CD44 antibody | YKIX337.8.7





Rat anti Dog CD44
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- YKIX337.8.7
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Specificity
- CD44
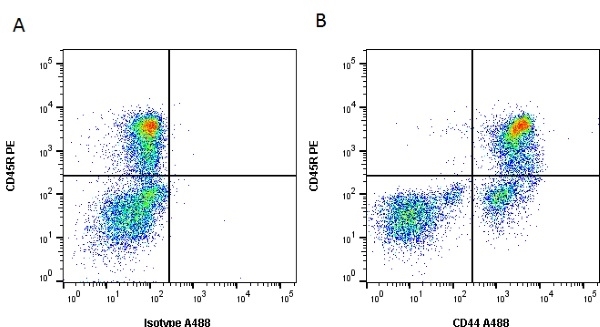
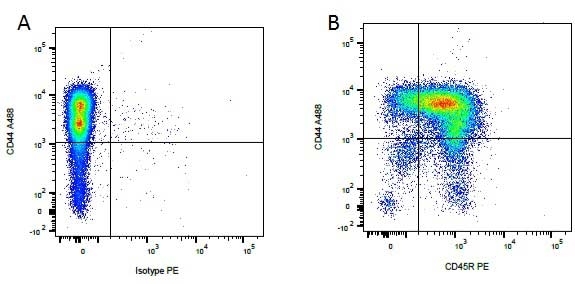
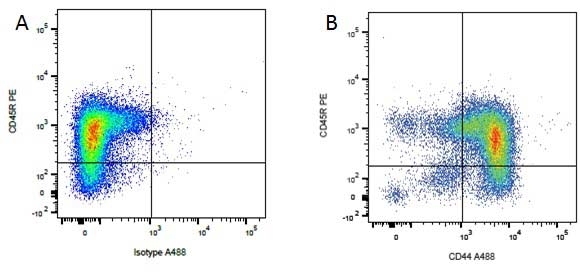
| Rat anti Dog CD44 antibody, clone YKIX337.8.7 recognizes canine CD44, also known as H-CAM, a single-pass type 1 membrane of approximately 90 kDa expressed by most leucocytes and epithelial cells. CD44 expression is markedly increased upon cell activation (Alldinger et al. 2000). CD44 is involved in cell-cell, cell adhesion and cell migration and is the principal cellular receptor for hyaluronate via it's LINK domain, additionally CD44 interacts with other ligands including collagens and metalloproteinases. Altered CD44 expression is detected in many forms of invasive and metastatic cancer, CD44 expression has been observed on canine mammary and melanocytic tumors (Serra et al. 2004). |
- Target Species
- Dog
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Raccoon - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% sodium azide (NaN3)
- Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- Concanavilin A activated canine T cells.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized DA rats were fused with cells of the rat Y3/Ag1.2.3.myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | 1/10 | 1/20 | |
| Immunohistology - Frozen |
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10μl of the suggested working dilution to label 106 cells in 100μl
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse anti Dog CD34:Alexa Fluor® 647 | MCA2411A647 | F | 100 Tests/1ml |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse anti Dog CD34:Alexa Fluor® 647 | ||||||
| Mouse anti Dog CD34:FITC | MCA2411F | F | 0.1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse anti Dog CD34:FITC | ||||||
| Mouse anti Dog CD34 | MCA2411GA | F WB | 0.1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse anti Dog CD34 | ||||||
| Mouse anti Dog CD34:RPE | MCA2411PE | F | 100 Tests | Log in | |||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
| Log in | |||||||
| Description | Mouse anti Dog CD34:RPE | ||||||
References for CD44 antibody
-
Cobbold, S. & Metcalfe,S. (1994) Monoclonal antibodies that define canine homologues of human CD antigens: summary of the First International Canine Leukocyte Antigen Workshop (CLAW).
Tissue Antigens. 43 (3): 137-54. -
Stein, V.M. et al. (2008) Immunophenotypical characterization of monocytes in canine distemper virus infection.
Vet Microbiol. 131:237-46. -
Salvatierra, A. et al. (2001) Antithrombin III prevents early pulmonary dysfunction after lung transplantation in the dog.
Circulation. 104: 2975-80. -
Sanchez, M.A. et al. (2004) Organ-specific immunity in canine visceral leishmaniasis: analysis of symptomatic and asymptomatic dogs naturally infected with Leishmania chagasi.
Am J Trop Med Hyg. 70: 618-24. -
Stein, V.M. et al. (2004) Characterization of canine microglial cells isolated ex vivo.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 99: 73-85. -
Heinrich, F. et al. (2015) Immunophenotyping of immune cell populations in the raccoon (Procyon lotor).
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 168 (3-4): 140-6. -
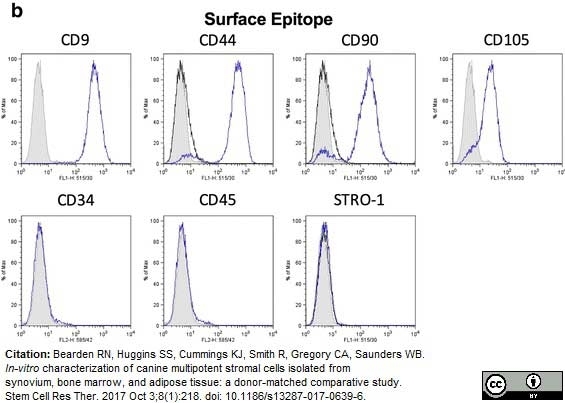
Bearden, R.N. et al. (2017) In-vitro characterization of canine multipotent stromal cells isolated from synovium, bone marrow, and adipose tissue: a donor-matched comparative study.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 8 (1): 218. -
Trindade, A.B. et al. (2017) Mesenchymal-like stem cells in canine ovary show high differentiation potential.
Cell Prolif. 50 (6): e12391
View The Latest Product References
-
Muir, P. et al. (2016) Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate Molecular Markers of Inflammation in Dogs with Cruciate Ligament Rupture.
PLoS One. 11 (8): e0159095. -
Salinas Tejedor, L. et al. (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells do not exert direct beneficial effects on CNS remyelination in the absence of the peripheral immune system.
Brain Behav Immun. 50: 155-65. -
Heinrich, F. et al. (2015) Passage-dependent morphological and phenotypical changes of a canine histiocytic sarcoma cell line (DH82 cells).
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 163 (1-2): 86-92. -
Wijekoon, H.M.S. et al. (2017) Differentiation potential of synoviocytes derived from joints with cranial cruciate ligament rupture and medial patella luxation in dogs.
Res Vet Sci. 114: 370-7. -
Hansmann, F. et al. (2018) Beneficial and detrimental impact of transplanted canine adipose-derived stem cells in a virus-induced demyelinating mouse model.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 202: 130-40. -
Elshafae, S.M. et al. (2017) The Effect of a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (AR-42) on Canine Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastasis.
Prostate. 77 (7): 776-93. -
Gouveia, G.M. et al. (2013) Analysis of cancer stem cells in dog’s mammary neoplasias.
Braz J Vet Med, 35(3), 229-35. -
Yamauchi, A. et al. (2023) Negative Influence of Aging on Differentiation and Proliferation of CD8(+) T-Cells in Dogs.
Vet Sci. 10 (9): 541. -
Yang, V.K. et al. (2021) Intravenous administration of allogeneic Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of dogs with congestive heart failure secondary to myxomatous mitral valve disease.
Am J Vet Res. 82 (6): 487-93. -
Crain, S.K. et al. (2019) Extracellular Vesicles from Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress CD4 Expressing T Cells Through Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Adenosine Signaling in a Canine Model.
Stem Cells Dev. 28 (3): 212-26. -
Utumi, P.H. et al. (2020) Cytotoxicity of fluconazole on canine dental pulp-derived stem cells.
J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 10 (4): 361-8.
- Synonyms
- H-CAM
- PGP-1
- UniProt
- Q28284
- Entrez Gene
- CD44
- GO Terms
- GO:0007155 cell adhesion
- GO:0016021 integral to membrane
- GO:0004872 receptor activity
- GO:0005540 hyaluronic acid binding
MCA1041GA
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Dog ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up