CD56 antibody | ERIC-1

Mouse anti Human CD56
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- ERIC-1
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- CD56
| Mouse anti Human CD56 antibody, clone ERIC-1 recognizes N-CAM expressed on developing and adult neuroectodermal tissues in humans. Neuroectodermal tumours also stain including Glioma, ependymoma, neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, retinoblastoma and teratoma. Oat cell carcinoma and Wilms tumour are also highly reactive. Mouse anti Human CD56 antibody, clone ERIC-1 will react on Natural Killer cells and recognizes 140, 180 and 120 kDa NCAM isoforms. |
- Target Species
- Human
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A from tissue culture supernatant.
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Human retinoblastoma tumour cells.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized BALB/c mice were fused with cells of the P3/X63.Ag8 mouse myeloma line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 80ng/ml | ||
| Flow Cytometry | |||
| Immunoblotting | |||
| Immunohistology - Frozen | 1/50 | 1/100 |
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Neuroblastoma
References for CD56 antibody
-
Bourne, S.P. et al. (1991) A monoclonal antibody (ERIC-1), raised against retinoblastoma, that recognizes the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) expressed on brain and tumours arising from the neuroectoderm.
J Neurooncol. 10 (2): 111-9. -
Criel, A. et al. (1997) Further characterization of morphologically defined typical and atypical CLL: a clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic and prognostic study on 390 cases.
Br J Haematol. 97 (2): 383-91. -
Cameron, A.L. et al. (2002) Natural killer and natural killer-T cells in psoriasis.
Arch Dermatol Res. 294 (8): 363-9. -
Quenby, S. et al. (2005) Prednisolone reduces preconceptual endometrial natural killer cells in women with recurrent miscarriage.
Fertil Steril. 84 (4): 980-4. -
McIntosh K et al. (2006) The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in vitro.
Stem Cells. 24 (5): 1246-53. -
Whitworth, M.K. et al. (2007) Cervical leukocyte sub-populations in idiopathic preterm labour.
J Reprod Immunol. 75: 48-55. -
Preuße, C. et al. (2012) Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy is characterized by a specific Th1-M1 polarized immune profile.
Am J Pathol. 181 (6): 2161-71. -
Debeer, S. et al. (2013) Comparative histology and immunohistochemistry of porcine versus human skin.
Eur J Dermatol. 23 (4): 456-66.
View The Latest Product References
-
Salvatore, G. et al. (2015) Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells turn into foamy dendritic cells with IL-17A.
J Lipid Res. 56 (6): 1110-22. -
Preuße, C. et al. (2016) Differential roles of hypoxia and innate immunity in juvenile and adult dermatomyositis.
Acta Neuropathol Commun. 4 (1): 45. -
Allenbach, Y. et al. (2016) Dermatomyositis With or Without Anti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene 5 Antibodies: Common Interferon Signature but Distinct NOS2 Expression.
Am J Pathol. 186 (3): 691-700. -
Siegert, E. et al. (2021) Systemic sclerosis-associated myositis features minimal inflammation and characteristic capillary pathology.
Acta Neuropathol. 141 (6): 917-27. -
Meinhardt, J. et al. (2021) Olfactory transmucosal SARS-CoV-2 invasion as a port of central nervous system entry in individuals with COVID-19.
Nat Neurosci. 24 (2): 168-75. -
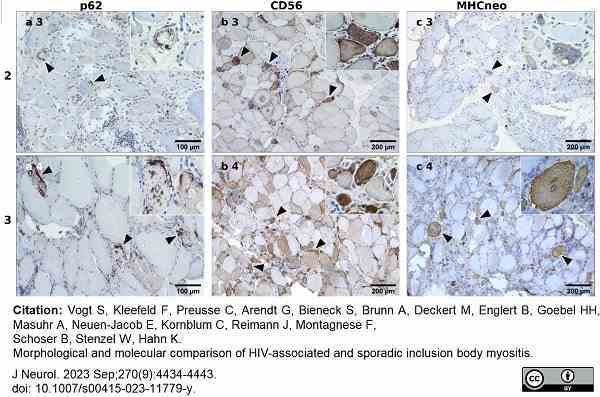
Vogt, S. et al. (2023) Morphological and molecular comparison of HIV-associated and sporadic inclusion body myositis.
J Neurol. 270 (9): 4434-43. -
Englert, B. et al. (2024) "Amyopathic" MDA5-positive dermatomyositis with severe lung involvement presenting with net myositic morphological features- Insights from an autopsy study
Neuromuscular Disorders. 03 Feb [Epub ahead of print].
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up