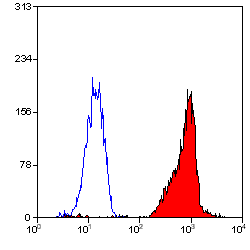
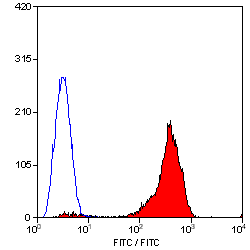
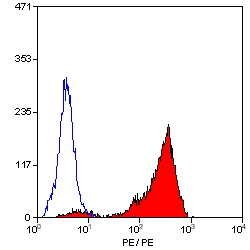
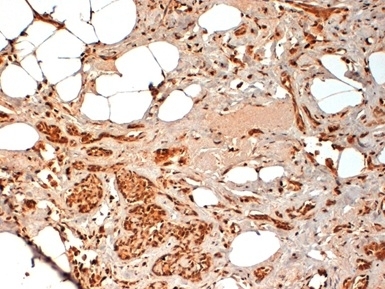
CD44 antibody | F10-44-2
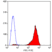
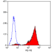




Mouse anti Human CD44
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- F10-44-2
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Specificity
- CD44
| Mouse anti Human CD44 antibody, clone F10-44-2 recognizes human CD44, also known as Epican, HCAM, Phagocytic Glycoprotein 1 (PGP-1) or Hyaluronate receptor . Human CD44 is a single pass, type I transmembrane glycoprotein of variable molecular weight ranging from ~90kDa to ~220kDa depending on alternate splicing of the variable region exons and on the degree of glycosylation. CD44 is expressed on multiple cell types and is involved in multiple functions including cell-cell interactions and cell-extracellular matrix binding. Hyaluronan, a high molecular weight polysaccharide component of the extracellular matrix acts as the principal ligand for the CD44 receptor (Laurent and Fraser 1992). CD44 isoforms containing one or more sequences encoded by the variant region exons have a much more restricted expression pattern both in terms of organ specificity and immune activation (Mackay et al. 1994). . Mouse anti Human CD44 antibody, clone F10-44-2 recognizes an epitope on human CD44 outside the regions coded for by the variable region exons and is thus expected to recognize all isoforms of human CD44 (Mackay et al. 1994). |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Cynomolgus monkey - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
0.09% Sodium Azide - Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Human T lymphocytes.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells of immunised BALB/c mice were fused with cells from the mouse NS1 myeloma line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | 1/10 | 1/20 | |
| Immunofluorescence | |||
| Immunohistology - Frozen | |||
| Immunohistology - Paraffin | 1/50 | 1/100 |
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10ul of the suggested working dilution to label 106 cells in 100ul.
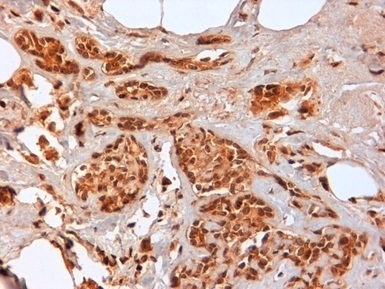
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Human Tonsil
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse IgG2a Negative Control | MCA929 | F | 100 Tests |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse IgG2a Negative Control | ||||||
References for CD44 antibody
-
Dalchau, R. et al. (1980) Monoclonal antibody to a human brain-granulocyte-T lymphocyte antigen probably homologous to the W 3/13 antigen of the rat.
Eur J Immunol. 10 (10): 745-9. -
Daar, A.S. & Fabre, J.W. (1981) Demonstration with monoclonal antibodies of an unusual mononuclear cell infiltrate and loss of normal epithelial membrane antigens in human breast carcinomas.
Lancet. 2 (8244): 434-8. -
Mackay, F. et al. (1993) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced cell adhesion to human endothelial cells is under dominant control of one TNF receptor type, TNF-R55.
J Exp Med. 177: 1277-86. -
Cattoretti, G. et al. (1993) Antigen unmasking on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections.
J Pathol. 171 (2): 83-98. -
Oshiro, N. et al. (1998) Phosphorylation of moesin by rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) plays a crucial role in the formation of microvilli-like structures.
J Biol Chem. 273: 34663-6. -
Ito, T. et al. (1999) A CD1a+/CD11c+ subset of human blood dendritic cells is a direct precursor of Langerhans cells.
J Immunol. 163: 1409-19. -
Roscic-Mrkic, B. et al. (2003) RANTES (CCL5) uses the proteoglycan CD44 as an auxiliary receptor to mediate cellular activation signals and HIV-1 enhancement.
Blood. 102: 1169-77. -
Sundström, M. (2003) Functional and phenotypic studies of two variants of a human mast cell line with a distinct set of mutations in the c-kit proto-oncogene.
Immunology. 108: 89-97.
View The Latest Product References
-
Avigdor, A. et al. (2004) CD44 and hyaluronic acid cooperate with SDF-1 in the trafficking of human CD34+ stem/progenitor cells to bone marrow.
Blood. 103: 2981-9. -
Chang, Y.C. et al. (2006) The glycosaminoglycan-binding domain of decoy receptor 3 is essential for induction of monocyte adhesion.
J Immunol. 176: 173-80. -
Hughes, G.J. et al. (2007) Virus immunocapture provides evidence of CD8 lymphocyte-derived HIV-1 in vivo.
AIDS. 21: 1507-13. -
Hughes, G.J. et al. (2007) Virus immunocapture provides evidence of CD8 lymphocyte-derived HIV-1 in vivo.
AIDS. 21: 1507-13. -
Stolzing, A. et al. (2008) Age-related changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: consequences for cell therapies.
Mech Ageing Dev. 129: 163-73. -
Horwitz, K.B. et al. (2008) Rare steroid receptor-negative basal-like tumorigenic cells in luminal subtype human breast cancer xenografts.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 105: 5774-9. -
Amirghofran, Z. et al. (2008) Evaluation of CD44 and CD44v6 in colorectal carcinoma patients: soluble forms in relation to tumor tissue expression and metastasis.
J Gastrointest Cancer. 39: 73-8. -
Walker, M.M. et al. (2008) The intercellular adhesion molecule, cadherin-10, is a marker for human prostate luminal epithelial cells that is not expressed in prostate cancer.
Mod Pathol. 2008 Feb;21: 85-95. -
Reim, F. et al. (2009) Immunoselection of breast and ovarian cancer cells with trastuzumab and natural killer cells: selective escape of CD44high/CD24low/HER2low breast cancer stem cells.
Cancer Res. 69: 8058-66. -
Norrmen, C. et al. (2010) Liprin (beta)1 is highly expressed in lymphatic vasculature and is important for lymphatic vessel integrity.
Blood. 115: 906-9. -
Hauser, P.V. et al. (2010) Stem cells derived from human amniotic fluid contribute to acute kidney injury recovery.
Am J Pathol. 177: 2011-21. -
Yin, S. et al. (2010) Chondrogenic transdifferentiation of human dermal fibroblasts stimulated with cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein 1.
Tissue Eng Part A. 16: 1633-43. -
Yi, T. et al. (2015) Manufacture of Clinical-Grade Human Clonal Mesenchymal Stem Cell Products from Single Colony Forming Unit-Derived Colonies Based on the Subfractionation Culturing Method.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 21 (12): 1251-62. -
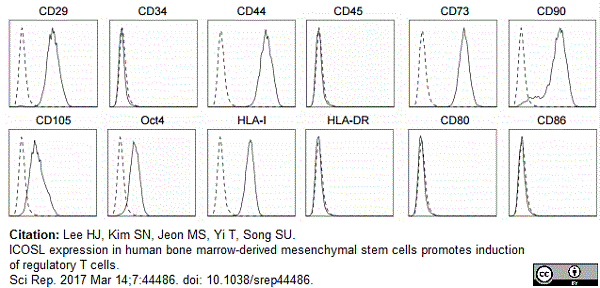
Lee, H.J. et al. (2017) ICOSL expression in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes induction of regulatory T cells.
Sci Rep. 7: 44486. -
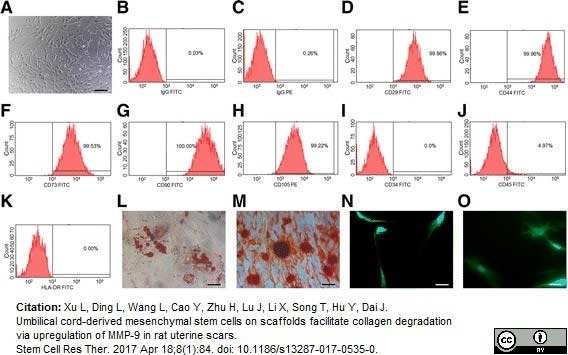
Xu, L. et al. (2017) Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds facilitate collagen degradation via upregulation of MMP-9 in rat uterine scars.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 8 (1): 84. -
Squillace, N. et al. (2018) Evaluation of adhesion molecules and immune parameters in HIV-infected patients treated with an atazanavir/ritonavir- compared with a lopinavir/ritonavir-based regimen.
J Antimicrob Chemother. 73 (8): 2162-70. -
Hou, B. et al. (2018) Xenogeneic acellular nerve scaffolds supplemented with autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells promote axonal outgrowth and remyelination but not nerve function.
J Biomed Mater Res A. 106 (12): 3065-78. -
Noda, G.S. et al. (2020) Specificities and isotypes of erythrocytes autoantibodies in patients with warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Rev Cubana Hematol Inmunol Hemoter 36(4): e1283
MCA89T
MCA89
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up