CD107b antibody | M3/84





Rat anti Mouse CD107b
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- M3/84
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- CD107b
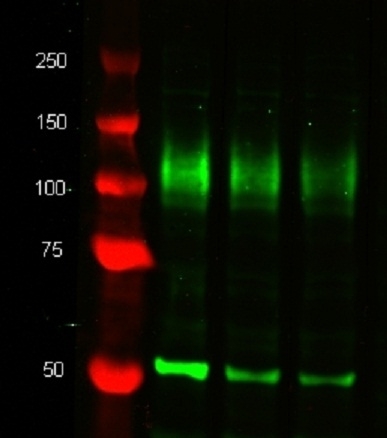
| Rat anti Mouse CD107b antibody, clone M3/84 recognizes murine CD107b, also known as MAC-3 and LAMP-2. CD107b is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is associated with lysosomal membranes and is primarily expressed on mononuclear phagocytes. Expression of CD107b does vary between cell populations and the molecular weight of CD107b can vary between ~92-120 kDa. CD107b is involved in aspects of leucocyte adhesion (Kannan et al. 1996). The expression of CD107b is predominantly cytoplasmic - flow cytometry results are improved by the use of a membrane permeabilization procedure prior to staining. |
- Target Species
- Mouse
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% sodium azide (NaN3)
- Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Glycoproteins purified from mouse peritoneal macrophage membranes.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunised Lewis rats were fused with cells of the mouse P3-NSI/1-Ag4-1 myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry 1 | 1/50 | 1/100 | |
| Immunohistology - Frozen | |||
| Immunohistology - Paraffin | |||
| Immunoprecipitation | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1 Membrane permeabilization is required for this application. The use of Leucoperm (Product Code BUF09) is recommended for this purpose.
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10μl of the suggested working dilution to label 1x106 cells in 100μl
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen Retrieval Buffer, pH8.0 | BUF025A | P | 500 ml | Log in | |||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
| Log in | |||||||
| Description | Antigen Retrieval Buffer, pH8.0 | ||||||
References for CD107b antibody
-
Springer, T.A. (1981) Monoclonal antibody analysis of complex biological systems. Combination of cell hybridization and immunoadsorbents in a novel cascade procedure and its application to the macrophage cell surface.
J Biol Chem. 256 (8): 3833-9. -
Flotte, T.J. et al. (1983) Dendritic cell and macrophage staining by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections and epidermal sheets.
Am J Pathol. 111 (1): 112-24. -
Ho, M.K. & Springer, T.A. (1983) Tissue distribution, structural characterization, and biosynthesis of Mac-3, a macrophage surface glycoprotein exhibiting molecular weight heterogeneity.
J Biol Chem. 258 (1): 636-42. -
Ulrich, R. et al. (2010) Machine learning approach identifies new pathways associated with demyelination in a viral model of multiple sclerosis.
J Cell Mol Med. 14 (1-2): 434-48. -
Amirbekian, V. et al. (2007) Detecting and assessing macrophages in vivo to evaluate atherosclerosis noninvasively using molecular MRI.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 104: 961-6. -
Fan, D. et al. (2014) Differential role of TIMP2 and TIMP3 in cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Res. 103 (2): 268-80. -
Higuchi, Y. et al. (2012) Upregulation of anticoagulant proteins, protein S and tissue factor pathway inhibitor, in the mouse myocardium with cardio-specific TNF-α overexpression.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302: H2352-62. -
Ishibashi, M. et al. (2004) Critical role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 receptor CCR2 on monocytes in hypertension-induced vascular inflammation and remodeling.
Circ Res. 94: 1203-10.
View The Latest Product References
-
Sato, A. et al. (2008) Thioredoxin-1 ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema in mice.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 325: 380-8. -
Xu, J. et al. (2007) Role of cardiac overexpression of ANG II in the regulation of cardiac function and remodeling postmyocardial infarction.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293: H1900-7. -
Zhao, Q. et al. (2004) Essential role of vascular endothelial growth factor in angiotensin II-induced vascular inflammation and remodeling.
Hypertension. 44: 264-70. -
Hansmann, F. et al. (2012) Highly malignant behavior of a murine oligodendrocyte precursor cell line following transplantation into the demyelinated and nondemyelinated central nervous system.
Cell Transplant. 21 (6): 1161-75. -
Herder, V. et al. (2015) Dynamic Changes of Microglia/Macrophage M1 and M2 Polarization in Theiler's Murine Encephalomyelitis.
Brain Pathol. 25 (6): 712-23. -
Bröer S et al. (2016) Brain inflammation, neurodegeneration and seizure development following picornavirus infection markedly differ among virus and mouse strains and substrains.
Exp Neurol. pii: S0014-4886(16)30033-4. -
Bobbala, D. et al. (2016) Interleukin-21-dependent modulation of T cell antigen receptor reactivity towards low affinity peptide ligands in autoreactive CD8(+) T lymphocytes.
Cytokine. 85: 83-91. -
Raddatz, B.B. et al. (2016) Central Nervous System Demyelination and Remyelination is Independent from Systemic Cholesterol Level in Theiler's Murine Encephalomyelitis.
Brain Pathol. 26 (1): 102-19. -
Ciurkiewicz, M. et al. (2018) Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell ablation enhances the capacity of regulatory T cells to delay viral elimination in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis.
Brain Pathol. 28 (3): 349-368. -
Fayyad, A. et al. (2018) Matrix metalloproteinases expression in spontaneous canine histiocytic sarcomas and its xenograft model.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 198: 54-64. -
Li, L. et al. (2015) Interferon-stimulated genes-essential antiviral effectors implicated in resistance to Theiler's virus-induced demyelinating disease.
J Neuroinflammation. 12: 242. -
Hansmann, F. et al. (2018) Beneficial and detrimental impact of transplanted canine adipose-derived stem cells in a virus-induced demyelinating mouse model.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 202: 130-40. -
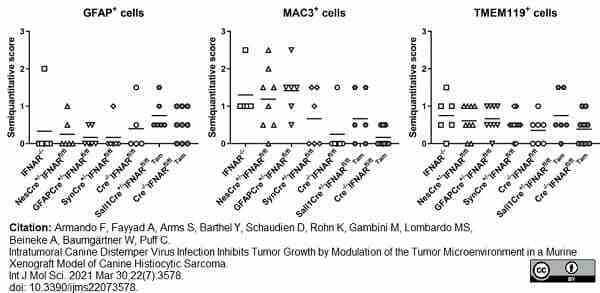
Armando, F. et al. (2021) Intratumoral Canine Distemper Virus Infection Inhibits Tumor Growth by Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment in a Murine Xenograft Model of Canine Histiocytic Sarcoma.
Int J Mol Sci. 2 (7): 3578. -
Ciurkiewicz, M. et al. (2018) Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell ablation enhances the capacity of regulatory T cells to delay viral elimination in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis.
Brain Pathol. 28 (3): 349-68. -
Waltl, I. et al. (2018) Microglia have a protective role in viral encephalitis-induced seizure development and hippocampal damage.
Brain Behav Immun. 74: 186-204. -
Wiedemann, G.M. et al. (2016) A novel TLR7 agonist reverses NK cell anergy and cures RMA-S lymphoma-bearing mice.
Oncoimmunology. 5 (7): e1189051. -
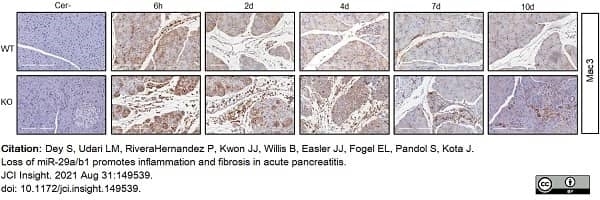
Dey, S. et al. (2021) Loss of miR-29a/b1 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in acute pancreatitis.
JCI Insight. 6 (19): e149539. -
Iwaki, T. et al. (2021) Plasminogen Deficiency Significantly Reduces Vascular Wall Disease in a Murine Model of Type IIa Hypercholesterolemia
Biomedicines. 9 (12): 1832. -
Bühler, M. et al. (2023) IFNAR signaling of neuroectodermal cells is essential for the survival of C57BL/6 mice infected with Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus.
J Neuroinflammation. 20 (1): 58. -
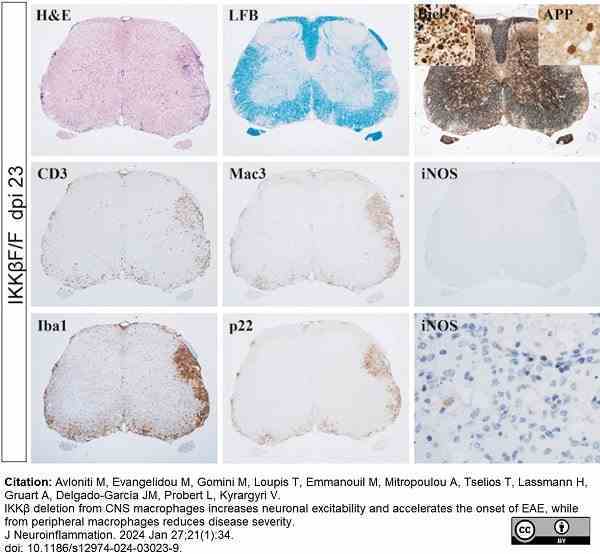
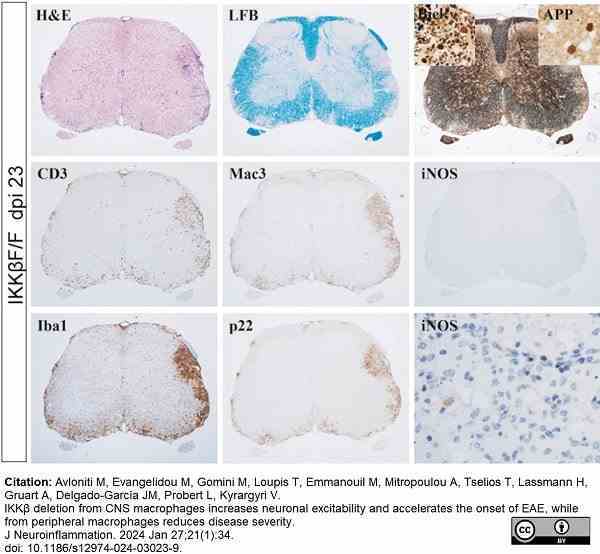
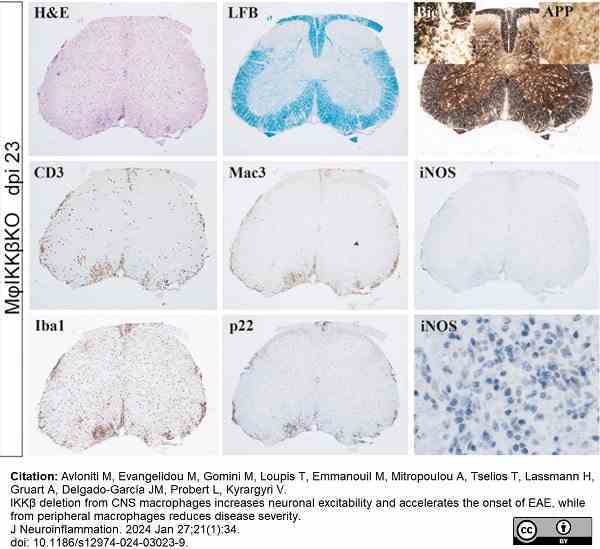
Avloniti, M. et al. (2024) IKKβ deletion from CNS macrophages increases neuronal excitability and accelerates the onset of EAE, while from peripheral macrophages reduces disease severity.
J Neuroinflammation. 21 (1): 34. -
Siddiqui, J.A. et al. (2021) Osteoblastic monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) mediation of parathyroid hormone's anabolic actions in bone implicates TGF-β signaling.
Bone. 143: 115762.
- Synonyms
- MAC-3
- RRID
- AB_2249788
- UniProt
- P17047
- Entrez Gene
- Lamp2
- GO Terms
- GO:0005886 plasma membrane
- GO:0016021 integral to membrane
- GO:0005765 lysosomal membrane
- GO:0005770 late endosome
- GO:0010008 endosome membrane
- GO:0030670 phagocytic vesicle membrane
MCA2293GA
MCA2293
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Mouse ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up