IgA antibody


Goat anti Chicken IgA:FITC
- Product Type
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Isotype
- Polyclonal IgG
- Specificity
- IgA
| Goat anti Chicken IgA antibody recognizes chicken immunoglobulin A and shows no cross-reactivity with other chicken immunoglobulin classes in immunoelectrophoresis. Goat anti Chicken IgA antibody may react with IgA from other species. |
- Target Species
- Chicken
- Product Form
- Purified IgG fraction conjugated to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Isomer 1 (FITC) - liquid
- Antiserum Preparation
- Antisera to chicken IgA were raised by repeated immunisation of goat with highly purified antigen. Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography.
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
0.09% Sodium Azide 0.2% Bovine Serum Albumin - Immunogen
- Purified chicken IgA.
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Max Ex/Em
-
Fluorophore Excitation Max (nm) Emission Max (nm) FITC 490 525 - Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
This product should be stored undiluted. This product is photosensitive and should be protected from light. Should this product contain a precipitate we recommend microcentrifugation before use.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | |||
| Immunohistology - Frozen | 1/200 | 1/2,000 |
References for IgA antibody
-
Wyszyśska A et al. (2004) Oral immunization of chickens with avirulent Salmonella vaccine strain carrying C. jejuni 72Dz/92 cjaA gene elicits specific humoral immune response associated with protection against challenge with wild-type Campylobacter.
Vaccine. 22 (11-12): 1379-89. -
Beal, R.K. et al. (2004) Age at primary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in the chicken influences persistence of infection and subsequent immunity to re-challenge.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 100 (3-4): 151-64. -
Beal, R.K. et al. (2004) Temporal dynamics of the cellular, humoral and cytokine responses in chickens during primary and secondary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.
Avian Pathol. 33 (1): 25-33. -
Barrow, P.A. et al. (2004) Faecal shedding and intestinal colonization of Salmonella enterica in in-bred chickens: the effect of host-genetic background.
Epidemiol Infect. 132 (1): 117-26. -
Withanage, G.S. et al. (2005) Cytokine and chemokine responses associated with clearance of a primary Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in the chicken and in protective immunity to rechallenge.
Infect Immun. 73 (8): 5173-82. -
Beal, R.K. et al. (2005) A strong antigen-specific T-cell response is associated with age and genetically dependent resistance to avian enteric salmonellosis.
Infect Immun. 73: 7509-16. -
Rezar, V. et al. (2007) Dose-dependent effects of T-2 toxin on performance, lipid peroxidation, and genotoxicity in broiler chickens.
Poult Sci. 86 (6): 1155-60. -
Zhang L et al. (2008) Enhancement of mucosal immune responses by intranasal co-delivery of Newcastle disease vaccine plus CpG oligonucleotide in SPF chickens in vivo.
Res Vet Sci. 85 (3): 495-502.
View The Latest Product References
-
Singh, R. (2010) Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of virosome based vaccines against Newcastle disease.
Trop Anim Health Prod. 42: 465-71 -
Buckley, A.M. et al. (2010) Evaluation of live-attenuated Salmonella vaccines expressing Campylobacter antigens for control of C. jejuni in poultry.
Vaccine. 28: 1094-105. -
Park, S.I. et al. (2010) Immune response induced by ppGpp-defective Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum in chickens.
J Microbiol. 48 (5): 674-81. -
Koppad, S. et al. (2011) Calcium phosphate coupled Newcastle disease vaccine elicits humoral and cell mediated immune responses in chickens.
Res Vet Sci. 91 (3): 384-90. -
Andersen, J.P. et al. (2013) No protection in chickens immunized by the oral or intra-muscular immunization route with Ascaridia galli soluble antigen.
Avian Pathol. 42 (3): 276-82. -
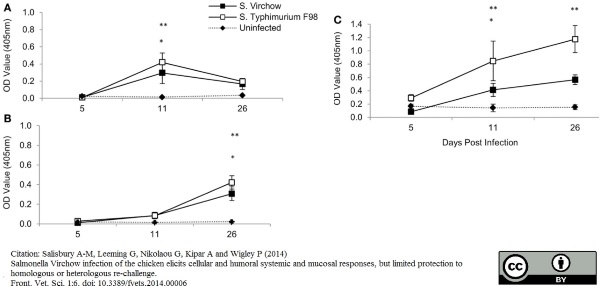
Salisbury Anne-Marie et al. (2014) Salmonella Virchow Infection of the Chicken Elicits Cellular and Humoral Systemic and Mucosal Responses, but Limited Protection to Homologous or Heterologous Re-Challenge
Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 1: 6. -
Barman, N.N. et al. (2014) Reflection of serum immunoglobulin isotypes in the egg yolk of laying hens immunized with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Veterinary World. 7 (9): 749-53. -
Park, E.H. et al. (2014) Protective efficacy of a single dose of baculovirus hemagglutinin-based vaccine in chickens and ducks against homologous and heterologous H5N1 virus infections.
Viral Immunol. 27 (9): 449-62. -
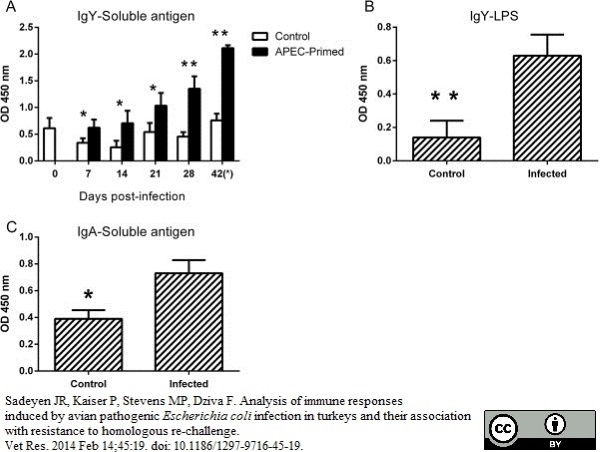
Sadeyen JR et al. (2014) Analysis of immune responses induced by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli infection in turkeys and their association with resistance to homologous re-challenge.
Vet Res. 45: 19. -
Bérto Letícia Dal et al. (2015) Live and Inactivated Salmonella enteritidis Vaccines: Immune Mechanisms in Broiler Breeders
World Journal of Vaccines. 05 (04): 155-164. -
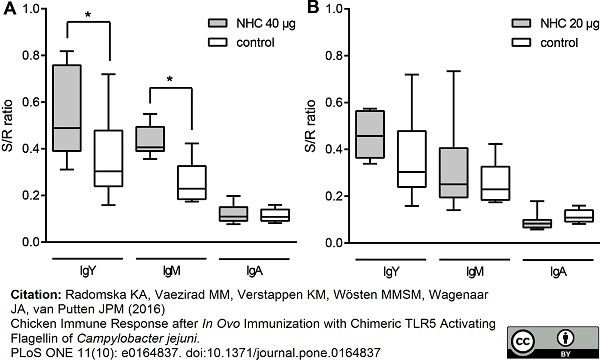
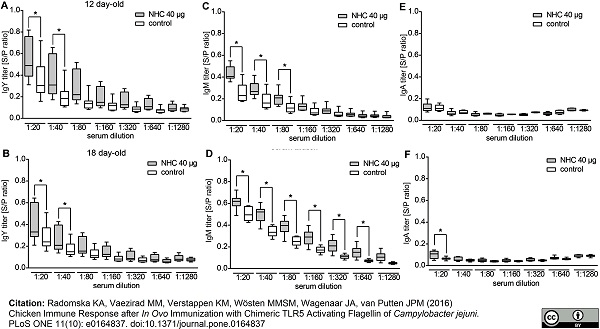
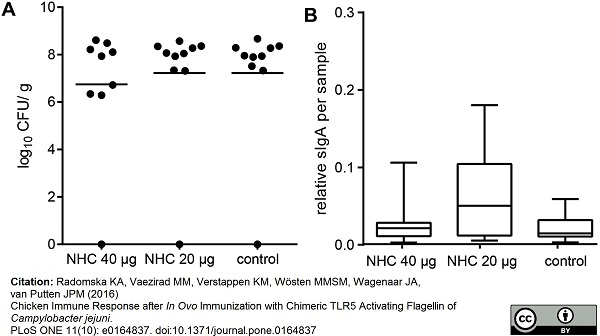
Radomska, K.A. et al. (2016) Chicken Immune Response after In Ovo Immunization with Chimeric TLR5 Activating Flagellin of Campylobacter jejuni.
PLoS One. 11 (10): e0164837. -
Beir˜o, B.C.B. et al. (2018) Effect of an Enterococcus faecium. probiotic on specific IgA following live Salmonella enteritidis. vaccination of layer chickens.
Avian Pathol. 47 (3): 325-33. -
Al-Karagoly, H. et al. (2019) Turkey humoral and cell-mediated immune responses to a Newcastle viscerotropic vaccine and its association with major histocompatibility complex.
Bulg J Vet Med. 22 (1): 26-40. -
Bonato, M. et al. (2020) Effects of yeast cell wall on immunity, microbiota, and intestinal integrity of Salmonella-infected broilers
Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 29 (3): 545-58. -
Śmiałek, M. et al. (2021) The influence of maternally derived antibodies on protection against aMPV/A infection in TRT vaccinated turkeys.
Poult Sci. 100 (5): 101086.
- RRID
- AB_323050
AAI28F
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Chicken ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up