Leishmania LPG antibody | CA7AE
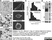
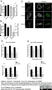
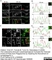

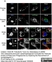

Mouse anti Leishmania LPG (Repeat Epitope)
- Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Clone
- CA7AE
- Isotype
- IgM
- Specificity
- Leishmania LPG
- Region
- (REPEAT EPITOPE)
| Mouse anti Leishmania lipophosphoglycan antibody, clone CA7AE recognizes lipophosphoglycan (LPG) the major cell surface glycoconjugate of Leishmania parasites. Mouse anti Leishmania lipophosphoglycan antibody, clone CA7AE recognizes the repeat carbohydrate epitope of most species of Leishmania LPG. The epitope is also found on the excreted acid phosphatase of Leishmania and is expressed on the surface of Leishmania infected macrophages (Tolson et al. 1990). Mouse anti Leishmania lipophosphoglycan antibody, clone CA7AE recognizes the promastigotes of Leishmania donovani but not those of the related species L. tropica (Jaffe and Sarfstein 1987, Sundar et al. 2001). Mouse anti Leishmania lipophosphoglycan antibody, clone CA7AE does however recognize a broad range of L. donovani and L. major strains and related species including L. infantum, L. m. mexicana, L. aethiopica and L. b. panamensis (Tolson et al. 1994). |
- Target Species
- Protozoan
- Product Form
- Ascites - lyophilized
- Reconstitution
- Reconstitute with 0.5 ml distilled water
Care should be taken during reconstitution as the protein may appear as a film at the bottom of the vial. Bio-Rad recommend that the vial is gently mixed after reconstitution. For long term storage the addition of 0.09% sodium azide is recommended. - Preservative Stabilisers
- None present
- Immunogen
- Heat killed Leishmania donovani promastigotes.
- Fusion Partners
- Spleen cells from immunised BALB/c mice were fused with cells of the murine SP2/0 myeloma cell line.
- Regulatory
- For research purposes only
- Guarantee
- 12 months from date of despatch
After reconstitution store at -20oC.
Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended. This product should be stored undiluted. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the antibody.
| Application Name | Verified | Min Dilution | Max Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 1/1000 | ||
| Immunoblotting | |||
| Immunofluorescence | 1/500 | 1/1000 |
References for Leishmania LPG antibody
-
Sundar, S. et al. (2001) Resistance to treatment in Kala-azar: speciation of isolates from northeast India.
Am J Trop Med Hyg. 65: 193-6. -
Tolson, D.L. et al. (1990) Expression of a repeating phosphorylated disaccharide lipophosphoglycan epitope on the surface of macrophages infected with Leishmania donovani.
Infect Immun. 58: 3500-7. -
Butcher, B.A. et al. (1996) Deficiency in beta1,3-galactosyltransferase of a Leishmania major lipophosphoglycan mutant adversely influences the Leishmania-sand fly interaction.
J Biol Chem. 271: 20573-9. -
Goyard, S. et al. (2003) An in vitro system for developmental and genetic studies of Leishmania donovani phosphoglycans
Mol Biochem Parasitol. 130: 31-42. -
Soares, R.P. et al. (2004) Leishmania tropica: intraspecific polymorphisms in lipophosphoglycan correlate with transmission by different Phlebotomus species.
Exp Parasitol. 107: 105-14. -
Amprey, J.L. et al. (2004) Inhibition of CD1 expression in human dendritic cells during intracellular infection with Leishmania donovani.
Infect Immun. 72: 589-92. -
Coelho-Finamore, J.M. et al. (2011) Leishmania infantum: Lipophosphoglycan intraspecific variation and interaction with vertebrate and invertebrate hosts.
Int J Parasitol. 41: 333-42. -
Capul, A.A. et al. (2007) Two Functionally Divergent UDP-Gal Nucleotide Sugar Transporters Participate in Phosphoglycan Synthesis in Leishmania major
J Biol Chem. 282: 14006-17.
View The Latest Product References
-
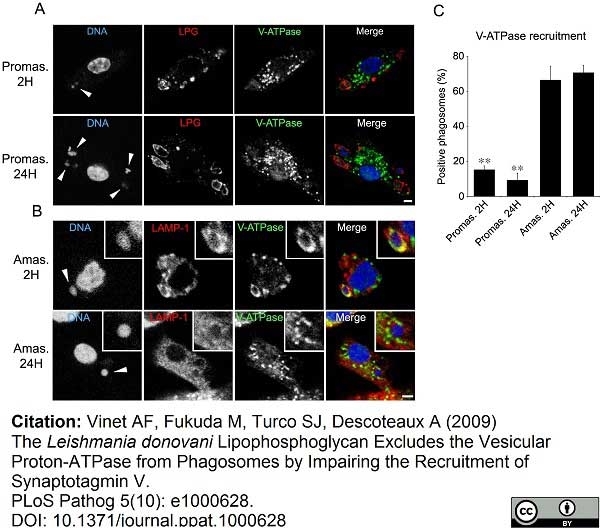
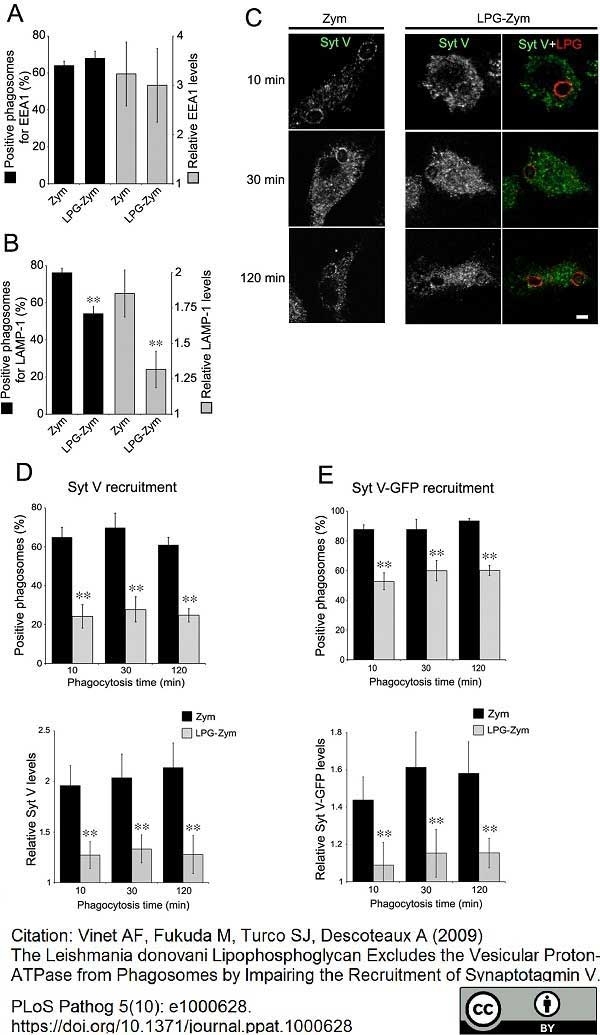
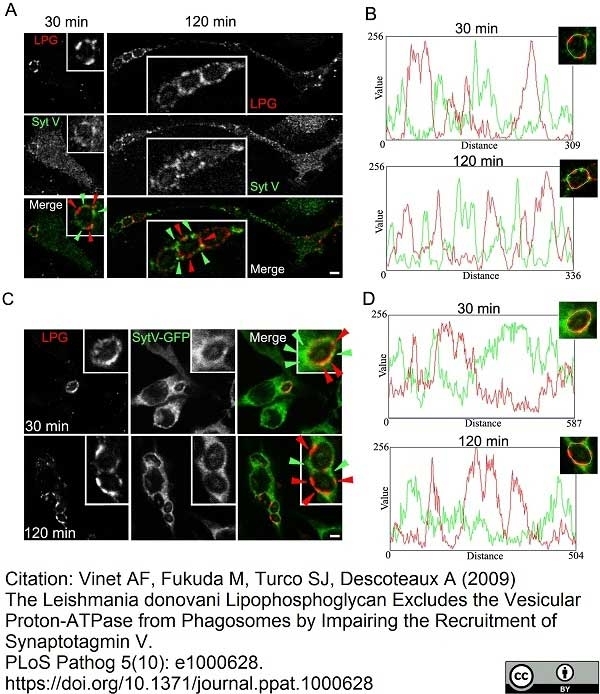
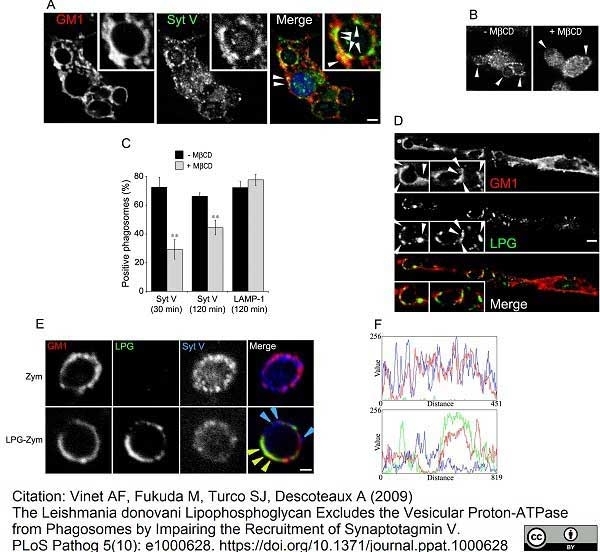
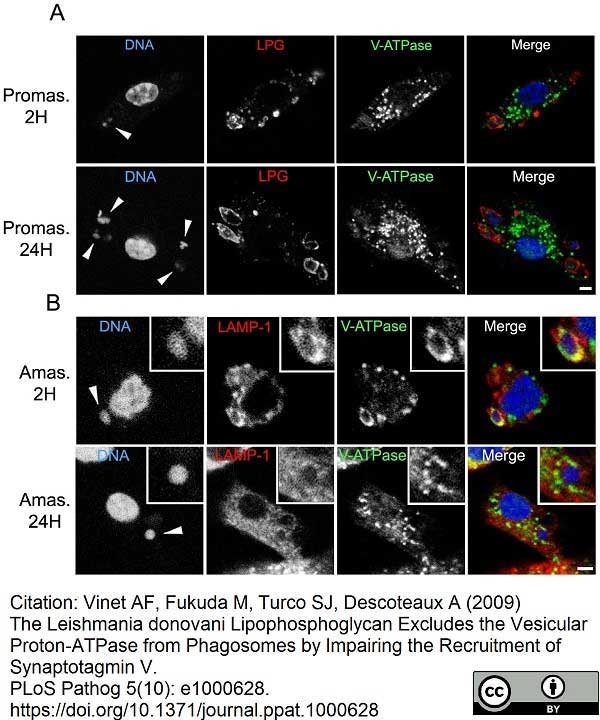
Vinet, A.F. et al. (2009) The Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan excludes the vesicular proton-ATPase from phagosomes by impairing the recruitment of synaptotagmin V.
PLoS Pathog. 5: e1000628. -
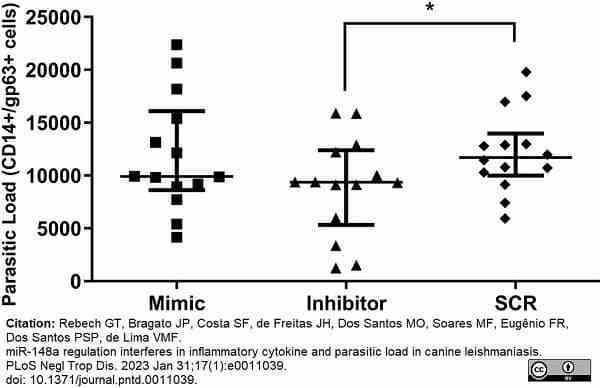
Rebech, G.T. et al. (2023) miR-148a regulation interferes in inflammatory cytokine and parasitic load in canine leishmaniasis.
PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 17 (1): e0011039.
- RRID
- AB_619110
OBT2002
If you cannot find the batch/lot you are looking for please contact our technical support team for assistance.
Please Note: All Products are "FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY"
View all Anti-Protozoan ProductsAlways be the first to know.
When we launch new products and resources to help you achieve more in the lab.
Yes, sign me up