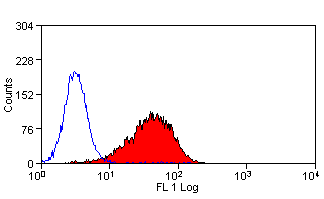
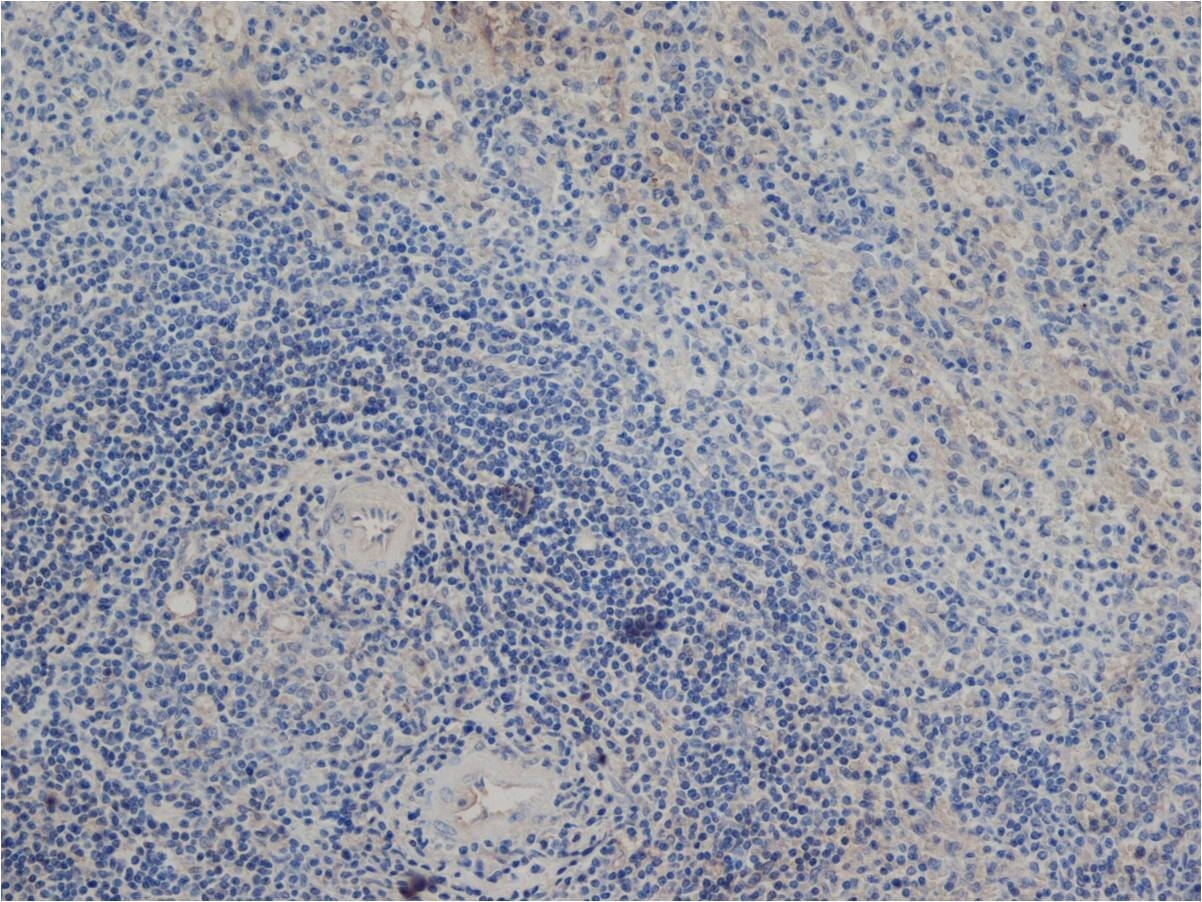
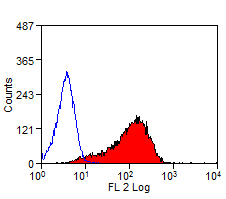
Delta-Like Protein 1 antibody | HMD1-5


Hamster anti Mouse Delta-Like Protein 1
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- HMD1-5
- Isotype
- IgG
- Specificity
- Delta-Like Protein 1
| Hamster anti Mouse Delta-Like Protein 1 antibody, clone HMD1-5 recognizes Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1), one of the five major ligands of the Notch signaling pathway, which is activated through the binding of specific ligands to the Notch receptors Notch 1-4. The Notch signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved pathway in multi-cellular organisms, which is vital for cell-cell communication, important during fundamental developmental and physiological processes, including regulation of cell fate decisions during neuronal, cardiac and endocrine development, stem cell hematopoiesis, thymic T-cell development, and both tumor progression and suppression. Ligation of Notch receptors by their specific ligands, Jagged1 (CD339), Jagged2, Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1), DLL3 and DLL4, on physically adjacent signal receiving cells, induces proteolysis of the receptors by ADAM-family metalloproteases and the gamma-secretase complex, within the transmembrane domain, releasing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) to translocate to the nucleus. Subsequent signal transduction then occurs through either the CSL-NICD-Mastermind complex cascade (canonical pathway), or NF-kappaB-NICD and CSL-NICD-Deltex complex signaling cascades (non-canonical pathway). The canonical pathway inhibits the differentiation of stem cells or progenitor cells, whilst the non-canonical pathway promotes differentiation. DLL1 is widely expressed, and acts as a mediator of cell fate decisions during hematopoiesis, and may play a role in cell-to-cell communication in mammalian embryos. DLL1 plays an important role in B and T cell differentiation, in embryonic somite formation and patterning, and associates with the scaffolding protein MAGI1 at adherens junctions on neuronal processes. Signaling through DLL1 and Notch 2 has been implicated in the development of marginal zone B cells (MZB). Hamster anti Mouse Delta-Like Protein 1 antibody, clone HMD1-5 blocks binding of Notch2 to Dll1 (Moriyama et al. 2008) |
- Target Species
- Mouse
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Rat Human Weak - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- DLL1-expressing CHO cells.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized Armenian hamsters were fused with cells of the P3U1 myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | |||
| Functional Assays 1 | |||
| Immunohistology - Frozen |
- 1 This product contains sodium azide, removal by dialysis is recommended prior to use in functional assays.
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10ul of the suggested working dilution to label 1x106 cells in 100ul.
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Mouse spleen
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hamster (Armenian) IgG Negative Control | MCA2356 | F | 0.25 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Hamster (Armenian) IgG Negative Control | ||||||
Source Reference
-
Moriyama, Y. et al. (2008) Delta-like 1 is essential for the maintenance of marginal zone B cells in normal mice but not in autoimmune mice.
Int Immunol. 20 (6): 763-73.
References for Delta-Like Protein 1 antibody
-
Sekine, C. et al. (2009) Differential regulation of splenic CD8- dendritic cells and marginal zone B cells by Notch ligands.
Int Immunol. 21 (3): 295-301. -
Sekine, C. et al. (2012) Differential regulation of osteoclastogenesis by Notch2/Delta-like 1 and Notch1/Jagged1 axes.
Arthritis Res Ther. 14: R45.
Further Reading
-
Hoyne, G.F. et al. (2001) Notch signalling in the regulation of peripheral immunity.
Immunol Rev. 182: 215-27. -
Iso, T. et al. (2003) Notch signaling in vascular development.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23 (4): 543-53. -
Bray, S.J. (2006) Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7 (9): 678-89. -
Hu, X. et al. (2008) Integrated regulation of Toll-like receptor responses by Notch and interferon-gamma pathways.
Immunity. 29 (5): 691-703.
- Synonyms
- DLL1
- RRID
- AB_10708982
- UniProt
- Q61483
- P97677
- O00548
- Entrez Gene
- DLL1
- Dll1
- Dll1
- GO Terms
- GO:0005509 calcium ion binding
- GO:0001709 cell fate determination
- GO:0005576 extracellular region
- GO:0005887 integral to plasma membrane
- GO:0005112 Notch binding
- GO:0007154 cell communication
- GO:0007219 Notch signaling pathway
- GO:0007220 Notch receptor processing
- GO:0030097 hemopoiesis
- View More GO Terms
- GO:0030155 regulation of cell adhesion
- GO:0016021 integral to membrane
- GO:0009912 auditory receptor cell fate commitment
- GO:0005886 plasma membrane
- GO:0001701 in utero embryonic development
- GO:0001757 somite specification
- GO:0007368 determination of left/right symmetry
- GO:0007386 compartment pattern formation
- GO:0031410 cytoplasmic vesicle
- GO:0042472 inner ear morphogenesis
- GO:0042475 odontogenesis of dentine-containing tooth
- GO:0045608 negative regulation of auditory receptor cell differentiation
MCA5705
MCA5705GA
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Mouse ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up