Antibodies to Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
Bio-Rad offers an extended range of HbA1c antibodies:
- Two Hemoglobin A1c antibody clones that show cross-reactivity with HbS, HbC, HbD and HbE
- Two Hemoglobin A1c antibody clones that cross-react with HbD and HbE, but not with HbS and HbC
For those interested in monitoring both HbA1c and the glycated forms of the most common genetic variants of hemoglobin, an antibody that detects all of these represents a valuable tool for inclusion in monitoring assays.
Antibodies to HbA1c
Cross-Reactivity with Glycated Form of Genetic Variants
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Product code
|
Clone
|
Format
|
HbS
|
HbC
|
HbD
|
HbE
|
|
15783
|
Fab
|
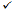
|
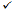
|
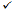
|
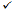
|
|
|
15785
|
Fab
|
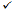
|
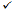
|
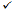
|
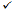
|
|
|
AbD15783-IgG
|
IgG1
|
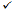
|
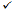
|
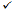
|
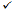
|
|
|
AbD15785-IgG
|
IgG1
|
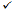
|
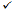
|
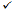
|
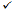
|
|
|
AbD15790-IgG
|
IgG1
|
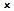
|
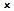
|
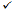
|
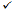
|
|
Table 1 Antibody Specificities
The choice of antibody clones and Fab or IgG formats offers greater flexibility for assay development, and the HuCAL® recombinant phage display technology used to generate the antibodies enables accurate reproduction, which ensures consistent performance and long-term supply.
Demonstration of the Performance of Anti-HbA1c Antibody HCA179
Sample
|
% of abnormal Variants1
|
HbA1c NGSP units2
|
HbA1c (measured using HCA179)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | [%] | ||
|
HbS
|
38
|
6.3
|
5.1 +/- 0.1
|
|
HbC
|
37
|
6.1
|
5.8 +/- 0.1
|
|
Elevated HbF
|
5
|
6.1
|
5.6 +/- 0.1
|
|
HbE
|
28
|
7.0
|
6.6 +/- 0.1
|
|
HbD
|
40
|
5.5
|
5.3 +/- 0.2
|
|
Control 1
|
0
|
5.1
|
5.3 +/- 0.1
|
|
Control 2
|
0
|
7.1
|
7.4 +/- 0.1
|
|
Control 3
|
0
|
9.5
|
9.9 +/- 0.1
|
Table 2 Performance of Anti-HbA1c Antibody HCA179
1 Samples were obtained from heterozygous donors; the values reflect the percentage of abnormal Hb carried by the donor.
2 Measured with affinity chromatography (IFCC/NGSP calibrated)
The data shown in the table demonstrates the performance of antibody HCA179 in the presence of abnormal hemoglobin (Hb) samples. The results show that the presence of these common variants does not affect the measurement of Hemoglobin A1c using antibody HCA179 and that the HbA1c values are similar to those measured via IFCC/ NGSP calibrated affinity chromatography
Data was obtained by measuring the HbA1c content of serum samples using HRP labeled HCA179 antibody. Patient samples with abnormal hemoglobin (Hb) were included. Besides binding to the normal glycated hemoglobin (Control 1, 2 and 3), HCA179 also recognizes the glycated versions of HbC, HbE, HbD and to a lesser degree HbS. Elevated HbF cannot be detected due to the absence of the hemoglobin β chain. Values are given as % HbA1c. Samples were obtained from heterozygous donors. The values reflect the percentage of abnormal Hb carried by the donor. *Data from triplicate experiments.
Why measure HbA1c?
The HbA1c concentration represents the average blood glucose level over a number of weeks, and for control of diabetes mellitus its concentration should remain within the defined reference range. An elevated HbA1c level suggests that the patient is not controlling the disease correctly, and in uncontrolled cases the level may be three to four times the normal concentration.
Hemoglobin A1c is routinely used to monitor long term glycemic control in people with diabetes mellitus. It is extremely important for the patient that the HbA1c level is measured accurately. Assays for HbA1c have been found to be sensitive to genetic variants of Hemoglobin (Hb) or even elevated fetal hemoglobin (HbF), and can show clinically significant interference in their presence, which has caused concern for clinicians over the validity of the test results. The most common genetic variants in the population are HbS, HbC, HbD and HbE.
HuCAL® is a registered trademark of MorphoSys AG.