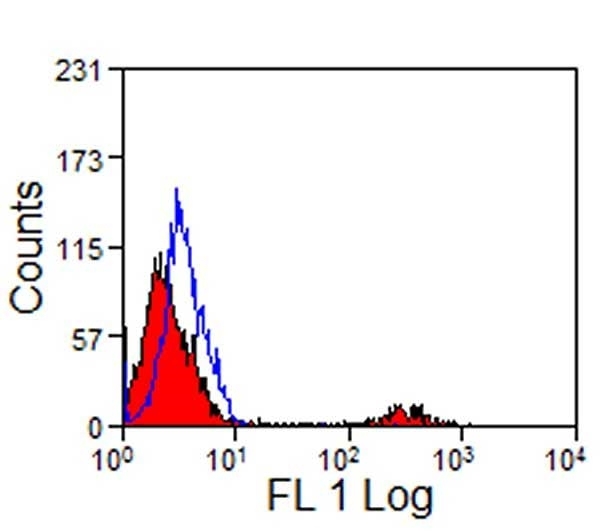
CD8 antibody | 12.C7





Mouse anti Rabbit CD8:FITC
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- 12.C7
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Specificity
- CD8
| Mouse anti Rabbit CD8 antibody, clone 12.C7 recognizes the rabbit CD8 cell surface antigen, expressed by a subset of T lymphocytes with cytotoxic/suppressor activity. |
- Target Species
- Rabbit
- Product Form
- Purified IgG conjugated to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Isomer 1 (FITC) - liquid
- Preparation
- Purified IgG prepared by affinity chromatography on Protein A from tissue culture supernatant
- Buffer Solution
- Phosphate buffered saline
- Preservative Stabilisers
- 0.09% Sodium Azide (NaN3)
1% Bovine Serum Albumin - Approx. Protein Concentrations
- IgG concentration 0.1 mg/ml
- Max Ex/Em
-
Fluorophore Excitation Max (nm) Emission Max (nm) FITC 490 525 - Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended. This product is photosensitive and should be protected from light.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry | Neat | 1/10 |
- Flow Cytometry
- Use 10μl of the suggested working dilution to label 106 cells in 100μl
| Description | Product Code | Applications | Pack Size | List Price | Your Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse IgG1 Negative Control:FITC | MCA928F | F | 100 Tests |
|
Log in | ||
| List Price | Your Price | ||||||
|
|
Log in | ||||||
| Description | Mouse IgG1 Negative Control:FITC | ||||||
References for CD8 antibody
-
De Smet, W. et al. (1983) Rabbit leukocyte surface antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies.
Eur J Immunol. 13: 919-28. -
Wilkinson, J.M. et al. (1992) A cytotoxic rabbit T-cell line infected with a gamma-herpes virus which expresses CD8 and class II antigens.
Immunology. 77: 106-8. -
Schock, A. and Reid, H.W. (1996) Characterisation of the lymphoproliferation in rabbits experimentally affected with malignant catarrhal fever.
Vet Microbiol. 53: 111-9. -
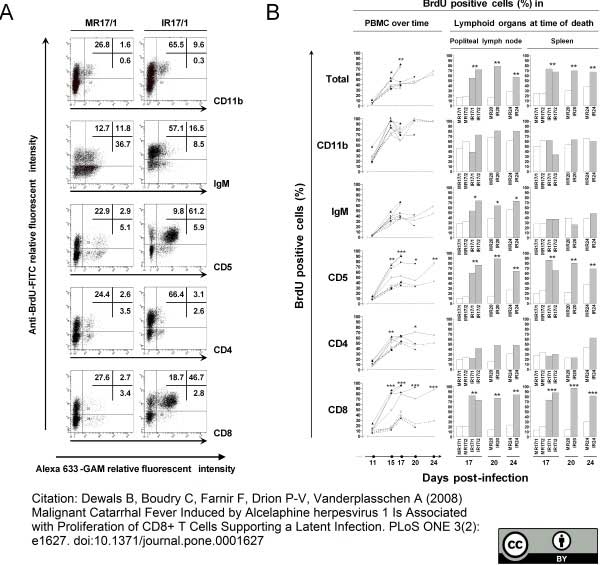
Dewals, B. et al. (2008) Malignant catarrhal fever induced by alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 is associated with proliferation of CD8+ T cells supporting a latent infection.
PLos ONE 3: e1627. -
Hanson, N.B. & Lanning, D.K. (2008) Microbial induction of B and T cell areas in rabbit appendix.
Dev Comp Immunol. 32 (8): 980-91. -
Anderson, I.E. et al. (2008) Production and utilization of interleukin-15 in malignant catarrhal fever.
J Comp Pathol. 138 (2-3): 131-44. -
Pakandl, M. et al. (2008) Dependence of the immune response to coccidiosis on the age of rabbit suckling.
Parasitol Res. 103 (6): 1265-71. -
Waclavicek, M. et al. (2009) Analysis of the early response to TSST-1 reveals Vbeta-unrestricted extravasation, compartmentalization of the response, and unresponsiveness but not anergy to TSST-1.
J Leukoc Biol. 85 (1): 44-54.
View The Latest Product References
-
Stich N et al. (2010) Staphylococcal superantigen (TSST-1) mutant analysis reveals that t cell activation is required for biological effects in the rabbit including the cytokine storm.
Toxins (Basel). 2 (9): 2272-88. -
Dewals, B. et al. (2011) Ex vivo bioluminescence detection of alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 infection during malignant catarrhal fever.
J Virol. 85 (14): 6941-54. -
Zhao, L. et al. (2011) Evaluation of immunocompatibility of tissue-engineered periosteum.
Biomed Mater.6:015005. -
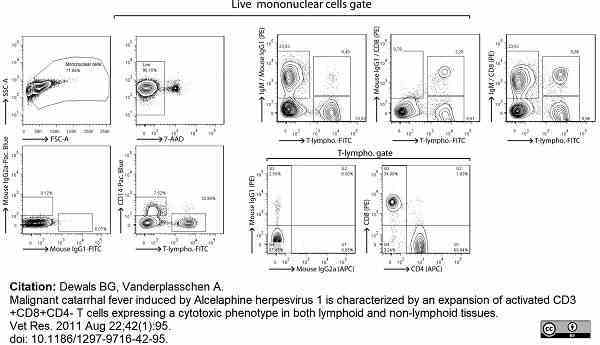
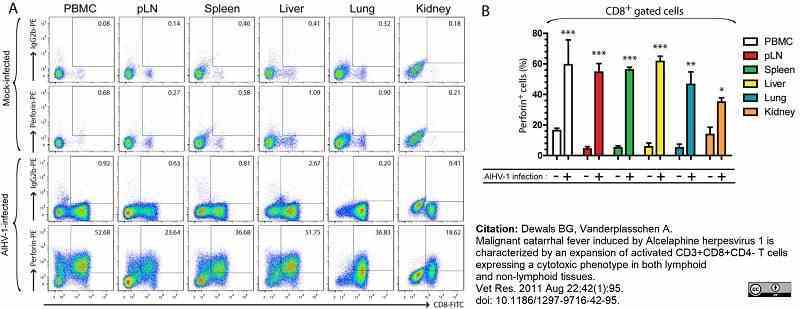
Dewals, B.G. & Vanderplasschen, A. (2011) Malignant catarrhal fever induced by Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 is characterized by an expansion of activated CD3+CD8+CD4- T cells expressing a cytotoxic phenotype in both lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues.
Vet Res. 42 (1): 95. -
Marques, R.M. et al. (2012) Early inflammatory response of young rabbits attending natural resistance to calicivirus (RHDV) infection.
Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 150: 181-8. -
Srivastava, R. et al. (2015) A Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Human Asymptomatic CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes-Based Vaccine Protects Against Ocular Herpes in a "Humanized" HLA Transgenic Rabbit Model.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56 (6): 4013-28. -
Myster, F. et al. (2015) Viral semaphorin inhibits dendritic cell phagocytosis and migration but is not essential for gammaherpesvirus-induced lymphoproliferation in malignant catarrhal fever.
J Virol. 89 (7): 3630-47. -
Khan AA et al. (2015) Therapeutic immunization with a mixture of herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein D-derived “asymptomatic” human CD8+ T-cell epitopes decreases spontaneous ocular shedding in latently infected HLA transgenic rabbits: association with low frequency of local PD-1+ TIM-3+ CD8+ exhausted T cells.
J Virol. 89 (13): 6619-32. -
Srivastava, R. et al. (2016) The Herpes Simplex Virus Latency-Associated Transcript Gene Is Associated with a Broader Repertoire of Virus-Specific Exhausted CD8+ T Cells Retained within the Trigeminal Ganglia of Latently Infected HLA Transgenic Rabbits.
J Virol. 90 (8): 3913-28. -
Khan, A.A. et al. (2018) Human Asymptomatic Epitope Peptide/CXCL10-Based Prime/Pull Vaccine Induces Herpes Simplex Virus-Specific Gamma Interferon-Positive CD107+ CD8+ T Cells That Infiltrate the Corneas and Trigeminal Ganglia of Humanized HLA Transgenic Rabbits and Protect against Ocular Herpes Challenge.
J Virol. 92 (16): e00535-18. -
Gates, K.V. & Griffiths, L.G. (2018) Chronic graft-specific cell-mediated immune response toward candidate xenogeneic biomaterial.
Immunol Res. 66 (2): 288-98. -
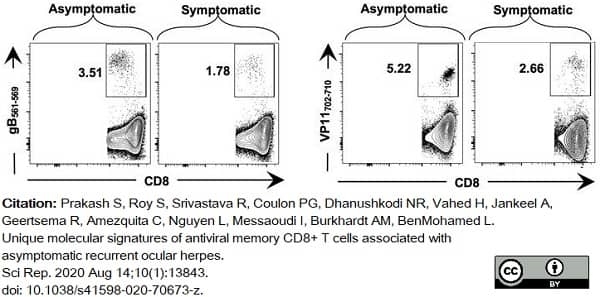
Prakash, S. et al. (2020) Unique molecular signatures of antiviral memory CD8+ T cells associated with asymptomatic recurrent ocular herpes.
Sci Rep. 10 (1): 13843. -
Jeklova, E. et al. (2020) Characterization of humoral and cell-mediated immunity in rabbits orally infected with Encephalitozoon cuniculi..
Vet Res. 51 (1): 79. -
Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. et al. (2020) B and T lymphocytes in rabbits change according to the sex and throughout the year.
Pol J Vet Sci. 23 (1): 37-42. -
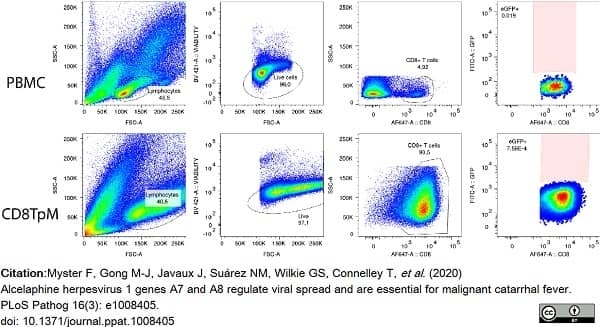
Myster, F. et al. (2020) Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 genes A7 and A8 regulate viral spread and are essential for malignant catarrhal fever.
PLoS Pathog. 16 (3): e1008405. -
Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. et al. (2022) Reactivity of selected markers of innate and adaptive immunity in rabbits experimentally infected with antigenic variants of RHD (Lagovirus europaeus/GI.1a).
Vet Res Commun. 46 (1): 233-42. -
Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. & Deptuła, W. (2023) Crosstalk between Apoptosis and Cytotoxic Lymphocytes (CTLs) in the Course of Lagovirus Europaeus GI.1a Infection in Rabbits.
J Vet Res. 67 (1): 41-47.
- RRID
- AB_566891
MCA1576F
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Rabbit ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up