Aspergillus antibody | WF-AF-1

Mouse anti Aspergillus SPP
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- WF-AF-1
- Isotype
- IgM
- Specificity
- Aspergillus
- Region
- SPP
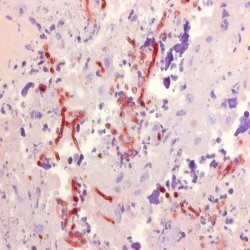
| Mouse anti Aspergillus spp., clone WF-AF-1, is raised against the wall fraction (WF) of Aspergillus fumigatus. This antibody specifically recognizes members of the Aspergillus spp. including A. flavus and A. niger, reacting strongly with walls and septae, and to a lesser extent within the cytoplasm of hyphae. A. fumigatus, a thermophilic, opportunistic and angio-invasive filamentous fungus, is the main causative agent of systemic bovine aspergillosis, a worldwide and often fatal respiratory disease of cattle. Clone WF-AF-1 has been successfully used in immunohistochemistry for the specific and consistent in situ diagnosis of bovine systemic aspergillosis, attributed to its binding to the major cell wall component, galactomannan. Clone WF-AF-1 has also been used for the identification of aspergillosis in human tissue sections. Mouse anti Aspergillus spp., clone WF-AF-1, does not bind to water-soluble somatic antigens (WSSA) of Aspergillus spp., but may react with galactomannans of members of the genus Penicillium. |
- Target Species
- Fungal
- Product Form
- Purified IgM - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgM prepared by ammonium sulfate precipitation from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
- Immunogen
- Wall fraction (WF) of Aspergillus fumigatus
- Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgM concentration 1.0 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized Balb/c ABom mice were fused with cells of the X63-Ag8.653 myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunohistology - Paraffin 1 | 1/300 | ||
| Immunoprecipitation | |||
| Western Blotting |
- 1This product requires protein digestion pre-treatment of paraffin sections e.g. See Jensen et al. (2000) for details.
- Histology Positive Control Tissue
- Aspergillus infected placenta.
- Western Blotting
- Mouse anti Aspergillus spp. antibody, clone WF-AF-1 detects a band of approximately 106kDa of Aspergillus fumigatus wall fraction (WF).
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goat anti Mouse IgM:Alk. Phos.(Human Adsorbed) | STAR138A | C E P WB | 1 ml |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Goat anti Mouse IgM:Alk. Phos.(Human Adsorbed) | ||||||
| Goat anti Mouse IgG/A/M:HRP (Human Adsorbed) | STAR87P | E | 1 mg |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Goat anti Mouse IgG/A/M:HRP (Human Adsorbed) | ||||||
References for Aspergillus antibody
-
Jensen, H.E. et al. (1996) Development of murine monoclonal antibodies for the immunohistochemical diagnosis of systemic bovine aspergillosis.
J Vet Diagn Invest. 8 (1): 68-75. -
Jensen, H.E. et al. (1996) Diagnosis of systemic mycoses by specific immunohistochemical tests.
APMIS. 104 (4): 241-58. -
Jensen, H.E. et al. (1997) The use of immunohistochemistry to improve sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of systemic mycoses in patients with haematological malignancies.
J Pathol. 181 (1): 100-5. -
Delaney, M.A. et al. (2013) Occlusive fungal tracheitis in 4 captive bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus).
Vet Pathol. 50 (1): 172-6. -
Goodpaster, T. & Randolph-Habecker, J. (2014) A flexible mouse-on-mouse immunohistochemical staining technique adaptable to biotin-free reagents, immunofluorescence, and multiple antibody staining.
J Histochem Cytochem. 62 (3): 197-204. -
Galiza Glauco J.N. et al. (2014) Usage of three immunohistochemical methods in the detection of aspergillosis and zygomycosis in animals
Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 34 (7): 637-642. -
Murase, H. et al. (2015) A clinical case of equine fungal placentitis with reference to hormone profiles and ultrasonography.
J Equine Sci. 26 (4): 129-33. -
Dagleish, M.P. et al. (2010) Immunohistochemical diagnosis of infectious diseases of sheep.
Small Ruminant Research. 92 (1-3): 19-35.
View The Latest Product References
-
Suzuta F et al. (2015) Variations in the morphology of Rhizomucor pusillus in granulomatous lesions of a Magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus).
J Vet Med Sci. 77 (8): 1029-31. -
Jin, J-H. et al. (2015) Real-time selective monitoring of allergenic Aspergillus molds using pentameric antibody-immobilized single-walled carbon nanotube-field effect transistors
RSC Adv. 5 (20): 15728-15735. -
Ogasawara, F. et al. (2016) Concurrent Fowlpox and Candidiasis Diseases in Backyard Chickens with Unusual Pox Lesions in the Bursa of Fabricius.
Avian Dis. 60 (3): 705-8. -
Haridy, M. et al. (2018) Candida parapsilosis. and Candida tropicalis. infections in an Okhotsk snailfish (Liparis ochotensis.).
J Vet Med Sci. 80 (11): 1676-1680. -
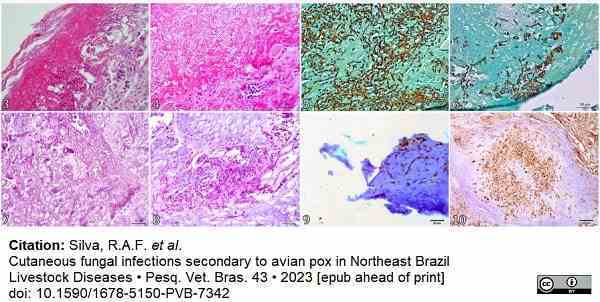
Silva, R.A.F. et al. (2023) Cutaneous fungal infections secondary to avian pox in Northeast Brazil
Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 43 8 Aug [Epub ahead of print].
- RRID
- AB_1100465
MCA2576
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Fungal ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up