Complement Factor H antibody | OX-23


Mouse anti Human Complement Factor H
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- OX-23
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- Complement Factor H
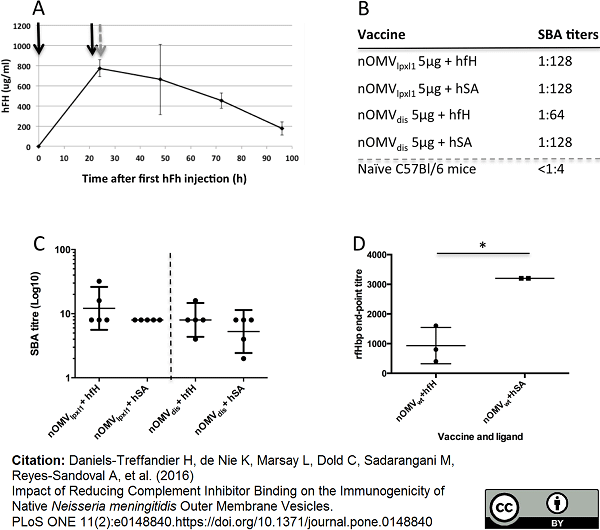
| Mouse anti Human Complement Factor H antibody, clone OX-23 recognizes intact human serum complement protein factor H, also known as H factor 1. Complement factor H is a 1213 amino acid ~155 kDa secreted glycoprotein bearing multiple disulphide bonds and is involved in the deactivation of C3b and dissociation of C3 convertase in the alternative complement pathway. Mouse anti Human Complement Factor H antibody, clone OX-23 also recognizes a ~43-49 kDa truncated form of factor H present at low level (1-5ug/ml) in plasma and urine. Mutations in the CFH gene can lead to the development of Complement Factor H deficiency (CFHD) which can be asymptomatic, present with recurrent bacterial infections or renal failure (Ault et al. 1997). Mutations can also lead to development of Basal laminar drusen (BLD), the deposition of extracellular deposits accumulating below the retinal pigment epithelium on Bruch membrane which can ultimately lead to vision loss (Boon et al. 2008). Additionally, mutations in the CFH gene can lead to increased susceptibility to Hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical 1 (AHUS1) or Macular degeneration, age-related, 4 (ARMD4). Mouse anti Human Complement Factor H antibody, clone OX-23 has been used successfully for the determination of levels of bound murine factor H in a sandwich ELISA (Daniels-Treffandier et al. 2016). |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Sheep Rabbit Bovine Chicken Primate Pig Mouse - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
0.09% Sodium Azide - Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Human complement factor H.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunised Balb/c mice were fused with cells of the NS-O mouse myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 1/50 | 1/200 | |
| Immunoprecipitation | |||
| Radioimmunoassays | |||
| Western Blotting |
Source Reference
-
Sim, E. et al. (1983) Monoclonal antibodies against the complement control protein factor H (beta 1 H).
Biosci Rep. 3 (12): 1119-31.
References for Complement Factor H antibody
-
Alsenz, J. et al. (1985) Structural and functional analysis of the complement component factor H with the use of different enzymes and monoclonal antibodies to factor H.
Biochem J. 232 (3): 841-50. -
Fontaine, M. et al. (1989) Truncated forms of human complement factor H.
Biochem J. 258 (3): 927-30. -
Daniels-Treffandier, H. et al. (2016) Impact of Reducing Complement Inhibitor Binding on the Immunogenicity of Native Neisseria meningitidis Outer Membrane Vesicles.
PLoS One. 11 (2): e0148840. -
Kelly, U. et al. (2010) Heparan sulfate, including that in Bruch's membrane, inhibits the complement alternative pathway: implications for age-related macular degeneration.
J Immunol. 185 (9): 5486-94. -
Smith J et al. (2007) Genes expressed by both mesangial cells and bone marrow-derived cells underlie genetic susceptibility to crescentic glomerulonephritis in the rat.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 18 (6): 1816-23. -
Clark, S.J. et al. (2014) Identification of factor H-like protein 1 as the predominant complement regulator in Bruch's membrane: implications for age-related macular degeneration.
J Immunol. 193 (10): 4962-70. -
Martínez, A. et al. (2003) Mapping of the Adrenomedullin-Binding Domains in Human Complement Factor H.
Hypertension Research. 26 (Suppl): S55-S59. -
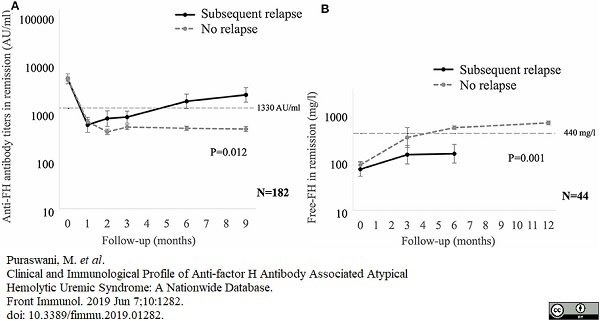
Puraswani, M. et al. (2019) Clinical and Immunological Profile of Anti-factor H Antibody Associated Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Nationwide Database.
Front Immunol. 10: 1282.
View The Latest Product References
- Synonyms
- H Factor 1
- RRID
- AB_2080129
- UniProt
- P08603
- Entrez Gene
- CFH
MCA508G
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up