IL-1 Beta antibody | 1D4





Mouse anti Sheep Interleukin-1 beta
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- 1D4
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- IL-1 Beta
| Mouse anti Sheep Interleukin-1 beta antibody, clone 1D4 recognizes ovine interleukin-1 beta, and shows no cross-reactivity with ovine IL-6, IL-8, TNF alpha or MCP-1. Mouse anti Sheep Interleukin-1 beta antibody, clone 1D4 demonstrates partial neutralizing activity of ovine IL-1 beta. |
- Target Species
- Sheep
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Goat Bovine Horse - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Antibody purified from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% sodium azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Recombinant ovine IL-1 Beta
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | |||
| Flow Cytometry 1 | 1/10 | ||
| Immunohistology - Frozen | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1 Membrane permeabilization is required for this application. The use of Leucoperm (Product Code BUF09) is recommended for this purpose.
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10μl of the suggested working dilution to label 1x106 cells in 100μl
- ELISA
- Mouse anti interleukin-1 beta antibody, clone 1D4 may be used as a capture antibody in a bovine IL-1 beta sandwich ELISA together with Rabbit anti Bovine interleukin-1β antibody (AHP851B) as the detection reagent for evaluation of IL-1β levels in bovine samples together with recombinant Bovine interleukin-1β (PBP008) used as standards.
Alternatively, Mouse anti Interleukin-1 beta antibody, clone 1D4 can be used as a capture reagent together with Rabbit anti Ovine interleukin-1β antibody (AHP423) as a detection reagent for the evaluation of IL-1β levels in ovine, bovine or caprine samples, again utilizing recombinant bovine IL-1&beta (PBP008) as an internal standard.
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goat anti Mouse IgG (H/L):FITC (Multi Species Adsorbed) | STAR117F | F | 0.5 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Goat anti Mouse IgG (H/L):FITC (Multi Species Adsorbed) | ||||||
| Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:RPE | STAR12A | F | 1 ml |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:RPE | ||||||
| Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:HRP (Human Adsorbed) | STAR13B | C E P RE WB | 1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:HRP (Human Adsorbed) | ||||||
| Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:FITC | STAR9B | F | 1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Rabbit F(ab')2 anti Mouse IgG:FITC | ||||||
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse IgG1 Negative Control | MCA928 | F | 100 Tests |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse IgG1 Negative Control | ||||||
References for IL-1 Beta antibody
-
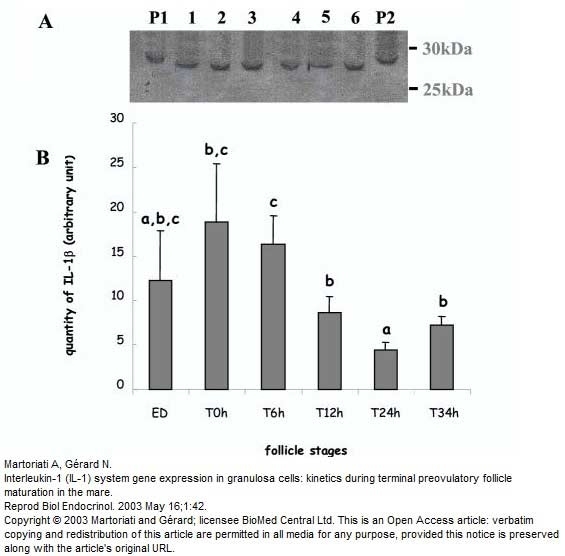
Martoriati, A. & Gérard, N. (2003) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) system gene expression in granulosa cells: kinetics during terminal preovulatory follicle maturation in the mare.
Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 1: 42-51. -
Bannerman, D.D. et al. (2004) Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus elicit differential innate immune responses following intramammary infection.
Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 11: 463-72. -
Bannerman, D.D. et al. (2004) Characterization of the bovine innate immune response to intramammary infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae.
J Dairy Sci. 87 (8): 2420-32. -
Leite, F. et al. (2005) Incubation of bovine PMNs with conditioned medium from BHV-1 infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells increases their susceptibility to Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 103 (3-4): 187-93. -
Matthews, K. et al. (2007) The effect of gene gun-delivered pGM-CSF on the immunopathology of the vaccinated skin.
Scand J Immunol. 65 (3): 298-307. -
Jacobsen, S. et al. (2007) The cytokine response of circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells is changed after intravenous injection of lipopolysaccharide in cattle.
Vet J. 174 (1): 170-5. -
Cox, R.A. et al. (2007) Production of pro-inflammatory polypeptides by airway mucous glands and its potential significance.
Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 20 (2): 172-7. -
Rainard P et al. (2008) Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid triggers inflammation in the lactating bovine mammary gland.
Vet Res. 39 (5): 52.
View The Latest Product References
-
Bougarn, S. et al. (2010) Muramyl dipeptide synergizes with Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid to recruit neutrophils in the mammary gland and to stimulate mammary epithelial cells.
Clin Vaccine Immunol. 17 (11): 1797-809. -
Rinaldi, M. et al (2010) A sentinel function for teat tissues in dairy cows: dominant innate immune response elements define early response to E. coli mastitis.
Funct Integr Genomics. 10: 21-38. -
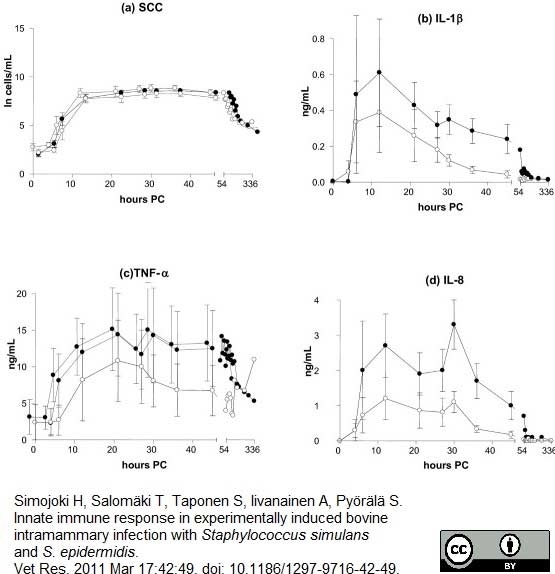
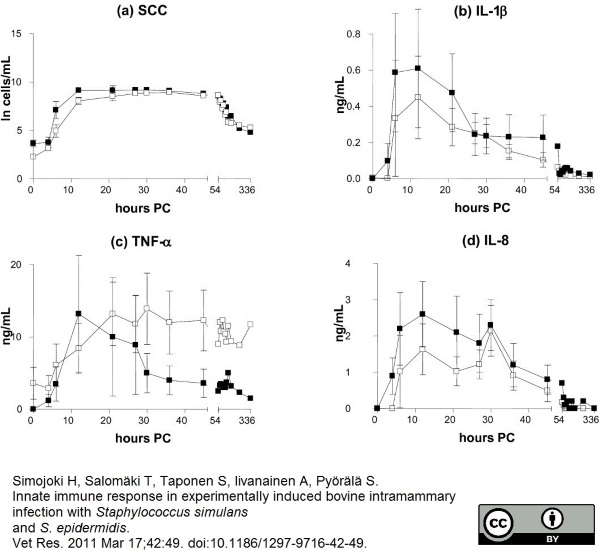
Simojoki, H. et al. (2011) Innate immune response in experimentally induced bovine intramammary infection with Staphylococcus simulans and S. epidermidis.
Vet Res. 42: 49. -
Redondo, E. et al. (2014) Induction of interleukin-8 and interleukin-12 in neonatal ovine lung following experimental inoculation of bovine respiratory syncytial virus.
J Comp Pathol. 150 (4): 434-48. -
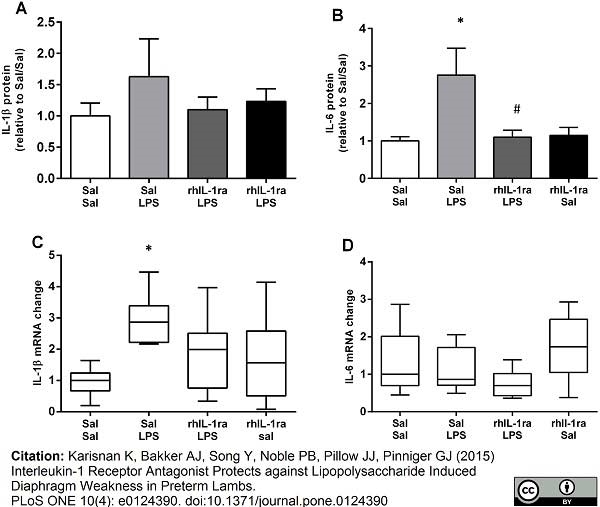
Karisnan K et al. (2015) Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Protects against Lipopolysaccharide Induced Diaphragm Weakness in Preterm Lambs.
PLoS One. 10 (4): e0124390. -
Doull, L. et al. (2015) Late production of CXCL8 in ruminant oro-nasal turbinate cells in response to Chlamydia abortus infection.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 168 (1-2): 97-102. -
Xu, A. et al. (2015) The Ovine Fetal and Placental Inflammatory Response to Umbilical Cord Occlusions With Worsening Acidosis.
Reprod Sci. 22 (11): 1409-20. -
Sobotta, K. et al. (2016) Coxiella burnetii. Infects Primary Bovine Macrophages and Limits Their Host Cell Response.
Infect Immun. 84 (6): 1722-34. -
Cortes, M. et al. (2017) RNAseq profiling of primary microglia and astrocyte cultures in near-term ovine fetus: A glial in vivo-in vitro multi-hit paradigm in large mammalian brain.
J Neurosci Methods. 276: 23-32. -
Canal AM et al. (2017) Immunohistochemical detection of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in granulomas in cattle with natural Mycobacterium bovis infection.
Res Vet Sci. 110: 34-39. -
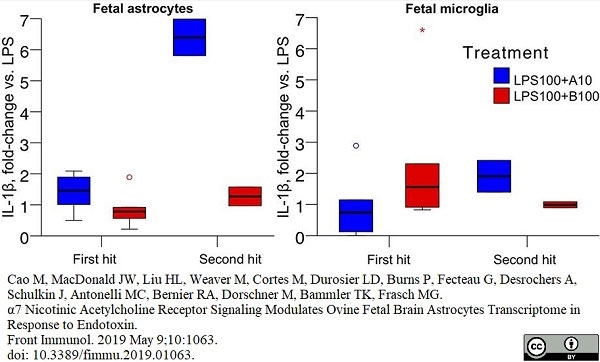
Cao, M. et al. (2019) α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling Modulates Ovine Fetal Brain Astrocytes Transcriptome in Response to Endotoxin.
Front Immunol. 10: 1063. -
Stassi, A.F. et al. (2019) Follicular structures of cows with cystic ovarian disease present altered expression of cytokines.
Zygote. 15: 1-14. -
Ciliberti, M.G. et al. (2022) Green extraction of bioactive compounds from wine lees and their bio-responses on immune modulation using in vitro. sheep model.
J Dairy Sci. Mar 17 [Epub ahead of print]. -
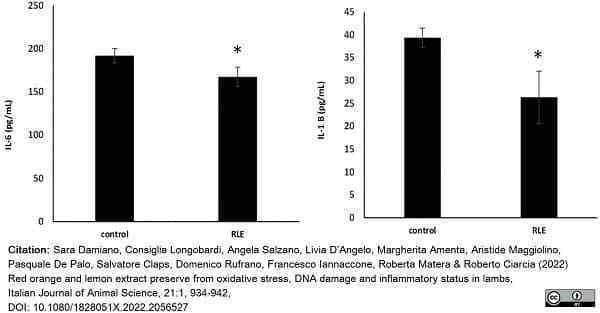
Damiano, S. et al. (2022) Red orange and lemon extract preserve from oxidative stress, DNA damage and inflammatory status in lambs
It J Anim Sci. 21 (1): 934-42. -
Stassi, A.F. et al. (2018) Altered expression of IL-1β, IL-1RI, IL-1RII, IL-1RA and IL-4 could contribute to anovulation and follicular persistence in cattle.
Theriogenology. 110: 61-73. -
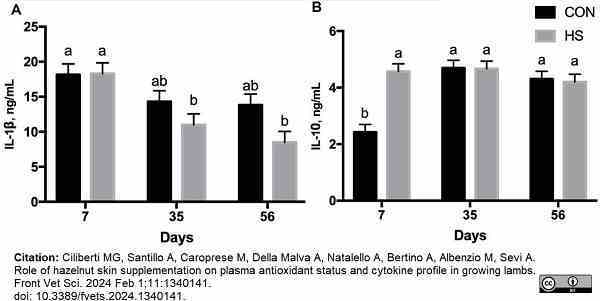
Ciliberti, M.G. et al. (2024) Role of hazelnut skin supplementation on plasma antioxidant status and cytokine profile in growing lambs.
Front Vet Sci. 11: 1340141.
Further Reading
-
Rothel, J.S. et al. (1997) Analysis of ovine IL-1 beta production in vivo and in vitro by enzyme immunoassay and immunohistochemistry.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 57 (3-4): 267-78.
- RRID
- AB_322126
- UniProt
- P21621
- Entrez Gene
- IL-1B
- GO Terms
- GO:0001660 fever generation
- GO:0005125 cytokine activity
- GO:0005149 interleukin-1 receptor binding
- GO:0005615 extracellular space
- GO:0006955 immune response
- GO:0008083 growth factor activity
- GO:0051781 positive regulation of cell division
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Sheep ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up