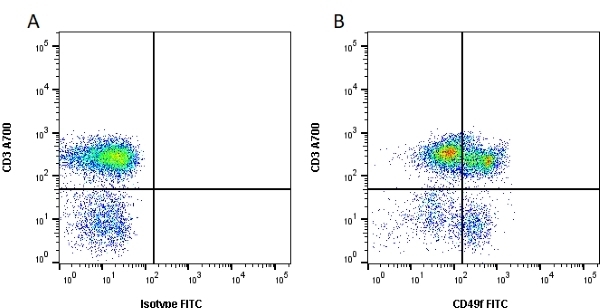
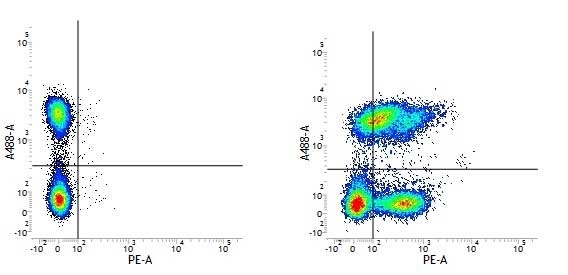
CD49f antibody | NKI-GoH3




Rat anti Human CD49f
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- NKI-GoH3
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Specificity
- CD49f
| Rat anti Human CD49f antibody, clone NKI-GoH3 recognizes CD49f, also known as the VLA-6 alpha chain. CD49f is a 1107 amino acid ~120 kDa cell surface glycoprotein that forms distinct complexes with CD29 (VLA beta-chain), resulting in the VLA-6 (alpha-6 beta-1) complex, expressed on human platelets, or with the beta-4 integrin resulting in the alpha-6 beta-4 complex expressed on various human epithelial cells. Rat anti Human CD49f antibody, clone NKI-GoH3 reacts with platelets, megakaryocytes, T lymphocytes and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (alpha-6 beta-1). In immunohistology the monoclonal antibody reacts with epithelial cells of a variety of tissues, peripheral nerves, microvascular endothelial cells, placenta cyto- and syncytotrophoblasts.VLA-6 is an important mediator of cell binding to laminin. Rat anti Human CD49f antibody, clone NKI-GoH3 blocks the binding of cells to the E8 fragment of laminin (Sonnenberg et al. 1998). |
- Target Species
- Human
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Mouse Dog Pig Cynomolgus monkey Sheep - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Carrier Free
- Yes
- Immunogen
- BALB/c mouse mammary tumor cells
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized Sprague-Dawley rats were fused with cells of the SP2/0 mouse myeloma cell line
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | 1/50 | 1/200 | |
| Immunofluorescence | |||
| Immunohistology - Frozen | |||
| Immunoprecipitation |
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10ul of the suggested working dilution to label 106 platelets in 100ul.
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Human Tonsil
References for CD49f antibody
-
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1986) Development of mouse mammary gland: identification of stages in differentiation of luminal and myoepithelial cells using monoclonal antibodies and polyvalent antiserum against keratin.
J Histochem Cytochem. 34 (8): 1037-46. -
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1987) A complex of platelet glycoproteins Ic and IIa identified by a rat monoclonal antibody.
J Biol Chem. 262 (21): 10376-83. -
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1988) Identification and characterization of a novel antigen complex on mouse mammary tumor cells using a monoclonal antibody against platelet glycoprotein Ic.
J Biol Chem. 263 (28): 14030-8. -
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1988) Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6.
Nature. 336 (6198): 487-9. -
Hemler, M.E. et al. (1988) Multiple very late antigen (VLA) heterodimers on platelets. Evidence for distinct VLA-2, VLA-5 (fibronectin receptor), and VLA-6 structures.
J Biol Chem. 263 (16): 7660-5. -
Workshop of the 4th International Conference on Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigens Vienna (1989) Workshop number p 055.
Oxford University Press. -
Soligo, D. et al. (1989) Immunohistochemical reacitivy on bone marrow and tissues of anti-VLA antibodies in the platelet panel, in Leucocyte Typing IV: White Cell Differentiation Antigens.
Edited by Knapp, W. et al. Oxford University Press p1029-1032. -
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1990) The alpha 6 beta 1 (VLA-6) and alpha 6 beta 4 protein complexes: tissue distribution and biochemical properties.
J Cell Sci. 96 ( Pt 2): 207-17.
View The Latest Product References
-
Sonnenberg, A. et al. (1990) Integrin recognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1, E3, E8) and evidence that alpha 6 beta 1 but not alpha 6 beta 4 functions as a major receptor for fragment E8.
J Cell Biol. 110 (6): 2145-55. -
Alais, S. et al. (2001) HEMCAM/CD146 downregulates cell surface expression of beta1 integrins.
J Cell Sci. 114: 1847-59. -
Dangerfield, J. et al. (2002) PECAM-1 (CD31) homophilic interaction up-regulates alpha6beta1 on transmigrated neutrophils in vivo and plays a functional role in the ability of alpha6 integrins to mediate leukocyte migration through the perivascular basement membrane.
J Exp Med. 196: 1201-11. -
Le Bellego, F. et al. (2005) Cytoskeleton reorganization mediates alpha6beta1 integrin-associated actions of laminin on proliferation and survival, but not on steroidogenesis of ovine granulosa cells.
Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 3: 19. -
Anderson, C. et al. (2009) Sonic hedgehog-dependent synthesis of laminin alpha1 controls basement membrane assembly in the myotome.
Development. 136: 3495-504. -
Jensen, K.B. et al. (2010) Assaying proliferation and differentiation capacity of stem cells using disaggregated adult mouse epidermis.
Nat Protoc. 5 (5): 898-911. -
da Silva, R.G. et al. (2010) Endothelial alpha3beta1-integrin represses pathological angiogenesis and sustains endothelial-VEGF.
Am J Pathol. 177: 1534-48. -
Collins, C.A. et al. (2011) Reprogramming adult dermis to a neonatal state through epidermal activation of β-catenin
Development.138: 5189-99. -
Schäfer, G. et al. (2013) The role of inflammation in HPV infection of the Oesophagus.
BMC Cancer. 13: 185. -
Moreira, M.L. et al. (2016) Vaccination against canine leishmaniosis increases the phagocytic activity, nitric oxide production and expression of cell activation/migration molecules in neutrophils and monocytes.
Vet Parasitol. 220: 33-45. -
Mastrogiannaki, M. et al. (2016) β-Catenin Stabilization in Skin Fibroblasts Causes Fibrotic Lesions by Preventing Adipocyte Differentiation of the Reticular Dermis.
J Invest Dermatol. 136 (6): 1130-42. -
Haining, E.J. et al. (2017) Tetraspanin Tspan9 regulates platelet collagen receptor GPVI lateral diffusion and activation.
Platelets. 28 (7): 629-42. -
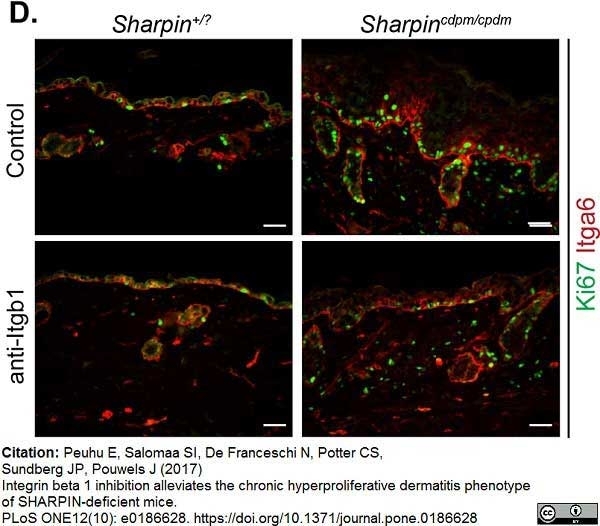
Peuhu. E, et al. (2017) Integrin beta 1 inhibition alleviates the chronic hyperproliferative dermatitis phenotype of SHARPIN-deficient mice
PLOS ONE. 12 (10): e0186628. -
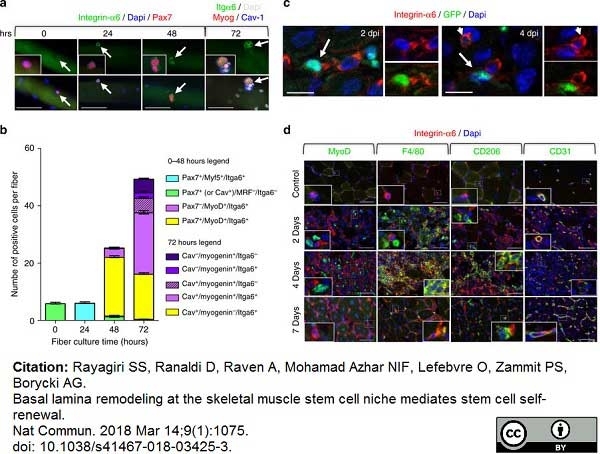
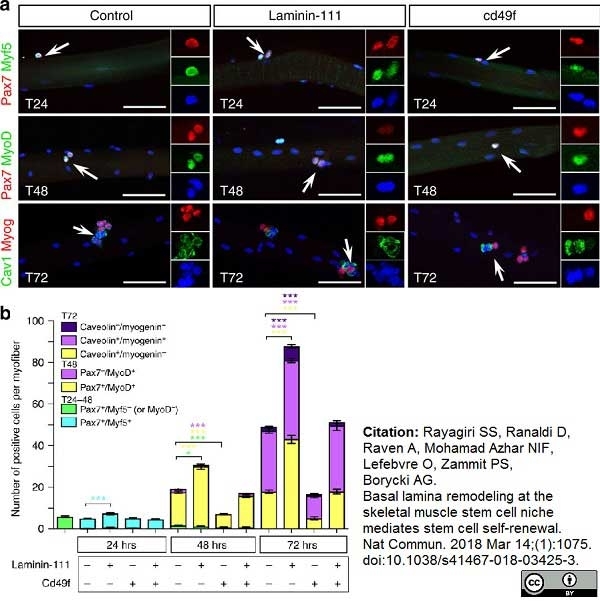
Rayagiri, S.S. et al. (2018) Basal lamina remodeling at the skeletal muscle stem cell niche mediates stem cell self-renewal.
Nat Commun. 9 (1): 1075. -
Loureiro, J. et al. (2019) Conjugation of the T1 sequence from CCN1 to fibrin hydrogels for therapeutic vascularization.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 104: 109847. -
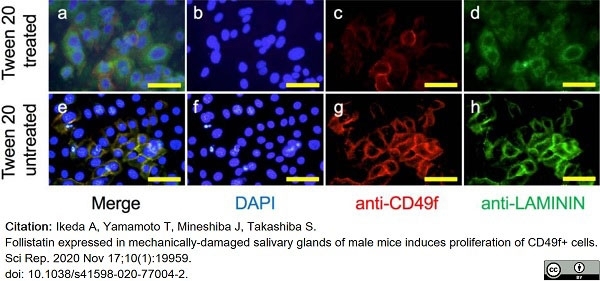
Ikeda, A. et al. (2020) Follistatin expressed in mechanically-damaged salivary glands of male mice induces proliferation of CD49f+ cells.
Sci Rep. 10 (1): 19959. -
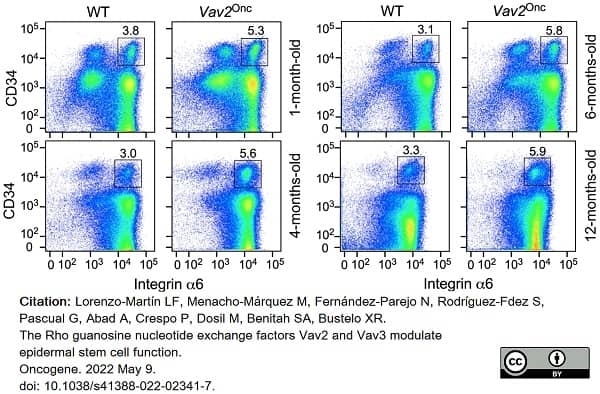
Lorenzo-Martín, L.F. et al. (2022) The Rho guanosine nucleotide exchange factors Vav2 and Vav3 modulate epidermal stem cell function.
Oncogene. May 09 [Epub ahead of print]. -
Lorenzo-Martín, L.F. & Bustelo, X.R. (2023) The Rho GTPase exchange factor Vav2 promotes extensive age-dependent rewiring of the hair follicle stem cell transcriptome.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 11: 1252834. -
Conway, J.R.W. et al. (2023) Defined extracellular matrix compositions support stiffness-insensitive cell spreading and adhesion signaling.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 120 (43): e2304288120. -
Lim, L.K.P. et al. (2023) Automated electrical stimulation therapy accelerates re-epithelialization in a 3D in vitro human skin wound model.
Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). Dec 07 [Epub ahead of print].
Further Reading
-
Piriou-Guzylack, L. (2008) Membrane markers of the immune cells in swine: an update.
Vet Res. 39: 54.
MCA699
MCA699T
MCA699GA
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Human ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up