cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway

- On This Page
- cGAS-STING
- cGAS-STING signaling pathway poster
- (KO) validated PrecisionAb Antibodies
- cGAS-STING antibody range
- References
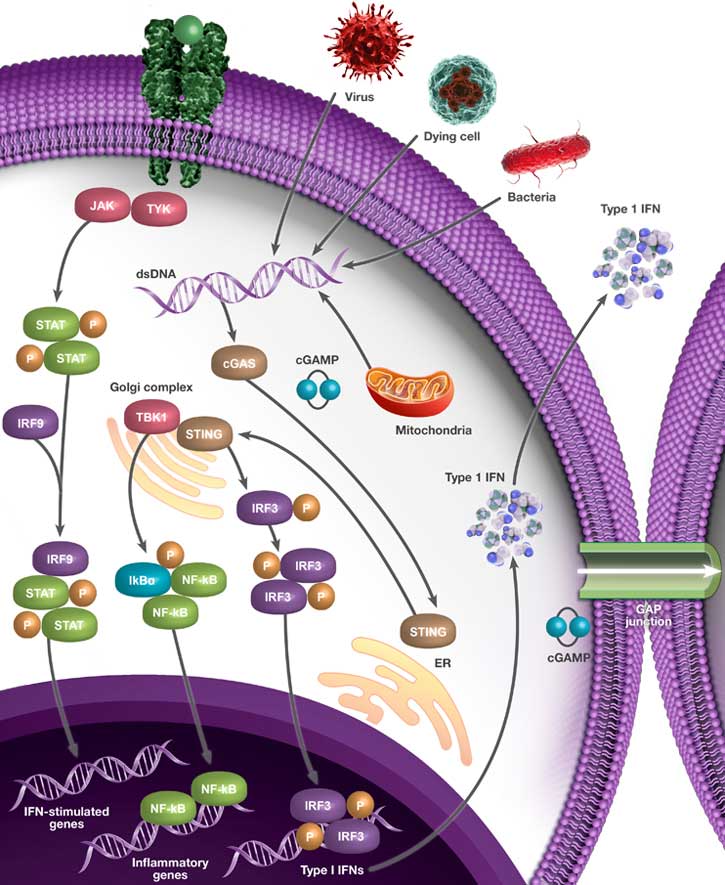
cGAS-STING Pathway Overview
The cGAS-STING pathway is important in microbial infection, autoimmune diseases, and cancer (Tao et al. 2016). DNA within the cytosol can be an indicator of pathogen invasion and is sensed by cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS). Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can also serve as a cGAS ligand in a certain context (Ma et al. 2020). As an example, during apoptosis, the mtDNA escapes into the cytoplasm and binds cGAS (McArthur et al. 2018).
cGAS binds double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in a sequence-independent manner, but with preference for long dsDNA (Luecke et al. 2017 and Ma et al. 2020). cGAS synthesizes cyclic dinucleotide GMP‐AMP (cGAMP) from GTP and ATP. cGAMP then binds stimulator of interferon genes (STING, also known as TMEM173) to initiate downstream signaling (Sun et al. 2013). Intracellular bacteria can secrete the cyclic-di-AMP, cyclic-di-GMP, and cyclic-GMP-AMP that also bind to STING. Moreover, cGAMP can be transferred from cells to cells through gap junctions (Ablasser et al. 2013) and through incorporation into virions (Bridgeman et al. 2015).
Effects of cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway Activation
Upon binding, STING undergoes oligomerization and translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to ER-Golgi compartments (Kwon and Bakhoum 2019). At the Golgi, STING is palmitoylated at Cys88/91 (Mukai et al. 2016). Further, the TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) phosphorylates STING on Ser366 (Tao et al. 2016). The interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) is also recruited to the signaling complex and phosphorylated by TBK1 (Liu et al. 2015). Phosphorylated IRF3 forms a homodimer and enters the nucleus to activate transcription from Type I IFNs, which are important for host protection.
Type I IFNs bind to interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1) and interferon alpha/beta receptor 2 (IFNAR2) and activates Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2). This results in phosphorylation of the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). STAT1, STAT2, and interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) translocates to nucleus and activates transcription of IFN target genes (Zhu et al. 2019) involved in host immune response. The cGAS-STING pathway can also activate NF-kB signaling leading to transcription of inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, activation of the cGAS-STING pathway leads to expression of various immunomodulatory genes and potent antimicrobial responses.
The effects of the cGAS-STING on cancer depend on various factors including the type of tumor, the immune status of the host, and the activated cell type. Positive regulation of the pathway is an attractive method to enhance the immune status, while negative regulation can control abnormal inflammation (Wan et al. 2020).
Therapies targeting this pathway look promising for being translated into clinical applications.
Interactive cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway Poster
We have compiled key proteins involved in the cGAS-STING signaling pathway into one handy poster you can download for your reference.
Click the pathway components within the images below to discover the key antibodies that Bio-Rad provides.
KO Validated PrecisionAb Antibodies to Study the cGAS-STING Pathway
Bio-Rad offers several knockout (KO) validated antibodies to study the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. Featured products include:
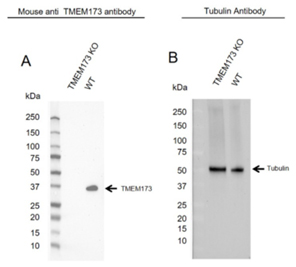
Fig. 1. Western blot analysis of TMEM173 knockout HeLa and wild type HeLa (WT) whole cell lysates probed with A, Mouse Anti-TMEM173 Antibody (VMA00456) and B, hFAB Rhodamine Anti-Tubulin Primary Antibody (12004166).
KO validated STING (TMEM173) Antibody
(VMA00456)
Mouse Anti-Human TMEM173 Antibody recognizes TMEM173, also known as N-terminal methionine-proline-tyrosine-serine plasma membrane tetraspanner, endoplasmic reticulum interferon stimulator, mitochondrial mediator of IRF3 activation, or STING.
This antibody detects a band at 37 kD and antibody specificity was verified by knockout validation. Band at the correct molecular weight disappears in the KO lysate.
Applications: Western Blotting
Learn more about the PrecisionAb Antibody range.
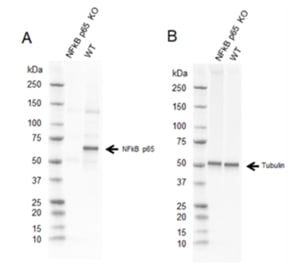
Fig. 2. Western blot analysis of NFkB p65 CRISPR knockout HeLa (NFkB p65 KO) and wild type HeLa (WT) whole cell lysates probed with A, Sheep Anti-NFkB p65 Antibody (VPA00015) and B, hFAB Rhodamine Anti-Tubulin Primary Antibody (12004166).
KO validated NFkB p65 Antibody
(VPA00015)
Sheep Anti-Human NFkB p65 Antibody recognizes human full length p65 (NFkB), also known as transcription factor p65 or nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3.
The antibody detects a band of approximately 65 kD in HEK293 cell lysates and it cross-reacts with rodent cell line lysates tested. Loss of signal in CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout confirms antibody specificity.
Applications: Western Blotting
References: 2
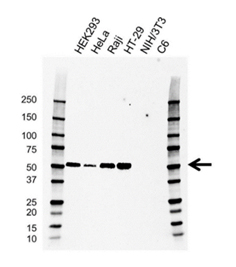
Fig. 3. Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates probed with Mouse Anti-Human IRF3 antibody, clone AB01/1D2 (VMA00640) followed by detection with HRP Conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (STAR207P) and visualized on the ChemiDoc MP Imager.
KO validated IRF3 Antibody
(VMA00640)
Mouse Anti-Human IRF3 Antibody recognizes interferon regulatory factor 3 and detects a band at 51 kD. The antibody has been extensively tested in western blotting using whole cell lysates.
Loss of signal in CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout confirms antibody specificity. You can view data alongside the relevant images on the product page.
Applications: Western Blotting
Bio-Rad’s cGAS-STING Pathway Antibody Range
Browse Bio-Rad’s range of antibodies against targets involved with the cGAS-STING pathway. Please use the filters to sort the attributes in the table below to find the antibody that meets your needs. If you need any further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact us.
cGAS-STING Pathway Antibodies
| Description | Target | Format | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|
References:
- Ablasser A et al. (2013). Cell intrinsic immunity spreads to bystander cells via the intercellular transfer of cGAMP. Nature 503, 530-534.
- Bridgeman A et al. (2015). Viruses transfer the antiviral second messenger cGAMP between cells. Science 349, 1,228-1,232.
- Kwon J and Bakhoum S (2019). The cytosolic DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway in cancer. Cancer Discov 10, 26-39.
- Liu S et al. (2015). Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 347:aaa2630.
- Luecke S et al. (2017). cGAS is activated by DNA in a length-dependent manner. EMBO Rep 18, 1,707-1,715.
- Ma R et al. (2020). The cGAS-STING pathway: the role of self-DNA sensing in inflammatory lung disease. FASEB J 34, 13,156-13,170.
- McArthur K et al. (2018). BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science 359:eaao6047.
- Mukai K et al. (2016). Activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi. Nat Commun 7, 11,932.
- Sun L et al. (2013). Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339, 786-791.
- Tao et al. (2016). cGAS-cGAMP-STING: The three musketeers of cytosolic DNA sensing and signaling. IUBMB Life 68, 858-870.
- Wan D (2020). Research advances in how the cGAS-STING pathway controls the cellular inflammatory response. Front Immunol 11, 615.
- Zhu et al. (2019). STING: a master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle. Mol Cancer 18, 152.


