Influenza A H1N1 antibody


Goat anti Influenza A H1N1
- Product Type
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Isotype
- Polyclonal IgG
- Specificity
- Influenza A H1N1
| Goat anti Influenza A H1N1 polyclonal antibody is specific for Influenza A virus H1N1 by Haemagglutination inhibition. This goat anti Influenza A H1N1 polyclonal antibody does not react with Influenza B, RSV, Para 1-3 or Adenovirus. It does not react with HEp-2 cells but may react with some chicken cellular proteins. Influenza type A viruses are divided into subtypes based on the antigenic differences of two viral surface proteins, hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N). On infection of the respiratory tract, the hemagglutinin molecule binds to sialic acid-containing receptors on the epithelial cells resulting in endocytosis. Once the virus has been engulfed, the hemagglutinin allows the viral membrane to fuse with the endosomal membrane. Neuraminidase functions to aid viral release from host cells by cleaving terminal sialic acid residues from carbohydrate moieties on the cell surface. Viral release also requires the interaction of the viral M1 protein with the cellular scaffold G-like protein RACK1 (Demirov et al. 2012). Subtype antigenic variations result from a process known as antigenic drift whereby these surface proteins constantly mutate in order to evade the host immune response. Subtype A(H1N1) was the cause of Spanish flu pandemic that killed approximately 50,000,000 people between 1918-1919. |
- Target Species
- Viral
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Influenza A, strain USSR (H1N1)
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haemagglutination | |||
| Immunofluorescence | |||
| Immunohistology - Paraffin |
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit anti Goat IgG (Fc):FITC | STAR122F | F | 1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Rabbit anti Goat IgG (Fc):FITC | ||||||
| Rabbit anti Goat IgG (Fc):HRP | STAR122P | C E WB | 1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Rabbit anti Goat IgG (Fc):HRP | ||||||
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen Retrieval Buffer, pH8.0 | BUF025A | P | 500 ml | Log in | |||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
| Log in | |||||||
| Description | Antigen Retrieval Buffer, pH8.0 | ||||||
References for Influenza A H1N1 antibody
-
Zielecki, F. et al. (2010) Virulence determinants of avian H5N1 influenza A virus in mammalian and avian hosts: The role of the C-terminal ESEV motif in the viral NS1 protein.
J Virol. 117: 439 - 48 -
Kash JC et al. (2011) Lethal synergism of 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae coinfection is associated with loss of murine lung repair responses.
MBio. 2(5). pii: e00172-11. -
Weinheimer, V.K. et al. (2012) Influenza A viruses target type II pneumocytes in the human lung.
J Infect Dis. 206 (11): 1685-94. -
Nicol, M.Q. et al. (2012) A novel family of peptides with potent activity against influenza A viruses.
J Gen Virol. 93: 980-6. -
Meunier, I. and von Messling, V. (2012) PB1-F2 Modulates Early Host Responses but Does not Affect the Pathogenesis of H1N1 Seasonal Influenza Virus.
J Virol. 86: 4271-8. -
Demirov, D. et al. (2012) Interaction of influenza A virus matrix protein with RACK1 is required for virus release.
Cell Microbiol. 14: 774-89. -
Kallfass, C. et al. (2013) Visualizing the beta interferon response in mice during infection with influenza A viruses expressing or lacking nonstructural protein 1.
J Virol. 87 (12): 6925-30. -
Schliehe, C. et al. (2015) The methyltransferase Setdb2 mediates virus-induced susceptibility to bacterial superinfection.
Nat Immunol. 16 (1): 67-74.
View The Latest Product References
-
Nicol, M.Q. et al. (2019) Lack of IFNγ signaling attenuates spread of influenza A virus in vivo and leads to reduced pathogenesis.
Virology. 526: 155-164. -
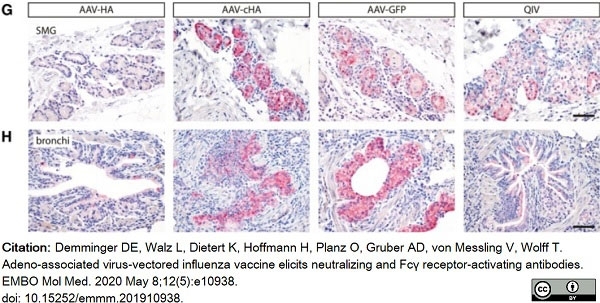
Demminger, D.E. et al. (2020) Adeno-associated virus-vectored influenza vaccine elicits neutralizing and Fcγ receptor-activating antibodies.
EMBO Mol Med. 12 (5): e10938. -
Goncheva, M.I. et al. (2020) Staphylococcus aureus Lipase 1 Enhances Influenza A Virus Replication.
mBio. 11 (4): e00975-20. -
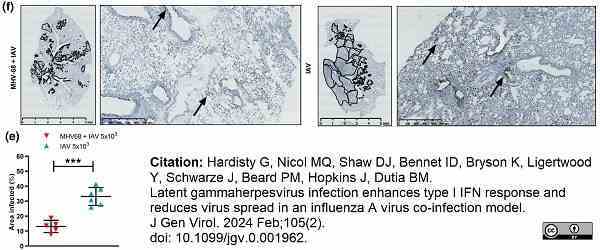
Hardisty, G. et al. (2024) Latent gammaherpesvirus infection enhances type I IFN response and reduces virus spread in an influenza A virus co-infection model.
J Gen Virol. 105 (2) 8 Feb [Epub ahead of print].
- RRID
- AB_620739
5315-0064
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Viral ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up