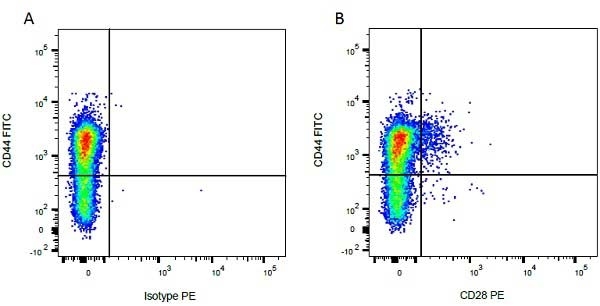
CD44 antibody | IL-A118
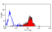


Mouse anti Bovine CD44:FITC
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- IL-A118
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- CD44
| Mouse anti Bovine CD44 antibody, clone IL-A118 recognizes bocine Phagocytic Glycoprotein-1 (PGP-1), also known as CD44, Hermes antigen, Extracellular matrix receptor III or HUTCH-1. Bovine CD44 is a 346 amino acid ~90 kDa type I single pass transmembrane glycoprotein containing a single Link domain, responsible for hyaluronan binding. Bovine CD44 is expressed by a wide range of bovine cells, including peripheral T and B lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, platelets and early erythroid cells. |
- Target Species
- Bovine
- Species Cross-Reactivity
-
Target Species Cross Reactivity Camel - N.B. Antibody reactivity and working conditions may vary between species.
- Product Form
- Purified IgG conjugated to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Isomer 1 (FITC) - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein G from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
0.09% Sodium Azide 1% Bovine Serum Albumin - Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 0.1 mg/ml
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunized BALB/c mice were fused with cells of the X63.Ag8.853 myeloma cell line.
- Max Ex/Em
-
Fluorophore Excitation Max (nm) Emission Max (nm) FITC 490 525 - Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended. This product is photosensitive and should be protected from light.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | Neat | 1/10 |
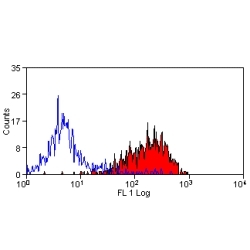
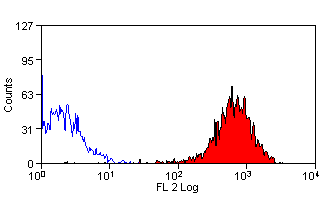
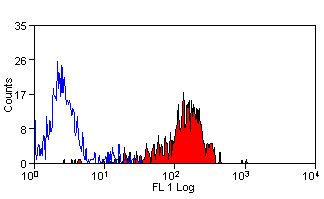
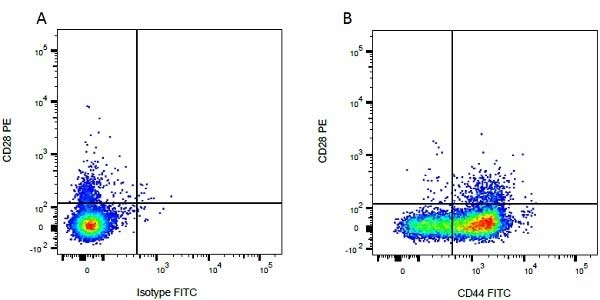
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10ul of the suggested working dilution to label 1x106 cells in 100ul
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse IgG1 Negative Control:FITC | MCA928F | F | 100 Tests |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse IgG1 Negative Control:FITC | ||||||
References for CD44 antibody
-
Naessens, J. & Nthale, J. (1993) Biochemical characterization of three non-lineage antigens defined by workshop antibodies.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 39 (1-3): 217-23. -
Naessens, J. et al. (1993) Cross-reactivity of workshop antibodies with cells from domestic and wild ruminants.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 39 (1-3): 283-90. -
Howard, C.J. & Naessens, J. (1993) Summary of workshop findings for cattle (tables 1 and 2).
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 39 (1-3): 25-47. -
Menge C et al. (2004) Bovine ileal intraepithelial lymphocytes represent target cells for Shiga toxin 1 from Escherichia coli.
Infect Immun. 72 (4): 1896-905. -
de Moraes, C.N. et al. (2016) Bovine endometrial cells: a source of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells.
Cell Biol Int. 40 (12): 1332-9. -
de Moraes, C.N.et al. (2017) Shotgun proteomic analysis of the secretome of bovine endometrial mesenchymal progenitor/stem cells challenged or not with bacterial lipopolysaccharide.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 187: 42-7. -
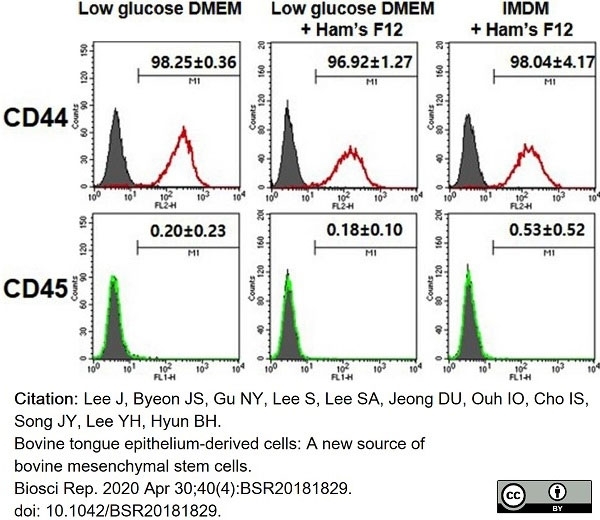
Lee, J. et al. (2020) Bovine tongue epithelium-derived cells: A new source of bovine mesenchymal stem cells.
Biosci Rep. 40 (4): BSR20181829. -
Molinos, M. et al. (2023) Alterations of bovine nucleus pulposus cells with aging.
Aging Cell. 22 (8): e13873.
View The Latest Product References
- Synonyms
- H-CAM
- RRID
- AB_1604795
- UniProt
- Q29423
- Entrez Gene
- CD44
- GO Terms
- GO:0007155 cell adhesion
- GO:0016021 integral to membrane
- GO:0004872 receptor activity
- GO:0005540 hyaluronic acid binding
MCA2433F
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Bovine ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up