IgE: Immunoglobulin E Class

- On This Page
- Properties of IgE
- IgE antibodies
- Related reading
Properties of IgE
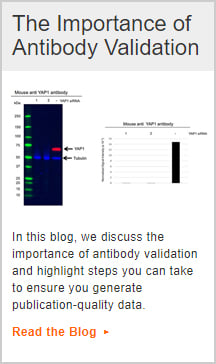
Human immunoglobulin E (IgE) is expressed on the surface of mature B cells. Human immunoglobulin IgE is the least abundant Ig in the serum and does not activate the complement pathway.
Fragment crystallization (Fc) receptors for IgE are found on eosinophils and IgE binds Fc receptors on mast cells and basophils even before interacting with antigen. As a result of its binding to basophils and mast cells, IgE is involved in allergic reactions. This happens when allergen is bound to IgE on cells and releases various pharmacological mediators which cause allergies.
| IgE |
|
|||
|
Heavy chain |
ε |
|||
|
Light chain |
κ or λ |
|||
|
Molecular formula |
ε2κ2 or ε2λ2 |
|||
|
Valency |
2 |
|||
|
Structure |
Monomer |
|||
|
Abundance in serum (in relation to total immunoglobulins present) |
0.002% |
|||
|
Carbohydrate content |
12% |
|||
|
Concentration in serum |
10 - 400 ng/ml |
|||
|
IgE subclasses |
None |
|||
|
Heavy chain MW (kDa) |
70 |
|||
|
Light chain MW (kDa) |
23 |
|||
|
Total MW (kDa) |
190 |
|||
|
Distribution |
Basophils and mast cells (in saliva and nasal secretions) |
|||
|
Function |
Protects against parasites |
|||
IgE Antibodies
Bio-Rad offers a range of human immunoglobulin antibodies for the IgE isotype. In addition to human, we also offer IgE antibodies for a wide range of other target species. Below you will find a list of all of our IgE antibodies. Use the buttons/filters to identify the antibody that fits your exact requirements.
Antibodies for IgE (Immunoglobulin E)
| Description | Target | Format | Clone | Applications | Citations | Code |
|---|
Related Reading
For a full overview of Immunoglobulin classes please visit our Immunoglobulins Classes / Sub-classes page. Alternatively you can view the following individual types:
- IgA Antibodies (Immunoglobulin A)
- IgD Antibodies (Immunoglobulin D)
- IgG Antibodies (Immunoglobulin G)
- IgM Antibodies (Immunoglobulin M)