H. et al. (1998) CD4+ T cells can induce airway hyperresponsiveness to allergen challenge in the brown norway rat.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 158 (6): 1863-70. -
Lacy, P. et al. (1998) Intracellular localization of interleukin-6 in eosinophils from atopic asthmatics and effects of interferon gamma.
Blood. 91 (7): 2508-16. -
Lacy, P. et al. (1999) Rapid mobilization of intracellularly stored RANTES in response to interferon-gamma in human eosinophils.
Blood. 94 (1): 23-32. -
Walsh, G.M. et al. (1999) Resting and cytokine-stimulated human small airway epithelial cells recognize and engulf apoptotic eosinophils.
Blood. 94 (8): 2827-35.
View The Latest Product References
-
Cameron, L. et al. (2000) Evidence for local eosinophil differentiation within allergic nasal mucosa: inhibition with soluble IL-5 receptor.
J Immunol. 164 (3): 1538-45. -
Mahmudi-azer, S. et al. (2002) Translocation of the tetraspanin CD63 in association with human eosinophil mediator release.
Blood. 99 (11): 4039-47. -
Lacy, P. et al. (2003) Divergence of mechanisms regulating respiratory burst in blood and sputum eosinophils and neutrophils from atopic subjects.
J Immunol. 170 (5): 2670-9. -
Isogai S et al. (2003) The effects of CD8+γδ T cells on late allergic airway responses and airway inflammation in rats.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 112 (3): 547-55. -
Al-Rabia, M.W. et al. (2004) Membrane receptor-mediated apoptosis and caspase activation in the differentiated EoL-1 eosinophilic cell line.
J Leukoc Biol. 75 (6): 1045-55. -
Tulic, M.K. et al. (2009) Thymic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive eosinophils in young children: potential role in maturation of the naive immune system.
Am J Pathol. 175 (5): 2043-52. -
Dellon, E.S. et al. (2012) Diagnostic utility of major basic protein, eotaxin-3, and leukotriene enzyme staining in eosinophilic esophagitis.
Am J Gastroenterol. 107 (10): 1503-11. -
Vanheel, H. et al. (2014) Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia.
Gut. 63 (2): 262-71. -
Cirillo, C. et al. (2015) Evidence for neuronal and structural changes in submucous ganglia of patients with functional dyspepsia.
Am J Gastroenterol. 110 (8): 1205-15. -
Wiersma, L.C. et al. (2015) Pathogenesis of infection with 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus in isogenic guinea pigs after intranasal or intratracheal inoculation.
Am J Pathol. 185 (3): 643-50. -
Wolf, W.A. et al. (2015) Predictors of response to steroid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis and treatment of steroid-refractory patients.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13 (3): 452-8. -
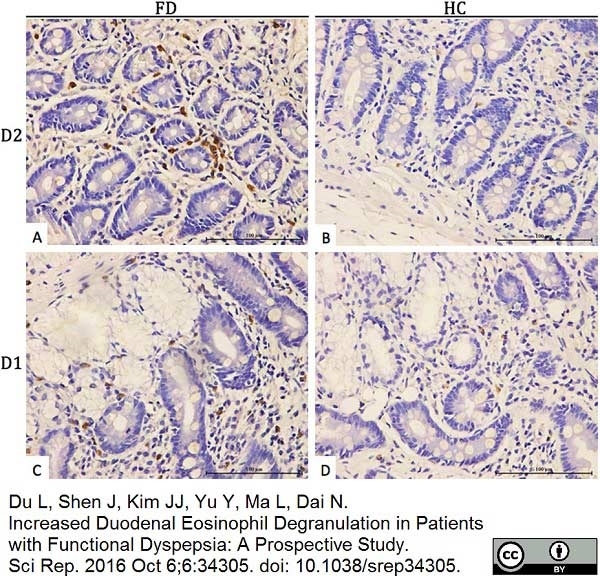
Du, L. et al. (2016) Increased Duodenal Eosinophil Degranulation in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Prospective Study.
Sci Rep. 6: 34305. -
Tyler, M.A. et al. (2017) Large-scale gene expression profiling reveals distinct type 2 inflammatory patterns in chronic rhinosinusitis subtypes.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 139 (3): 1061-1064.e4. -
Whelan, K.A. et al. (2019) Persistent Basal Cell Hyperplasia is Associated with Clinical and Endoscopic Findings in Patients With Histologically Inactive Eosinophilic Esophagitis.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Sep 06 [Epub ahead of print]. -
Dellon, E.S. et al. (2020) Utility of major basic protein, eotaxin-3, and mast cell tryptase staining for prediction of response to topical steroid treatment in eosinophilic esophagitis: analysis of a randomized, double-blind, double dummy clinical trial.
Dis Esophagus. 33(6):doaa003. -
Duan, S. et al. (2021) Eosinophil-associated microinflammation in the gastroduodenal tract contributes to gastric hypersensitivity in a rat model of early-life adversity.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 320 (2): G206-G216. -
Duan, S. et al. (2022) Yokukansan Suppresses Gastric Hypersensitivity and Eosinophil-associated Microinflammation in Rats With Functional Dyspepsia.
J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 28 (2): 255-64.
- RRID
- AB_10671914
- UniProt
- P13727
- Entrez Gene
- PRG2
- GO Terms
- GO:0042742 defense response to bacterium
- GO:0005576 extracellular region
- GO:0005529 sugar binding
- GO:0030133 transport vesicle
- GO:0006955 immune response
- GO:0008201 heparin binding
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up