ELISA Synblock
ELISA Synblock
- Product Type
- Accessory Reagent
- Specificity
- ELISA Synblock
| ELISA Synblock is an ELISA buffer designed to avoid false positive results associated with buffers containing animal proteins (e.g. BSA) and reduce non-specific background signals in ELISA assays without the addition of the usual protein additives. |
- Intended Use
-
BUF034A, BUF034B: ELISA SynBlock is a novel protein-free blocking buffer suitable for use in all ELISA formats requiring maximum blocking strength. With Tween and synthetic blocking agents, the inert nature of this unique buffer, enables maximum reduction of non-specific binding and interference associated particularly with sandwich ELISA assays.
Additional molecular stabilizers and an antimicrobial agent provide a long-term stable environment for coating antigen or capture antibody. Plates can be blocked at room temperature and stored once dried for up to a year at +4°C.
N.B. SYNBLOCK is not suitable for use on Immunolon-2 plates. Bio-Rad recommends the use of BUF033A for this purpose. -
BUF034C: ELISA SynBlock is a novel protein-free blocking buffer suitable for use in all ELISA formats requiring maximum blocking strength. With detergent and synthetic blocking agents, the inert nature of this unique buffer enables maximum reduction of non-specific binding and interference associated particularly with sandwich ELISA assays.
Additional molecular stabilizers and an antimicrobial agent provide a long-term stable environment for coating antigen or capture antibody. Plates can be blocked at room temperature and stored once dried for up to a year at +4°C.
N.B. SynBlock is not suitable for use on Immunlon® 2 plates. Bio-Rad recommends the use of BUF033A for this purpose. - Product Form
- Ready to use - liquid
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- BUF034A: <0.1% sodium azide (NaN3)
-
BUF034B, BUF034C:
0.05% Sodium Azide - Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- Guaranteed until date of expiry. Please see product label.
DO NOT FREEZE
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | Neat |
- Instructions For Use
- 1. Coat ELISA plate with antibody or antigen as required.
2. After incubation, remove the coating solution and wash the plate x2 with wash buffer. BUF031A can be used for this purpose.
3. Add 300-400ul of BUF034A and incubate for 2-24 hours. Use a volume equal to or greater than the volume of coating solution.
4. After removal of the blocking buffer continue with the assay or dry the plate for long-term storage at +4°C. - 1. Coat ELISA plate with antibody or antigen as required.
2. After incubation, remove the coating solution and wash the plate x2 with wash buffer. BUF031A can be used for this purpose.
3. Add 300-400ul of BUF034B and incubate for 2-24 hours. Use a volume equal to or greater than the volume of coating solution.
4. After removal of the blocking buffer continue with the assay or dry the plate for long-term storage at +4°C. - 1. Coat ELISA plate with antibody or antigen as required.
2. After incubation, remove the coating solution and wash the plate x2 with wash buffer. BUF031A can be used for this purpose.
3. Add 300-400ul of BUF034C and incubate for 2-24 hours. Use a volume equal to or greater than the volume of coating solution.
4. After removal of the blocking buffer continue with the assay or dry the plate for long-term storage at +4°C.
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5x ELISA Coating Buffer | BUF030A | E | 100 ml | Log in | |||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
| Log in | |||||||
| Description | 5x ELISA Coating Buffer | ||||||
| 10x ELISA Wash Buffer | BUF031A | E | 100 ml | Log in | |||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
| Log in | |||||||
| Description | 10x ELISA Wash Buffer | ||||||
References for ELISA Synblock
-
Afrough, B. et al. (2007) Identification and elimination of false-positives in an ELISA-based system for qualitative assessment of glycoconjugate binding using a selection of plant lectins.
Biotechniques. 43 (4): 458, 460, 462 passim. -
Dalley, D. et al. (2008) Development and evaluation of a gamma-interferon assay for tuberculosis in badgers (Meles meles).
Tuberculosis (Edinb). 88: 235-43. -
Ahmed, R.R. et al. (2010) BACE1 and BACE2 enzymatic activities in Alzheimer's disease.
J Neurochem. 112: 1045-53. -
Chambers, M.A. et al. (2009) Performance of TB immunodiagnostic tests in Eurasian badgers (Meles meles) of different ages and the influence of duration of infection on serological sensitivity.
BMC Vet Res. 5: 42. -
Thompson, R. et al. (2011) Optimization of the enzyme-linked lectin assay for enhanced glycoprotein and glycoconjugate analysis.
Anal Biochem. 413: 114-22. -
Kuramitz, H. et al. (2012) Multiplexed assay for proteins based on sequestration electrochemistry using the protein binding electroactive magnetic microbeads.
Anal Sci. 28 (1): 77. -
Dwek, M.V. et al. (2010) A sensitive assay to measure biomarker glycosylation demonstrates increased fucosylation of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in patients with prostate cancer compared with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Clin Chim Acta. 411 (23-24): 1935-9. -
Verhelst, R. et al. (2010) The effects of plant polyphenols on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli adhesion and toxin binding
Livestock Science. 133 (1-3): 101-3
View The Latest Product References
-
Verhelst, R. et al. (2013) E. coli heat labile toxin (LT) inactivation by specific polyphenols is aggregation dependent.
Vet Microbiol. 163 (3-4): 319-24. -
Greenwell P et al. (2008) Purification and analysis of DNases of Tritrichomonas foetus: evidence that these enzymes are glycoproteins.
Int J Parasitol. 38 (7): 749-56. -
Beckett, T.L. et al. (2013) A ketogenic diet improves motor performance but does not affect β-amyloid levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Brain Res. 1505: 61-7. -
Abdul, H.M. et al. (2009) Cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease is associated with selective changes in calcineurin/NFAT signaling.
J Neurosci. 29 (41): 12957-69. -
Niedowicz DM et al. (2013) Leptin regulates amyloid β production via the γ-secretase complex.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832 (3): 439-44. -
Martin SB et al. (2014) Synaptophysin and synaptojanin-1 in Down syndrome are differentially affected by Alzheimer's disease.
J Alzheimers Dis. 42 (3): 767-75. -
Wilcock, D.M. et al. (2015) Down syndrome individuals with Alzheimer's disease have a distinct neuroinflammatory phenotype compared to sporadic Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 36 (9): 2468-74. -
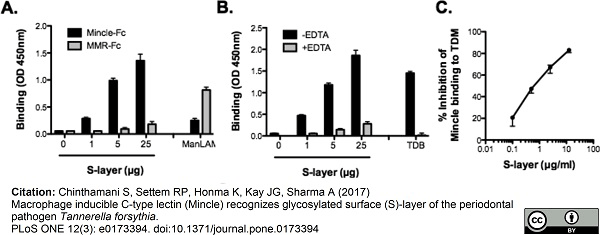
Chinthamani S et al. (2017) Macrophage inducible C-type lectin (Mincle) recognizes glycosylated surface (S)-layer of the periodontal pathogen Tannerella forsythia.
PLoS One. 12 (3): e0173394. -
LeVine, H. 3rd.et al. (2017) Down syndrome: age-dependence of PiB binding in postmortem frontal cortex across the lifespan.
Neurobiol Aging. 54: 163-9.
BUF034A
BUF034B
BUF034C
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
Always be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up