CD4 antibody | Du CD4-2





Mouse anti Duck CD4
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- Du CD4-2
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Specificity
- CD4
| Mouse anti Duck CD4 antibody, clone Du CD4-2 recognizes Pekin duck CD4, shown to be expressed by thymocytes, splenocytes and peripheral lymphoid cells. Most avian immune research has been carried out on chickens, relatively little is known about the immune system of ducks, though there is a resemblance between the main lymphoid organs, the spleen, thymus and bursa of Fabricius. At the cellular level, like mammalian T cells, duck lymphocytes are responsive to phytohaemagglutinin, and all cells reacting with clone Du CD4-2 have been identified as CD3+ T cells (Kothlow et al. 2005). Clone Du CD4-2 can be used to identify duck T helper cells. Mouse anti Duck CD4 antibody, clone Du CD4-2 does not appear to react with Mallard. |
- Target Species
- Duck
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Chicken Goose - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- <0.1% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- 293T cells expressing Pekin duck CD4.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunised Balb/c mice were fused with cells of the SP2/0 mouse myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | 1 | 10 ug/ml | |
| Immunohistology - Paraffin | |||
| Immunoprecipitation |
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10ul of the suggested working dilution to label 106 cells in 100ul.
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goat anti Mouse IgG (H/L):FITC (Multi Species Adsorbed) | STAR117F | F | 0.5 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Goat anti Mouse IgG (H/L):FITC (Multi Species Adsorbed) | ||||||
References for CD4 antibody
-
Kothlow, S. et al. (2005) Characterization of duck leucocytes by monoclonal antibodies.
Dev Comp Immunol. 29 (8): 733-48. -
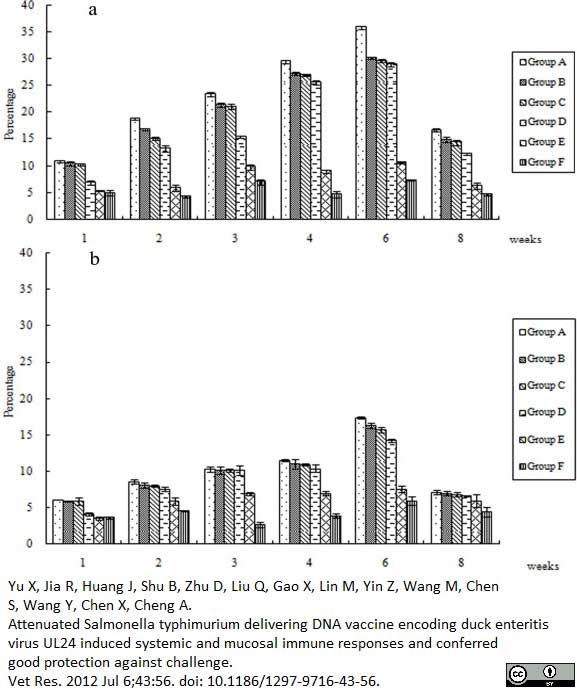
Yu, X. et al. (2012) Attenuated Salmonella typhimurium delivering DNA vaccine encoding duck enteritis virus UL24 induced systemic and mucosal immune responses and conferred good protection against challenge.
Vet Res. 43: 56. -
Shanmugasundaram, R. and Selvaraj, R.K. (2012) Regulatory T cell properties of thymic CD4(+)CD25(+) cells in ducks.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 149: 20-7. -
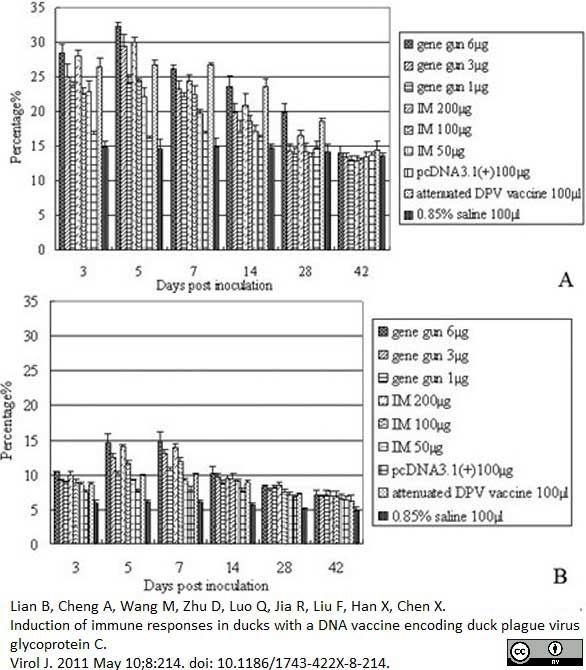
Lian, B. et al. (2011) Induction of immune responses in ducks with a DNA vaccine encoding duck plague virus glycoprotein C.
Virol J. 8: 214. -
Huang, J. net al. (2014) An attenuated duck plague virus (DPV) vaccine induces both systemic and mucosal immune responses to protect ducks against virulent DPV infection.
Clin Vaccine Immunol. 21: 457-62. -
Chen, S. et al. (2015) Age-related development and tissue distribution of T cell markers (CD4 and CD8a) in Chinese goose.
Immunobiology. 220 (6): 753-61. -
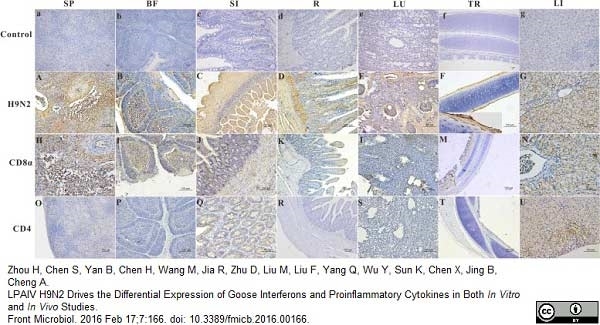
Zhou, H. et al. (2016) LPAIV H9N2 Drives the Differential Expression of Goose Interferons and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Both In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.
Front Microbiol. 7: 166. -
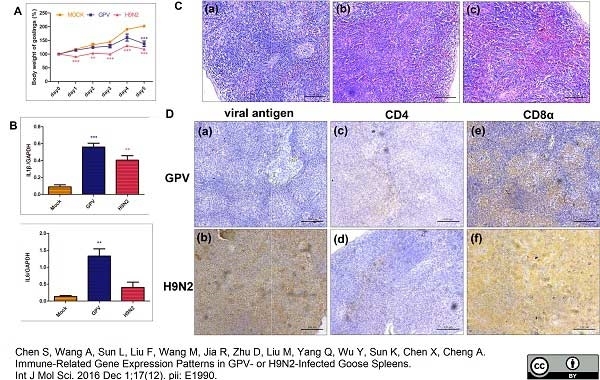
Chen, S. et al. (2016) Immune-Related Gene Expression Patterns in GPV- or H9N2-Infected Goose Spleens.
Int J Mol Sci. 17 (12): pii: E1990.
View The Latest Product References
-
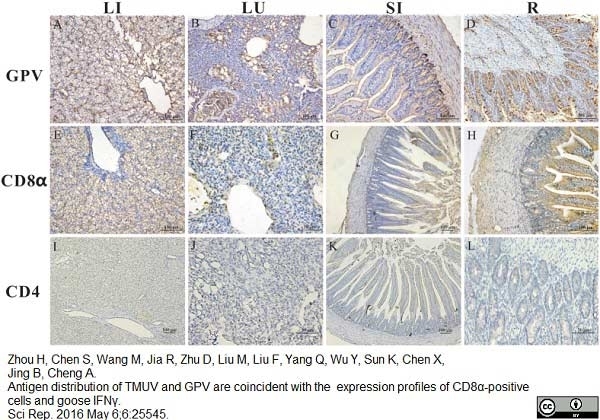
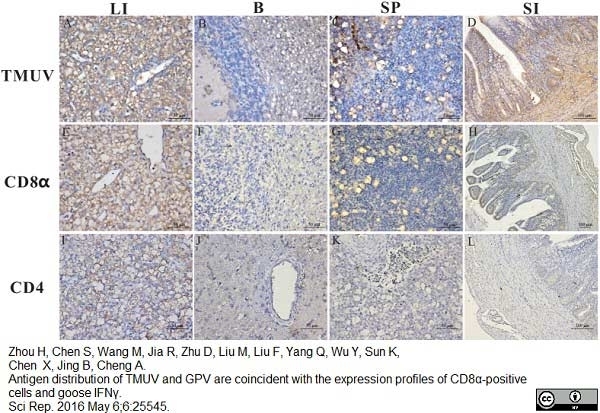
Zhou H et al. (2016) Antigen distribution of TMUV and GPV are coincident with the expression profiles of CD8α-positive cells and goose IFNγ.
Sci Rep. 6: 25545. -
Cornelissen, J.B. et al. (2013) Differences in highly pathogenic avian influenza viral pathogenesis and associated early inflammatory response in chickens and ducks.
Avian Pathol. 42 (4): 347-64. -
Wu, Y. et al. (2019) Changes in the small intestine mucosal immune barrier in Muscovy ducklings infected with Muscovy duck reovirus
Veterinary Microbiology. 233: 85-92. -
Apinda, N. et al. (2022) Simultaneous Protective Immune Responses of Ducks against Duck Plague and Fowl Cholera by Recombinant Duck Enteritis Virus Vector Expressing Pasteurella multocida OmpH Gene.
Vaccines (Basel). 10 (8): 1358.
Further Reading
-
Higgins, D.A. & Teoh, C.S. (1988) Duck lymphocytes. II. Culture conditions for optimum transformation response to phytohaemagglutinin.
J Immunol Methods. 106 (1): 135-45.
- RRID
- AB_609597
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Duck ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up